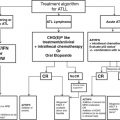
Fig. 1
Principles of treatment of HNSCC
3 Treatment of Resectable Tumors
Despite no direct comparison, it seems that similar results are obtained with surgery or radiotherapy. So surgical approach should be considered in tropical areas.
The most efficient action for reducing recurrence is stopping tobacco. For example, for laryngeal cancer, a study demonstrated, after complete resection, 28.7 % and 55.26 % (p = 0.0022) recurrence for patients who stopped smoking versus patients who continued [2].
After complete surgery for tumors of stage III or IV, radiation therapy decreased the risk of disease. A study of 8795 patients within the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database showed that adjuvant RT improved the 5-year overall survival (43.2 % [95 % confidence interval (95 % CI), 41.9–44.4 %] for surgery + RT vs. 33.4 % [95 % CI, 30.7–36.0 %] for surgery alone; P < .001) and cancer-specific survival (50.9 % for surgery + RT vs. 42.1 % for surgery) on univariate analysis [3]. On multivariate analysis, adjuvant RT (hazard ratio [HR] of 0.78; 95 % CI, 0.71–0.86 [P < .001]) is a strong independent prognosis factor. For patients with high risk of relapse (marginal resection or capsular effraction of an involved node), addition of chemotherapy by three cycles of cisplatin at the dose of 100 mg/m2 decreased again the level of recurrence. In a phase III study, 334 patients were randomized to radiotherapy alone (66 Gy over a period of 6 1/2 weeks) without or with cisplatin. The overall survival rate was also significantly higher in the combined-therapy group (P = 0.02 by the log-rank test; hazard ratio for death, 0.70; 95 % confidence interval, 0.52–0.95), with five-year Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival of 53 % and 40 %, respectively [4]. The estimated 5-year cumulative incidence of local or regional relapses (considering death from other causes as a competing risk) was 31 % after radiotherapy and 18 % after combined therapy.
So, for resectable disease, after surgery, radiotherapy clearly decreases the risk of relapse, but its benefit is inferior to this of smoking cessation, and in countries where radiotherapy is poorly available, it should be reserved to patients who stopped tobacco.
For operable disease but with a mutilating surgery, organ preservation could be tempted. Since it seems that results are similar between surgery and radiochemotherapy, if surgery is mutilating, radiotherapy should be preferred. Induction chemotherapy demonstrated its benefit. For laryngeal or hypopharyngeal cancer, if radiotherapy is available, patients should receive an induction chemotherapy by TPF (cisplatin 75 mg/m2 D1, 5FU 750 mg/m2/d D1 to D5, docetaxel 75 mg/m2 D1) every 3 weeks. The response rate was 80 %, and these patients were irradiated (without potentiation) and could avoid surgery, and after a median follow-up of 36 months, the 3-year actuarial larynx preservation rate was 70.3 % [5]. After induction chemotherapy, no study focused on the possibilities to avoid radiotherapy (i.e., exclusive chemotherapy in the case of complete response or the possibility of surgery of residual tumor after partial response).
4 Treatment of Unresectable Tumors
For non-resectable tumor, the pillar treatment is radiotherapy potentiated by based chemotherapy. In a large meta-analysis including 50 concomitant trials, the addition of concomitant cisplatin-based chemotherapy allowed a hazard ratio of 0.81 (p < 0.0001) with an absolute benefit of 6.5 % at 5 years in overall survival [6]. If radiotherapy is unavailable, we can propose an induction chemotherapy (the TPF regimen allowed a response rate of 68 % with 8.5 % of complete response) [7] followed by surgery if possible.
5 Type of Potentiation of the Radiotherapy
If radiotherapy is available, it should be largely used in HNSCC as adjuvant or exclusive setting. The standard chemotherapy for potentiation is cisplatin at the dose of 100 mg/m2 every 3 weeks for three cycles. Cetuximab, an inhibitor of EGFR, demonstrated a benefit for inoperable disease in combination with radiotherapy. In the pivotal phase III study, the median overall survival was increased from 29 to 49 months [8], but the control arm was radiotherapy alone, without cisplatin. No direct comparison of the potentiation by cisplatin or cetuximab was done. A small study suggests that cisplatin could be better [9]. The costs of cetuximab being largely superior to that of cisplatin will be chosen. The addition of cetuximab to cisplatin in combination with radiotherapy brought more toxicity without clinical interest [10]. So the better type of chemotherapy for potentiation of the radiotherapy is the less expensive drug.
6 Recurrent or Metastatic Disease
In this situation, if locoregional treatment is not possible, we propose palliative chemotherapy. Five types of molecules showed clinical benefit: methotrexate, cisplatin, 5FU, taxanes, and EGFR inhibitors that give about 10–15 % of objective response in monotherapy and an overall survival of about 6–8 months [11]. The combination of cisplatin (100 mg/m2) and 5FU (1,000 mg/m2/d for 5 days) every 3 weeks is a good standard because with low cost, despite the overall survival not increased, the response rate is higher to about 25 %, and for these relapsing patients, often symptomatic, the increase of response rate brings a gain of quality of life [12]. The standard treatment is the triple combination of cisplatin, 5FU, and cetuximab (250 mg/m2 every week): the response rate is increased from 26 to 36 %, and the median overall survival is significantly increased from 7.4 to 10.1 months [13]. Due to its costs, cetuximab is rarely available in tropical areas, and the median overall survival is minored for 2.5 months. Studies demonstrated that with sequential treatment with the five efficient drugs, long survival could be achieved [14].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree