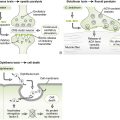
Chapter 20 I Laboratory Identification of Viruses 1. Bacterial or fungal etiology for an infection should be excluded before undertaking laboratory analysis for viral infection. 2. Appropriate specimens for analysis are determined by the site of infection and presumptive diagnosis based on symptoms. B Microscopic examination of clinical specimens 1. Light microscopy can detect virus-induced histologic changes, called viral cytopathic effects (CPEs), in cells and tissues. • Common CPEs include vacuolization, necrosis, syncytia formation, and various types of inclusion bodies. 2. Electron microscopy can visualize virions directly in cells or stool specimens. 1. Unlike bacteria or fungi, viruses replicate only within cells and must be isolated and grown in cells that support their replication. 2. Some viruses cannot be grown in the laboratory because no suitable culture system has been developed. D Laboratory assays for detecting viral proteins 1. Hemagglutination: viral hemagglutinin (HA) protruding from the surface of some enveloped viruses binds to erythrocytes of specific species, causing them to clump. • Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI): specific antibody blocking of hemagglutination can identify the virus strain causing HA. Patient serum that can block HA of a specific strain of virus indicates prior infection with that strain of virus (e.g., influenza A H1N1) • Hemadsorption is the binding of certain erythrocytes to viral HA expressed in the membrane of infected cells. • Virus-specific antibody is used to detect free virions and free or cell-associated viral proteins. a. Antibody-antigen binding is detected by a probe such as a fluorescent marker, radiolabel, or enzyme (e.g., horseradish peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, and β-galactosidase) that produces a colored product on addition of substrate. • Immunofluorescence (IF) and enzyme immunoassay (EIA) detect viral proteins expressed on the surface of infected cells (see Fig. 5-3). • Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and radioimmunoassay (RIA) detect and quantitate free virions or viral proteins in a sample. • Direct versus indirect assays E Laboratory assays for detecting viral nucleic acids • Assays for viral nucleic acids are particularly useful in identifying slowly replicating viruses or those that do not have obvious cytopathic effects. 1. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (DNA), reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) (RNA), and related technologies, which permit amplification of specific nucleic acid sequences, are especially helpful in rapid detection of viruses
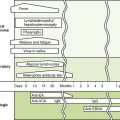
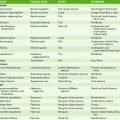
Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prevention of Viral Diseases