CATECHOLAMINES IN THE INFANT AND CHILD
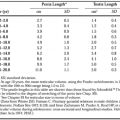
The physiology of the adrenal medulla has been discussed in Chapter 85. The normal values in pediatric patients for excretion of urinary catecholamines and their metabolites are shown in Table 87-1 and Table 87-2. Values have been published according to age, body weight, and surface area, and in relation to milligrams of urinary creatinine.1,2,3,4,5 and 6 In children, the daily urinary excretion of catecholamines and metabolites increases with age and is independent of the size of individuals.1 No sex difference is found. The dietary content does not significantly alter the quantity of catecholamines, vanillylmandelic acid, homovanillic acid, or metanephrine excreted in the urine.7
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree