Causes of Cancer
Epidemiology and Causal Criteria
Known Cancer Risk Factors
Smoking
Table 7-1
Carcinogens in Tobacco Smoke
| Carcinogen Class | No. of Compounds | Example Compound |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | 10 | Benzo[a]pyrene 5-Methylchrysene Dibenz[a,h]anthracene |
| Aza-arenes | 3 | Dibenz[a,h]acridine |
| N-nitrosamines | 7 | 4-(Methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) N-Nitrosodiethylamine |
| Aromatic amines | 3 | 4-Aminobiphenyl |
| Heterocyclic amines | 8 | 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5–f]quinoline |
| Aldehydes | 2 | Formaldehyde |
| Miscellaneous organic compounds | 15 | 1,3-Butadiene Ethyl carbamate |
| Inorganic compounds | 7 | Nickel Chromium Cadmium Arsenic |
| Total | 55 |
Adapted from Hecht SS. Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1999;91:1194.
Diet
Occupation
Table 7-2
Environmental Carcinogens Associated with Occupation
| Occupation | Carcinogen Exposure | Associated Cancer Type |
| Iron and steel founding | PAH, chromium, nickel, formaldehyde | Lung |
| Copper mining and smelting | Arsenic | Skin, bronchus, liver |
| Underground mining | Radon (ionizing radiation ) | Lung |
| Aluminum production | PAH | Lung |
| Coke production | PAH | Lung, kidney |
| Painting | Chromium, solvents | Lung |
| Furniture and cabinet making | Wood dust | Nasal sinus |
| Boot and shoe manufacture | Leather dust, benzene | Nasal sinus, leukemia |
| Rubber industry | Aromatic amines, solvents | Bladder, leukemia |
| Nickel refining | Nickel | Nasal sinus, bronchus |
| Vinyl chloride manufacture | Vinyl chloride | Liver |
| Dye and textile production | Benzidine-based dyes | Bladder |
PAH, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Causes of Cancer by Organ Site
Classes and Types of Carcinogens
Carcinogen Evaluation and Classification
Table 7-3
Exposures Associated with Human Cancers, as Identified by the IARC (Partial Listing)
| Cancer Site | Carcinogenic Agents with Sufficient Evidence in Humans | Agents with Limited Evidence in Humans |
| Oral cavity | Alcohol, betel quid, HPV, tobacco smoking, smokeless tobacco | Solar radiation |
| Stomach | Helicobacter pylori, rubber production industry, tobacco smoking, x-rays, gamma radiation | Asbestos, Epstein-Barr virus, lead, nitrate, nitrite, pickled vegetables, salted fish |
| Colon and rectum | Alcohol, tobacco smoking, radiation | Asbestos, Schistosoma japonicum |
| Liver and bile duct | Aflatoxins, alcohol, Clonorchis sinensis, estrogen-progestin contraceptives, HBV, HCV, Opisthorchis viverrini, plutonium, thorium-232, vinyl chloride | Androgenic steroids, arsenic, betel quid, HIV, polychlorinated biphenyls, Schistosoma japonicum, trichloroethylene, x-rays, gamma radiation |
| Pancreas | Tobacco smoking, smokeless tobacco | Alcohol, thorium-232, x-rays, gamma radiation, radioiodines |
| Lung | Tobacco smoking, aluminum production, arsenic, asbestos, beryllium, bis (chloromethyl) ether, chloromethyl methyl ether, cadmium, chromium, coal combustion and coal tar pitch, coke production, hematite mining, iron and steel founding, MOPP, nickel, painting, plutonium, radon, rubber production, silica dust, soot, sulfur mustard, x-rays, gamma radiation | Acid mists, manufacture of glass, indoor emissions from household combustion, carbon electrode manufacture, chlorinated toluenes and benzoyl chloride, cobalt metal with tungsten carbide, creosotes, engine exhaust, insecticides, dioxin, printing processes, welding fumes |
| Skin—melanoma | Solar radiation, UV-emitting tanning devices | |
| Other skin cancers | Arsenic, azathiopurine, coal tar pitch, coal tar distillation, cyclosporine, methoxsalen plus UVA, mineral oils, shale oils, solar radiation, soot, x-rays, gamma radiation | Creosotes, HIV, HPV, nitrogen mustard, petroleum refining, UV-emitting tanning devices |
| Mesothelioma | Asbestos, erionite, painting | |
| Breast | Alcohol, diethylstilbestrol, estrogen-progesterone contraceptive and menopausal therapy, x-rays, gamma radiation | Estrogen menopausal therapy, ethylene oxide, shift work resulting in circadian disruption, tobacco smoking |
| Uterine cervix | Diethylstilbestrol (exposure in utero), estrogen-progestogen contraception, HIV, HPV, tobacco smoking | Tetrachloroethylene |
| Ovary | Asbestos, estrogen menopausal therapy, tobacco smoking | Talc-based body powder, x-rays, gamma radiation |
| Prostate | Androgenic steroids, arsenic, cadmium, rubber production industry, thorium-232, x-rays, gamma radiation, diethylstilbestrol (exposure in utero) | |
| Kidney | Tobacco smoking, x-rays, gamma radiation | Arsenic, cadmium, printing processes |
| Urinary Bladder | Aluminum production, 4-aminobiphenyl, arsenic, auramine production, benzidine, chlornaphazine, cyclophosphamide, magenta production, 2-naphthylamine, painting, rubber production, Schistosoma haematobium, tobacco smoking, toluidine, x-rays, gamma radiation | Coal tar pitch, coffee, dry cleaning, engine exhaust, printing processes, occupational exposures in hair dressing and barbering, soot, textile manufacturing |
| Brain | X radiation, gamma radiation | |
| Leukemia and/or lymphoma | Azathiopurine, benzene, busulfan, 1,3-butadiene, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, Epstein-Barr virus, etoposide with cisplatin and bleomycin, fission products, formaldehyde, Helicobacter pylori, HCV, HIV, human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1, Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus, melphalan, MOPP, phosphorus-32, rubber production, semustine, thiotepa, thorium-232, tobacco smoking, treosulfan, X radiation, gamma radiation | Bischloroethyl nitrosourea, chloramphenicol, ethylene oxide, etoposide, HBV, magnetic fields, mitoxantrone, nitrogen mustard, painting, petroleum refining, polychlorophenols, radioiodines, radon-222, styrene, teniposide, tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, dioxin, tobacco smoking (childhood leukemia in smokers’ children) |
HBV, Hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HPV, human papillomavirus; IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer; MOPP, mustargen-oncovin-procarbazine-prednisone chemotherapy; UVA, ultraviolet A light.
Adapted from Cogliano et al. Preventable exposures associated with human cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011;103:1835.
Table 7-4
IARC Classification of Suspected Carcinogenic Agents
IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer.
Types of Carcinogens
Physical Carcinogens
Table 7-5
Selected IARC Known Human Carcinogens
| 4-Aminobiphenyl | Hepatitis B virus |
| Arsenic | Hepatitis C virus |
| Asbestos | Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 |
| Azathioprine | Human papillomavirus |
| Benzene | Human T-cell lymphotropic virus |
| Benzidine | Melphalan |
| Benzo[a]pyrene | 8-Methoxypsoralen |
| Beryllium | Mustard gas |
| N,N-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-2-naphthylamine | 2-Naphthylamine |
| Bis(chloromethyl)ether | Nickel compounds |
| Chloromethyl methyl ether | N′-Nitrosonornicotine (NNN) |
| 1,4-Butanediol dimethanesulfonate | Phosphorus-32 |
| Cadmium | Plutonium-239 |
| Chlorambucil | Radioiodines |
| 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1-nitrosourea | Radium-224 |
| Chromium[VI] | Radium-226 |
| Cyclosporine | Radium-228 |
| Cyclophosphamide | Radon-222 |
| Diethylstilbestrol | Silica |
| Epstein-Barr virus | Solar radiation |
| Erionite | Talc-containing asbestiform fibers |
| Estrogen-progestogen menopausal therapy | Tamoxifen |
| Estrogen-progestogen oral contraceptives | 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-para-dioxin |
| Estrogen therapy | Thiotepa |
| Ethylene oxide | Treosulfan |
| Etoposide | Vinyl chloride |
| Formaldehyde | X- and gamma (γ)-radiation |
| Gallium arsenide | Aflatoxins |
| Helicobacter pylori | Soots Tobacco Wood dust |
IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer.
Biologic Carcinogens
Chemical Carcinogens
Organic Carcinogens
Benzene
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
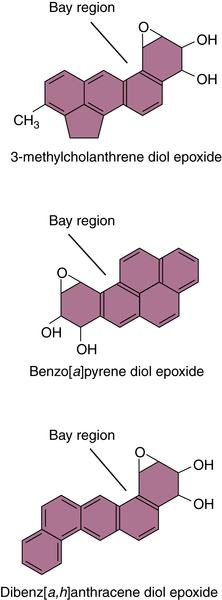
Aflatoxin B1
Benzidine
Nitrosamines and Heterocyclic Amines
Inorganic Carcinogens
Beryllium
Cadmium
Arsenic
Chromium
Fibers
Asbestos
Hormones
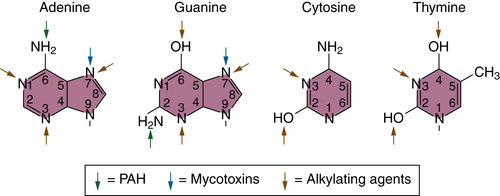
Mechanisms of Chemical Carcinogenesis
Multistage Nature of Carcinogenesis and the Multistage Model of Mouse Skin Carcinogenesis
Initiation and Mutational Theory of Carcinogenesis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree