DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS AND CLINICAL APPROACH TO HYPERPROLACTINEMIA
Part of “CHAPTER 13 – PROLACTIN AND ITS DISORDERS“
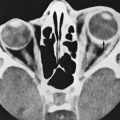
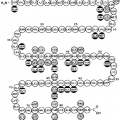
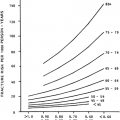
As shown in Table 13-1 and Table 13-2, hyperprolactinemia has multiple causes. The measurement of prolactin level should be repeated with the patient in a nonstimulated state, and, if possible, after an overnight fast in a nonstressed state. Because prolactin may be secreted to a modest degree after a breast examination, a subsequent mild increase in prolactin levels would warrant a repeat determination. Although Table 13-2 demonstrates the existence of several pathologic causes of prolactin elevation, pituitary tumors are clinically the most important. Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumors and may account for as many as 40% to 50% of all pituitary tumors.43 Hyperprolactinemia may be detected in as many as 40% of patients with acromegaly and has been reported in patients with Cushing disease. Hyper-prolactinemic patients with suggestive clinical manifestations should be evaluated for acromegaly and Cushing disease.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree