EMBRYOLOGY
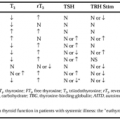
The fetal gonads remain undifferentiated until about the seventh week of gestation (see Chap. 90). At that time, in normal 46,XY fetuses, the gene encoding the sex-determining factor of the Y chromosome (i.e., SRY) is transcribed and testicular differentiation begins. SRY initiates a complex cascade of events3 in which other genes are inhibited (e.g., DAX-1, important in ovarian determination) or activated (e.g., SOX9 and SF-1, important in Sertoli cell differentiation and indirectly involved in ovarian inhibition via antimüllerian hormone, AMH). Testosterone secretion begins by ˜8 weeks of fetal life. In normal 46,XX fetuses, the absence of high local concentrations of AMH allows differentiation of the ovaries, beginning at ˜10 weeks’ gestation (see Chap. 90).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree