Neuroblastomas are heterogeneous neuroblastic tumors that occur almost exclusively in childhood. Most neuroblastomas occur in the abdomen, usually in the adrenal gland. Catecholamine secretion may occur in approximately 70% of cases. Patient age at diagnosis, stage of disease, and cytogenetics have prognostic implications
Case Report
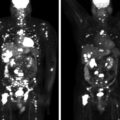
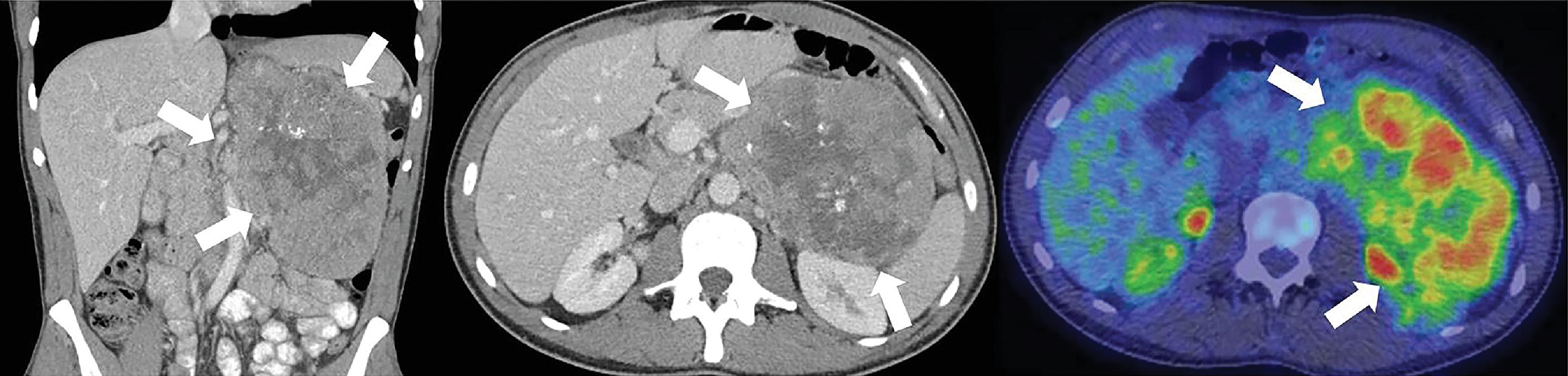
The patient was a 39-year-old man who initially presented with abdominal discomfort and symptoms of radiculopathy. In addition, he reported occasional spells with anxiety and episodic elevated blood pressure. Initially, he was treated with physical therapy to improve his symptoms of radiculopathy. However, because of incomplete improvement, spine imaging was recommended. Unexpectedly, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine demonstrated metastatic bone disease, and further imaging revealed a large adrenal mass ( Fig. 78.1 ).
INVESTIGATIONS
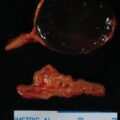
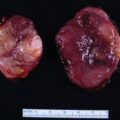
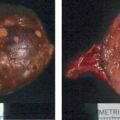
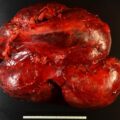
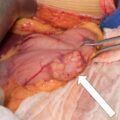
Workup for catecholamine excess was pursued and demonstrated elevated urinary normetanephrine and dopamine ( Table 78.1 ). A preliminary diagnosis of pheochromocytoma with bone metastases was considered, and open left adrenalectomy was recommended. Appropriate preparation with α- and β-adrenergic blockade was initiated before adrenalectomy. During surgery, in addition to the left adrenal mass, multiple lymph nodes were removed. Surprisingly, pathologic diagnosis was neuroblastoma with lymph node metastases.
| Biochemical Test | Result | Reference Range |
| Cortisol after overnight 1-mg DST, mcg/dL | Not performed | <1.8 |
| Cortisol, mcg/dL | 12 | 7–21 |
| ACTH, pg/mL | Not performed | 7.2–63 |
| DHEA-S, mcg/dL | 172 | 65–344 |
| Aldosterone, ng/dL | 13 | <21 |
| Plasma renin activity, ng/mL per hour | Not performed | 2.9–10.8 |
| 24-Hour urine metanephrine, mcg/24 h | 126 | <400 |
| 24-Hour urine normetanephrine, mcg/24 h | 1582 | <900 |
| 24-Hour urine epinephrine, mcg/24 h | 3 | <21 |
| 24-Hour urine norepinephrine, mcg/24 h | 72 | 15–80 |
| 24-Hour urine dopamine, mcg/24 h | 1016 | 65–400 |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree