Primary Tumor (T) |
TX |
Primary tumor cannot be assessed |
T0 |
No evidence of primary tumor |
Tis |
Carcinoma in situ. |
Tis (DCIS) |
DCISa |
Tis (LCIS) |
LCISa |
Tis (Paget’s) |
Paget’s disease of the nipple is NOT associated with invasive carcinoma and/or carcinoma in situ (DCIS and/or LCIS) in the underlying breast parenchyma. Carcinomas in the breast parenchyma associated with Paget’s disease are categorized based on the size and characteristics of the parenchymal disease, although the presence of Paget’s disease should still be noted |
T1 |
Tumor ≤20 mm in greatest dimension |
|
T1mi |
Tumor ≤1 m in greatest dimension |
|
T1a |
Tumor >1 mm but ≤5 m in greatest dimension |
|
T1b |
Tumor >5 mm but ≤10 mm in greatest dimension |
|
T1c |
Tumor >10 mm but ≤20 mm in greatest dimension |
T2 |
Tumor >20 mm but ≤50 mm in greatest dimension |
T3 |
Tumor >50 mm in greatest dimension |
T4 |
Tumor of any size with direct extension to the chest wall and/or to the skin (ulceration or skin nodules)b |
|
T4a |
Extension to the chest wall, not including only pectoralis muscle adherence/invasion |
|
T4b |
Ulceration and/or ipsilateral satellite nodules and/or edema (including peau d’orange) of the skin which do not meet the criteria for inflammatory carcinoma |
|
T4c |
Both T4a and T4b |
|
T4d |
Inflammatory carcinomac |
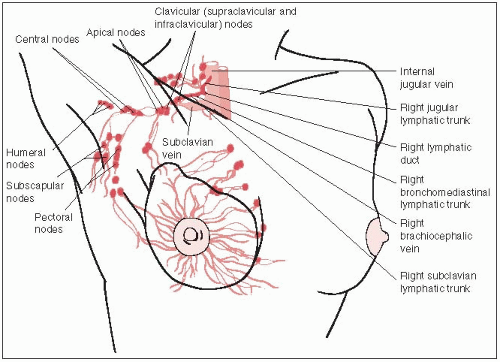
Regional Lymph Nodes (N) |
NX |
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed (e.g., previously removed) |
N0 |
No regional lymph node metastasis |
N1 |
Metastases to movable ipsilateral level I, II axillary lymph node(s) |
N2 |
Metastases in ipsilateral level I, II axillary lymph nodes that are clinically fixed or matted; or in clinically detectedd ipsilateral internal mammary nodes in the absence of clinically evident axillary lymph node metastases |
|
N2a |
Metastases in ipsilateral axillary lymph nodes fixed to one another (matted) or to other structures |
|
N2b |
Metastases only in clinically detectede ipsilateral internal mammary nodes and in the absence of clinically evident axillary lymph node metastases |
N3 |
Metastases in ipsilateral infraclavicular (level III axillary) lymph node(s) with or without level I, II axillary lymph node involvement; or in clinically detectedd ipsilateral internal mammary lymph node(s) with clinically evident level I, II axillary lymph node metastases; or metastases in ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node(s) with or without axillary or internal mammary lymph node involvement |
|
N3a |
Metastases in ipsilateral infraclavicular lymph node(s) |
|
N3b |
Metastases in ipsilateral internal mammary lymph node(s) and axillary lymph node(s) |
|
N3c |
Metastases in ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node(s) |
Pathologic Classification (pN) |
pNX |
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed (e.g., previously removed or not removed for pathologic study) |
pN0 |
No regional lymph node metastasis identified histologically |
|
pN0(i-) |
No regional lymph node metastases histologically, negative IHC |
|
pN0(i+) |
Malignant cells in regional lymph node(s) no >0.2 mm (detected by H&E or IHC including ITC) |
|
pN0(mol-) |
No regional lymph node metastases histologically, negative molecular findings (RT-PCR) |
|
pN0(mol+) |
Positive molecular findings (RT-PCR), but no regional lymph node metastases detected by histology or IHC |
pN1 |
Micrometastases; or metastases in one to three axillary lymph nodes; and/or in internal mammary nodes with metastases detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy but not clinically detectedf |
|
pN1mi |
Micrometastases (>0.2 mm and/or more than 200 cells, but none >2.0 mm) |
|
pN1a |
Metastases in one to three axillary lymph nodes, at least one metastasis >2.0 mm |
|
pN1b |
Metastases in internal mammary nodes with micrometastases or macrometastases detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy but not clinically detectedf |
|
pN1c |
Metastases in one to three axillary lymph nodes and in internal mammary lymph nodes with micrometastases or macrometastases detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy but not clinically detectedf |
pN2 |
Metastasis in four to nine axillary lymph nodes; or in clinically detected(f) internal mammary lymph nodes in the absence of axillary lymph node metastases |
|
pN2a |
Metastases in four to nine axillary lymph nodes (at least one tumor deposit >2.0 mm) |
|
pN2b |
Metastases in clinically detectede internal mammary lymph nodes in the absence of axillary lymph node metastases |
pN3 |
Metastases in ten or more axillary lymph nodes; or in infraclavicular (level III axillary) lymph nodes; or in clinically detectede ipsilateral internal mammary lymph nodes in the presence of 1 or more positive level I, II axillary lymph nodes; or in more than three axillary lymph nodes and in internal mammary lymph nodes with micrometastases or macrometastases detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy but not clinically detectedf; or in ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph nodes |
|
pN3a |
Metastases in ten or more axillary lymph nodes (at least one tumor deposit >2.0 mm); or metastases to the infraclavicular (level III axillary lymph) nodes |
|
pN3b |
Metastases in clinically detectede ipsilateral internal mammary lymph nodes in the presence of one or more positive axillary lymph nodes; or in more than three axillary lymph nodes and in internal mammary lymph nodes with micrometastases or macrometastases detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy but not clinically detectedf |
|
pN3c |
Metastases in ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph nodes |
Distant Metastasis (M) |
M0 |
No clinical or radiographic evidence of distant metastases (no pathologic M0; use clinical M to complete stage group) |
cM0(i+) |
No clinical or radiographic evidence of distant metastases, but deposits of molecularly or microscopically detected tumor cells in circulating blood, bone marrow or other nonregional nodal tissue that are no larger than 0.2 mm in a patient without symptoms or signs of metastases |
M1 |
Distant detectable metastases as determined by classic clinical and radiographic means and/or histologically proven larger than 0.2 mm |
Note:
1. Definitions for classifying the primary tumor (T) are the same for clinical and pathologic classification. If the measurement is made by physical examination, the examiner will use the major headings (T1, T2, orT3). If other measurements, such as mammographic or pathologic, are used, the telescoped subsets of T1 can be used. Tumors should be measured to the nearest 1-mm increment
2. Isolated tumor cell (ITC) clusters are defined as small clusters of cells not greater than 0.2 mm, or single tumor cells, or a cluster of fewer than 200 cells in a single histologic cross-section. ITCs may be detected by routine histology or by immunohistochemical (IHC) methods. Nodes containing only ITCs are excluded from the total positive node count for purposes of N classification but should be included in the total number of nodes evaluated aDCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; LCIS, lobular carcinoma in situ
bInvasion of the dermis alone does not qualify as T4.
cInflammatory carcinoma is restricted to cases with typical skin changes involving a third or more of the skin of the breast. While the histologic presence of invasive carcinoma invading dermal lymphatics is supportive of the diagnosis, it is not required, nor is dermal lymphatic invasion without typical clinical findings sufficient for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer.
dClassification is based on axillary lymph node dissection with or without sentinel lymph node biopsy. Classification based solely on sentinel lymph node biopsy without subsequent axillary lymph node dissection is designated (sn) for “sentinel node,” for example, pN0(sn).
eClinically detected is defined as detected by imaging studies (excluding lymphoscintigraphy) or by clinical examination and having characteristics highly suspicious for malignancy or a presumed pathologic macrometastasis based on fine-needle aspiration biopsy with cytologic examination. Confirmation of clinically detected metastatic disease by fine-needle aspiration without excision biopsy is designated with an (f) suffix, for example, cN3a(f). Excisional biopsy of a lymph node or biopsy of a sentinel node, in the absence of assignment of a pT, is classified as a clinical N, for example, cN1. Information regarding the confirmation of the nodal status will be designated in site-specific factors as clinical, fine-needle aspiration, core biopsy, or sentinel lymph node biopsy. Pathologic classification (pN) is used for excision or sentinel lymph node biopsy only in conjunction with a pathologic T assignment.
fNot-clinically detected is defined as not detected by imaging studies (excluding lymphoscintigraphy) or not detected by clinical examination.
Source: TNM Staging from Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, eds. AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer Verlag, 2009; with permission. |