EFFECTS ON THE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
OVARIAN EFFECTS
OVARIAN CYSTS
Combined Oral Contraceptives.
Progestin-Only Contraceptives.
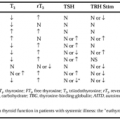
An increased incidence of follicular cysts has been noted with LN implant (Norplant) use. The continuous low level of LN allows follicles to develop, and follicular cysts often result.60a These cysts only need to be evaluated sonographically or laparoscopically if they become large and painful. Similar to LN implants, the low dose of progestin in POPs allows follicles to develop and follicular cysts to form. However, one large cohort study evaluating ovarian cysts in COC users also looked at progestin-only pill users, and found no cases of follicular cysts in 219 person-months of observation.59 In contrast to POPs and implants, DMPA effectively suppresses follicular development and ovulation; thus, follicular cysts are rare among DMPA users.
OVARIAN CANCER
Combined Oral Contraceptives.
Women using COCs have a markedly reduced risk of ovarian cancer, with increasing duration of use increasing the protective effect.61,62 and 63 A 10% decrease in risk is noted after 1 year of COC use, and a ˜50% decrease in risk is achieved after 5 years of use.62 This protective effect has been found to extend to women at highest risk of ovarian cancer, including women with BRCA-1 and BRCA-2 mutations64 (see also Chap. 223).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree