21 Cancers of the haematopoietic system
Hodgkin’s disease
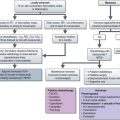
Aetiology
Pathology
The WHO classification of HD is shown in Table 21.1. Nodular sclerosis is the common subtype in young adults (more common in females), which presents with early stage supradiaphragmatic disease whereas mixed cellularity presents with generalized lymphadenopathy or extranodal disease with B symptoms. Lymphocyte depletion type presents with advanced stage disease with extranodal involvement and aggressive clinical course.
Table 21.1 WHO classification of Hodgkin’s lymphoma
| Classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin’s lymphoma (grades 1 and 2) | 60–70% |
| Mixed cellularity Hodgkin’s lymphoma | 20–30% |
| Lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma (LRCHL) | 3–5% |
| Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin’s lymphoma (LDHL) | 0.8–1% |
| Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma (LPHL) | 3–5% |
LRCHL usually presents in young males with localized cervical node involvement with no B symptoms.
Investigations and staging
Imaging
Staging
Cotswolds modification of the Ann Arbor Classification is used for staging (Table 21.2).
Table 21.2 The Cotswolds modification of Ann Arbor staging for lymphoma
| Stage I | Involvement of a single lymph node region or lymphoid structure or involvement of a single extralymphatic site (IE) |
| Stage II | Involvement of two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm; localized contiguous involvement of only one extranodal organ or site and lymph node region(s) on the same side of the diaphragm (IIE) |
| Stage III | Involvement of lymph node regions on both sides of the diaphragm (III),which may also be accompanied by involvement of the spleen (IIIS) or by localized contiguous involvement of only one extranodal organ site (IIIE) or both (IIISE) |
| Stage IV | Diffuse or disseminated involvement of one or more extranodal organs or tissues, with or without associated lymph node involvement |
| Designations applicable to any disease stage | |
| A: | No B symptoms |
| B: | Presence of B symptoms |
| X: | Bulky disease (a widening of the mediastinum by more than one third of the chest or presence of a nodal mass with a maximal dimension greater than 10 cm) |
Management
Patients with early stage disease (clinical stage I/II) are categorized as favourable and unfavourable group based on risk factors (Table 21.3). Prognosis of patients with advanced-stage (stage III and IV) disease is defined using the International Prognostic Score (IPS) (Box 21.1).
Table 21.3 EORTC risk grouping of early stage HD
| Treatment group | Definition |
|---|---|
| Favourable | CS I–II without risk factors |
| Unfavourable | CS I–II with ≥ 1 risk factors |
| Risk factors |
* Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (≥50 mm/h without or ≥30 mm/h with B-symptoms).
Classical HD
Early-stage favourable
The current standard treatment is combined modality treatment, consisting of two to four cycles of ABVD chemotherapy (Boxes 21.2 and 21.3), followed by 30–35 Gy in 15–20 fractions of involved field radiotherapy (IF-RT).
Box 21.2
Radiotherapy techniques in lymphoma
Early-stage unfavourable
These patients are also treated with combined modality treatment; however, the optimal chemotherapy regime and radiotherapy fractionation are yet be determined. The current treatment is four courses of ABVD followed by involved field radiotherapy of 30–35 Gy in 15–20 fractions (Boxes 21.2 and 21.3). With this treatment 5% patients progress during or immediately after treatment and 15% relapse within 5 years.
Follow-up
Two-thirds of relapses occur within 3 years of initial treatment and more than 90% occur within 5 years. Since a significant proportion of patients who relapse can be successfully salvaged, all patients need regular follow-up (Box 21.4). Follow-up is also helpful in identifying and managing long term side effects such as endocrine dysfunction.
Box 21.4
Follow-up and screening after treatment for HD
Survivorship issues
The major causes of excess death in survivors of HD are second malignancies and ischaemic heart disease (p. 58).
One of the most common second malignancies is lung cancer which is attributed to mediastinal radiotherapy, chemotherapy and smoking. Patients who had thoracic radiotherapy are encouraged not to smoke. There is 20–50% risk of second breast cancer after mediastinal/axillary radiotherapy in young females and these patients should be screened for breast cancer. Common haematological neoplasms include acute myeloid leukaemia, myelodysplastic syndrome (develops within 3–5 years) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (develops after 5–15 years).
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Pathology
The cell of origin is different for each subtype of lymphoma. Classification is by the updated WHO modification of the REAL (revised European and American lymphoma) classification system which is broadly divided into B-cell, T-cell/natural killer cell and Hodgkin’s disease (Table 21.4). Table 21.5 shows cytogenetic and molecular characteristics of NHL.
Table 21.4 Abridged WHO/REAL classification of NHL
| B-cell neoplasms |
| T-cell and putative NK-cell neoplasms |
Table 21.5 Cytogenetic and molecular characteristics of NHL
| Lymphoma | Cytogenetics | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Burkitt’s | ||
| Follicular lymphoma | t(14:18)(q32;q21) | |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | t(14:18)(q32;q21)+others such as p53, p16, p15 | |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | t(11;14)(q13;q32) | BCL-1 or PRAD1 (11q) Ig heavy chain (14q) |
| Anaplastic lymphoma | t(2;5)(p23:q35) |
Evaluation and staging
Imaging
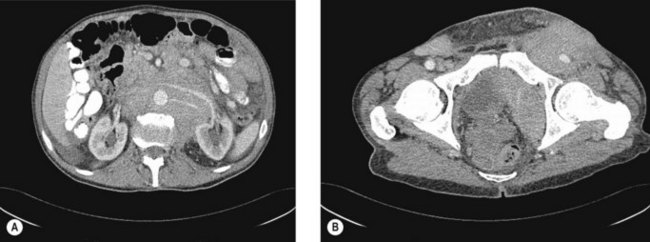
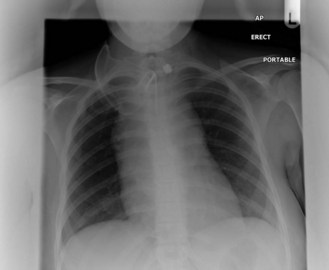
CT scans of the neck, chest, abdomen and pelvis are carried out to assess lymphadenopathy and organ involvement (Figure 21.3).
Other investigations
Prognostic factors
Stage, age, LDH and performance status have prognostic value. The Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (FLIP) score is used for indolent lymphomas (Box 21.5). The international prognostic index (IPI) is used for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Box 21.6).
Treatment
Follicular lymphoma
Early stage
Only about one-third of patients with follicular lymphoma present with stages I and II or limited stage III (with up to five involved lymph nodes areas) disease. Treatment options include watchful waiting, or radiotherapy (Box 21.2).
Advanced stage
The commonly used regime is either single agent chlorambucil or fludarabine. Chlorambucil results in 50–75% response rate with no complete response, whereas fludarabine can result in a complete response (15%). Combination chemotherapy (e.g. CVP and CHOP) (Table 21.6
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



 thorax)
thorax)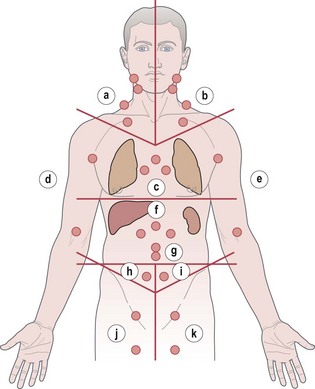
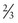 of cases are due to two specific subtypes: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.
of cases are due to two specific subtypes: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.