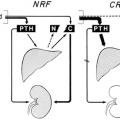
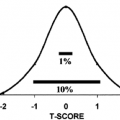
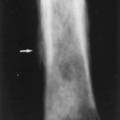
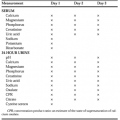
MEDIASTINAL EXPLORATION
The mediastinum is explored through either a cervical incision23 or a median sternotomy (see Fig. 62-4B). If the
enlarged parathyroid gland is visible in the thymus, it should be selectively excised. If no parathyroid is evident, the entire thymus should be removed and sectioned. The parathyroid tumor may not be identified until the pathologist reviews the permanent sections of the submitted tissue. The surgeon should also explore the entire mediastinum around the great vessels and the pericardium. After an enlarged parathyroid gland is identified, if doubt exists that normal parathyroid tissue remains in the neck, the resected parathyroid gland should be sliced into 1-mm × 3-mm pieces and cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen.24 If the patient has been rendered hypoparathyroid, then the viably frozen tissue can be autotransplanted into a forearm muscle.
enlarged parathyroid gland is visible in the thymus, it should be selectively excised. If no parathyroid is evident, the entire thymus should be removed and sectioned. The parathyroid tumor may not be identified until the pathologist reviews the permanent sections of the submitted tissue. The surgeon should also explore the entire mediastinum around the great vessels and the pericardium. After an enlarged parathyroid gland is identified, if doubt exists that normal parathyroid tissue remains in the neck, the resected parathyroid gland should be sliced into 1-mm × 3-mm pieces and cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen.24 If the patient has been rendered hypoparathyroid, then the viably frozen tissue can be autotransplanted into a forearm muscle.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree