DIAGNOSIS
Part of “CHAPTER 58 – PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM“
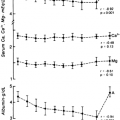
The diagnostic hallmarks of primary hyperparathyroidism are hypercalcemia and an elevated level of PTH. Just as a normal circulating PTH concentration is a relatively unusual finding in primary hyperparathyroidism, a normal level of serum calcium is also most unusual in primary hyperparathyroidism. When this occurs, the circulating serum proteins may be low, and the “normal” serum calcium value may be associated with an elevated ionized calcium concentration (see Chap. 49). Only in this unusual situation of suspected primary hyperparathyroidism—elevated PTH and normal serum calcium—may ionized serum calcium values be a valuable adjunct to other diagnostic tests. Nonetheless, primary hyperparathyroidism is seen occasionally with a truly normal serum calcium concentration. The name normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism was given to this clinical presentation; over time, however, the serum calcium level does become elevated.66 Presumably, this situation reflects increased parathyroid glandular activity that has not yet caused frank hypercalcemia. Rarely can primary hyperparathyroidism be shown to be present in an individual for whom serum calcium determinations are always normal.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree