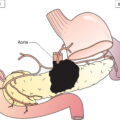
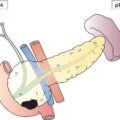
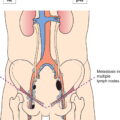
The definitions of the T, N, and M categories correspond to the FIGO stages. Both systems are included for comparison. The classification applies to sarcomas except for carcinosarcoma, which is classified as carcinoma of the endometrium. There should be histological confirmation and division of cases by histologic type. The FIGO stages are based on surgical staging. TNM stages are based on clinical and/or pathological classification. The regional lymph nodes are the pelvic (hypogastric [obturator, internal iliac] (3), common (5) and external (4) iliac, parametrial (2), and sacral (6)) and the para‐aortic nodes (7). Note Note The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note
UTERUS – UTERINE SARCOMAS (LEIOMYOSARCOMA, ENDOMETRIAL STROMAL SARCOMA, ADENOSARCOMA) (ICD‐O‐3 C53, 54, 55)
Rules for Classification
Anatomical Subsites (Fig . 424)
Histological Types of Tumours
Leiomyosarcoma
ICD‐O‐3 M 8890/3
Endometrial stromal sarcoma
ICD‐O‐3 M 8930/3
Endometrial stromal sarcoma, low grade Adenosarcoma
ICD‐O‐3 M 8931/3ICD‐O‐3 M 8933/3
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 425)
Leiomyosarcoma, Endometrial stromal sarcoma
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TNM Categories
FIGO Stages
Definition
T1
I
Tumour limited to the uterus
T1a
IA
Tumour 5 cm or less in greatest dimension (Fig. 442)
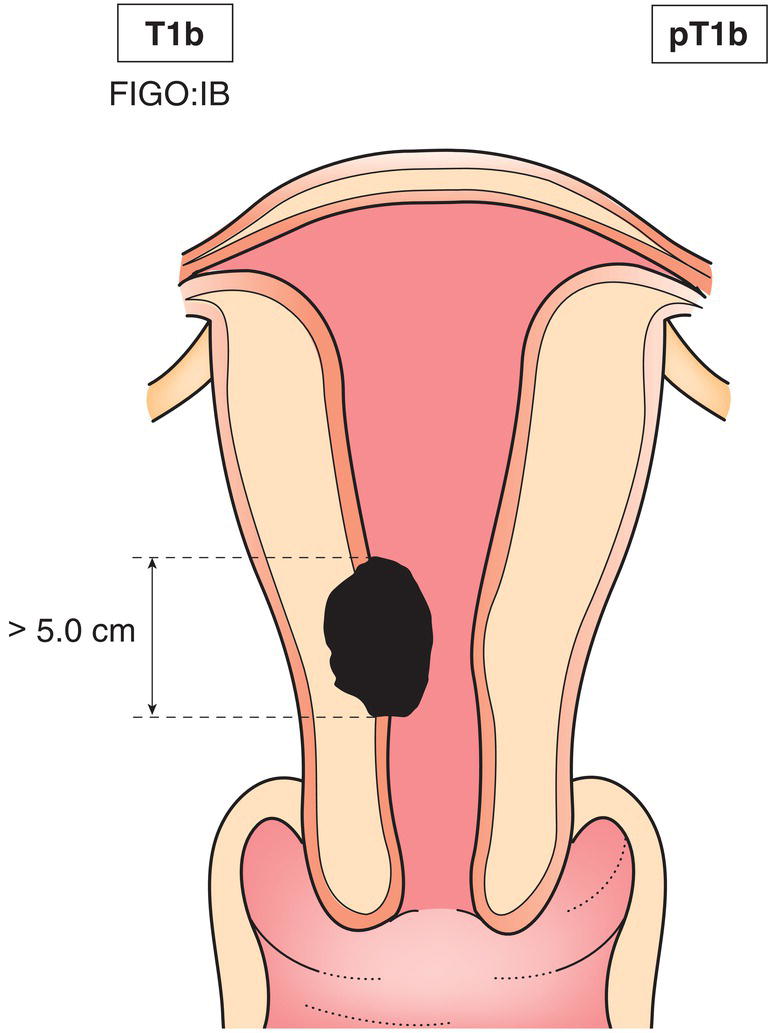
T1b
IB
Tumour more than 5 cm in greatest dimension (Fig. 443)
T2
II
Tumour extends beyond the uterus, within the pelvis (Fig. 444)
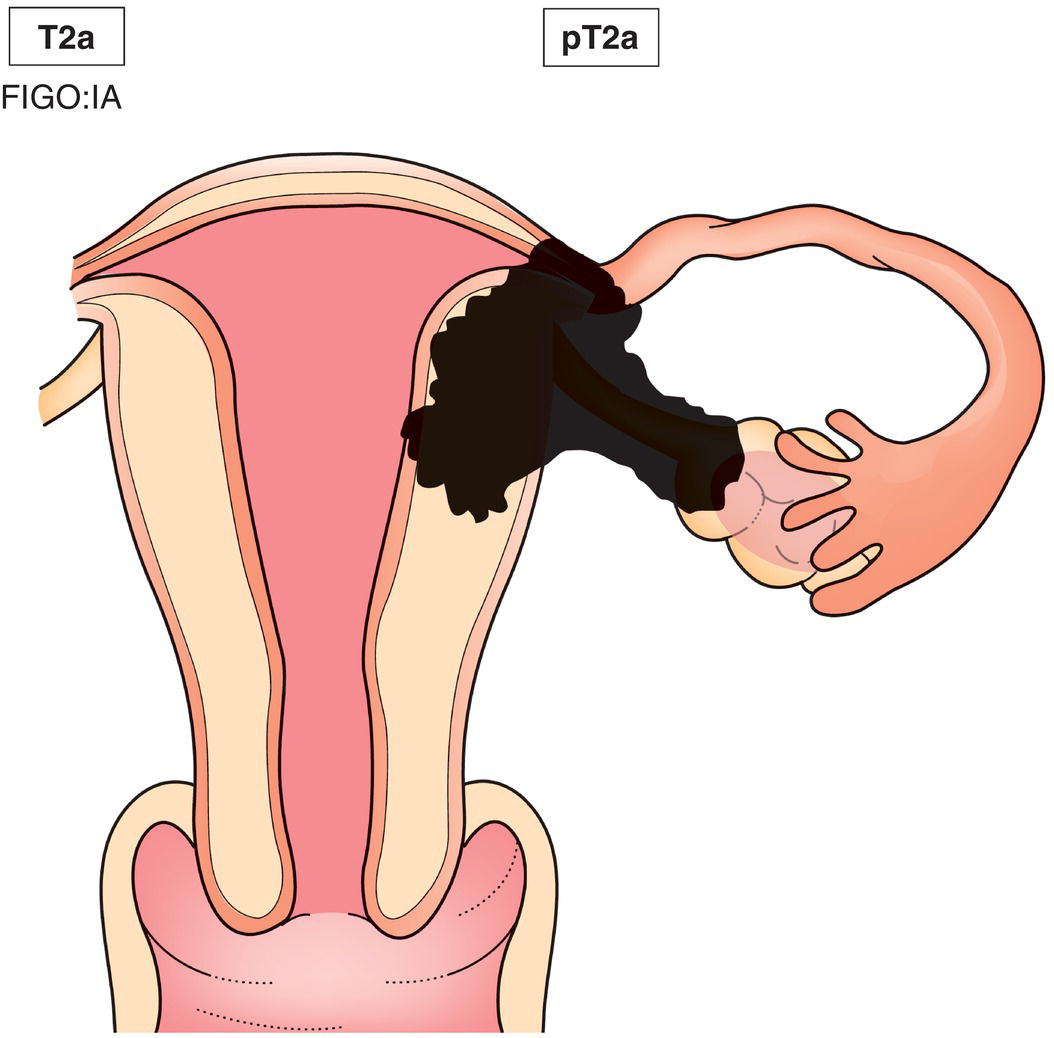
T2a
IIA
Tumour involves adnexa (Fig. 444)
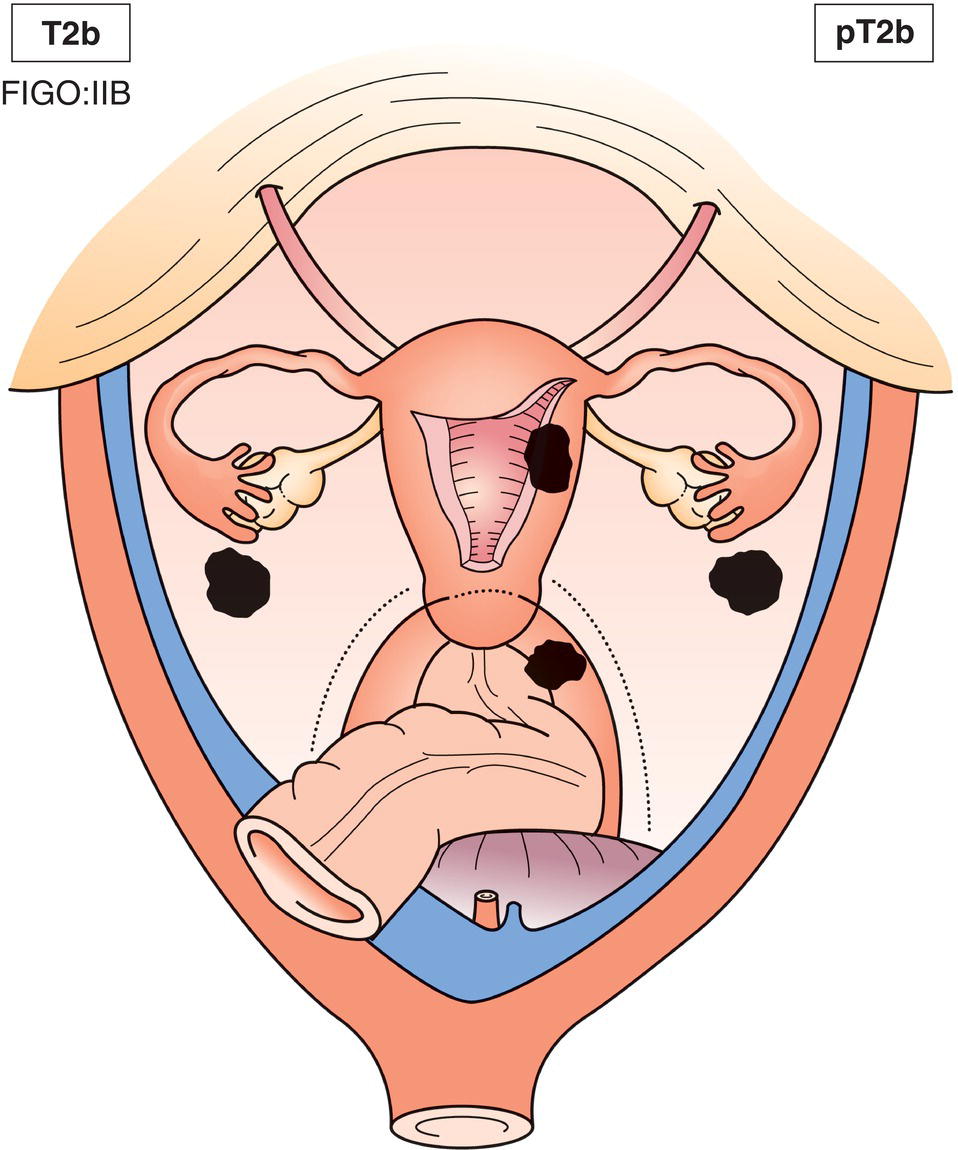
T2b
IIB
Tumour involves other pelvic tissues (Fig. 445)
T3
III
Tumour infiltrates abdominal tissues
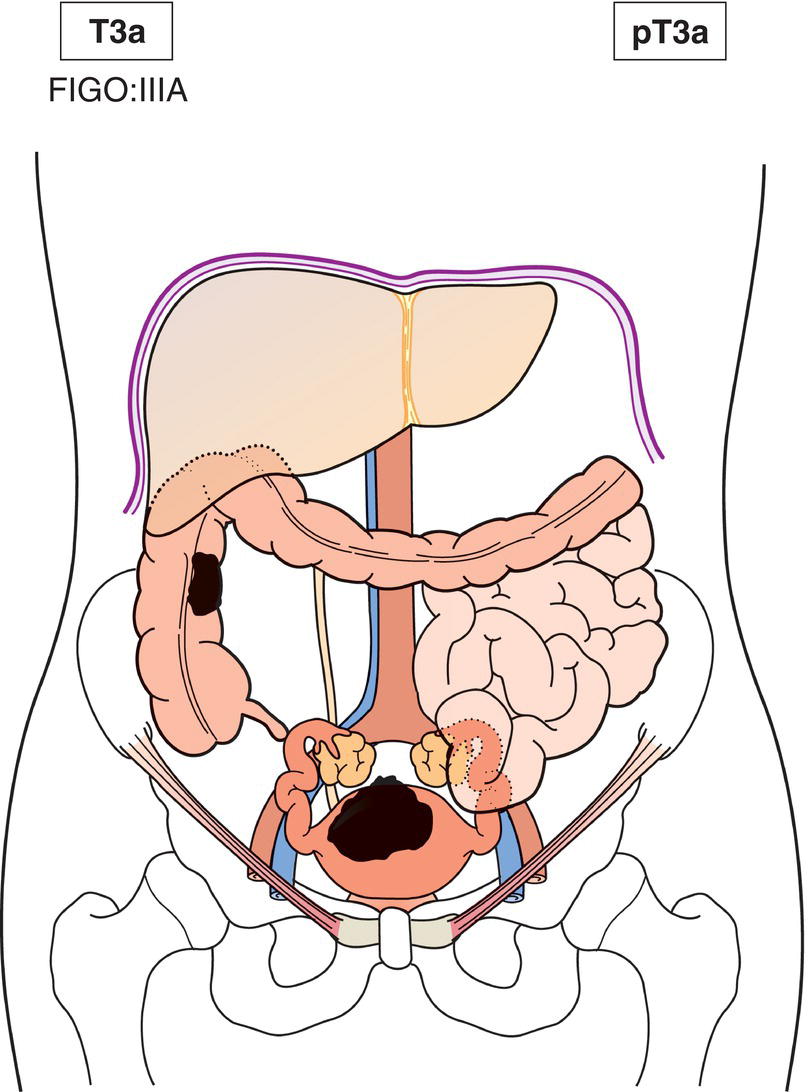
T3a
IIIA
One site (Fig. 446)
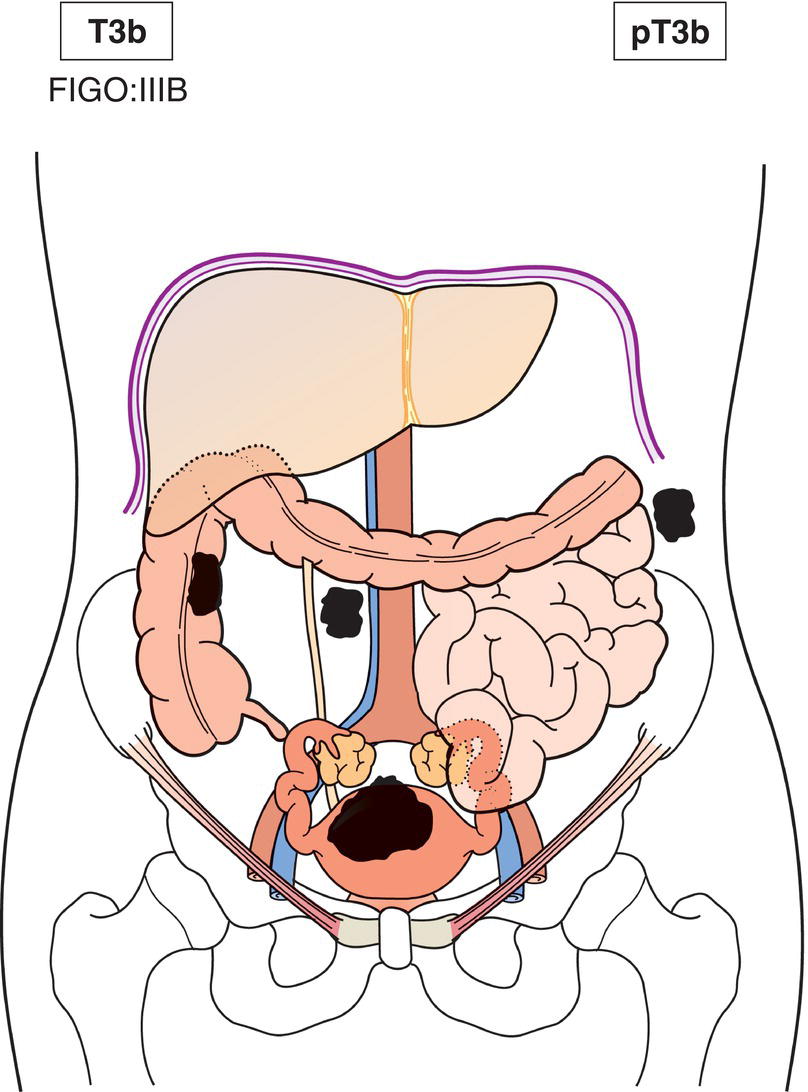
T3b
IIIB
More than one site (Fig. 447)
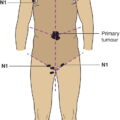
N1
IIIC
Metastasis to regional lymph nodes
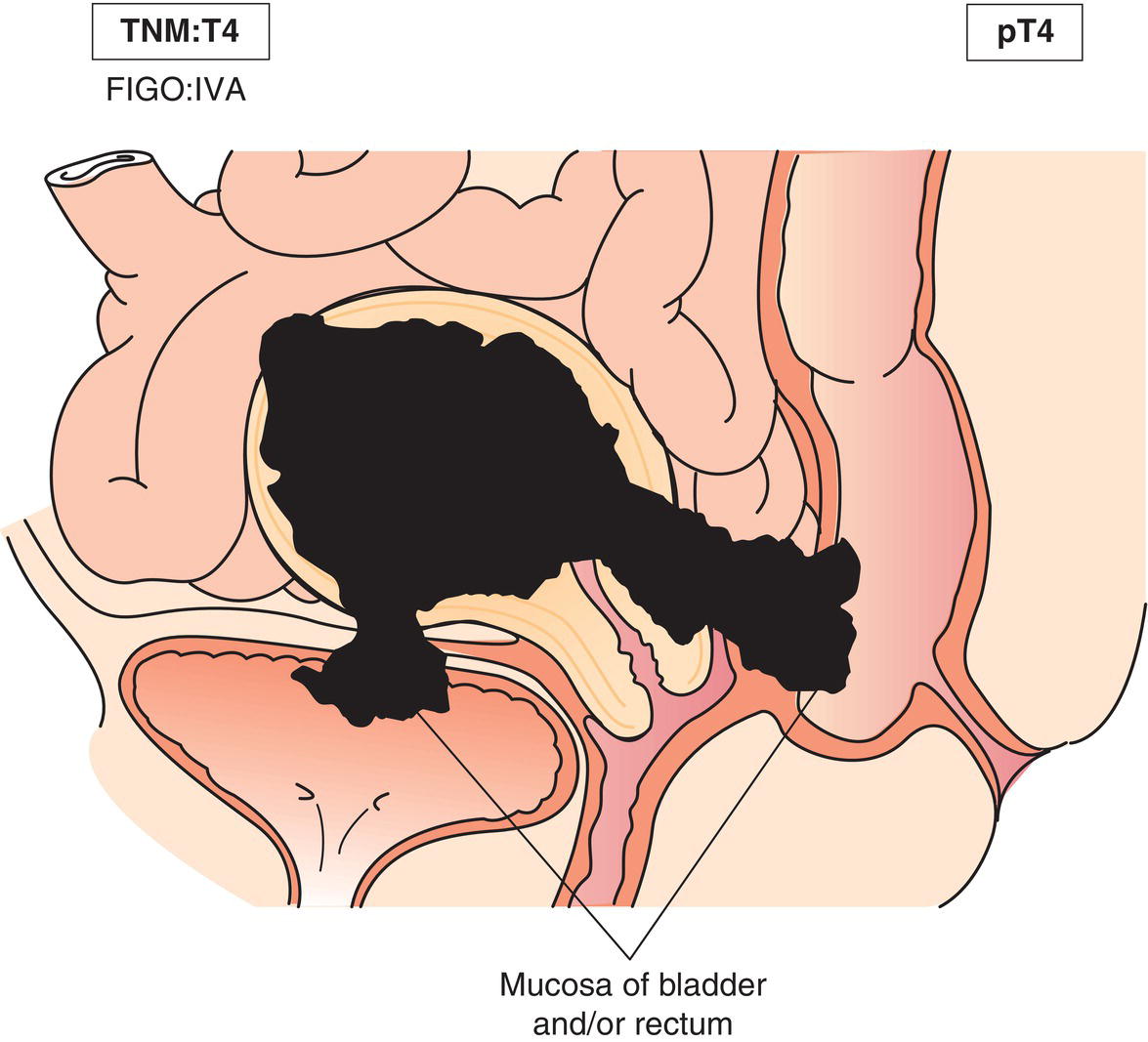
T4
IVA
Tumour invades bladder or rectum (Fig. 448)
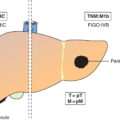
M1
IVB
Distant metastasis
Simultaneous tumours of the uterine corpus and ovary/pelvis in association with ovarian/pelvic endometriosis should be classified as independent primary tumours.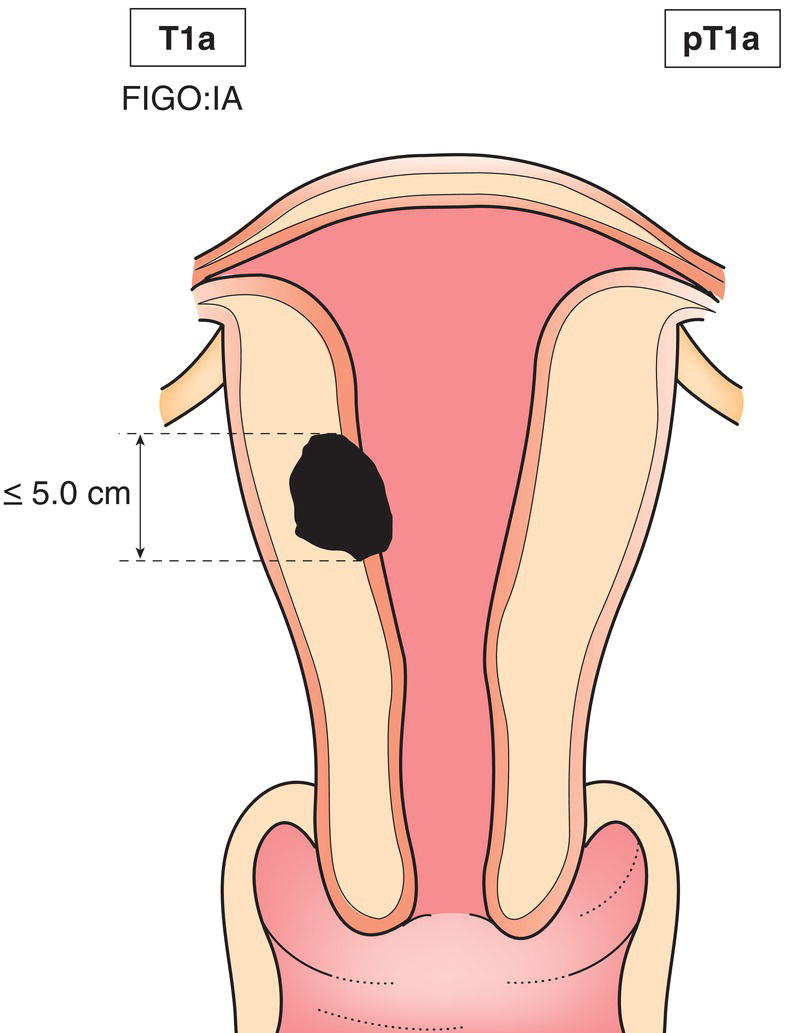
Adenosarcoma
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TNM Categories
FIGO Stage
Definition
T1
I
Tumour limited to the uterus
ΌT1a
ΌIA
ΌTumour limited to the endometrium/endocervix (Fig. 449)
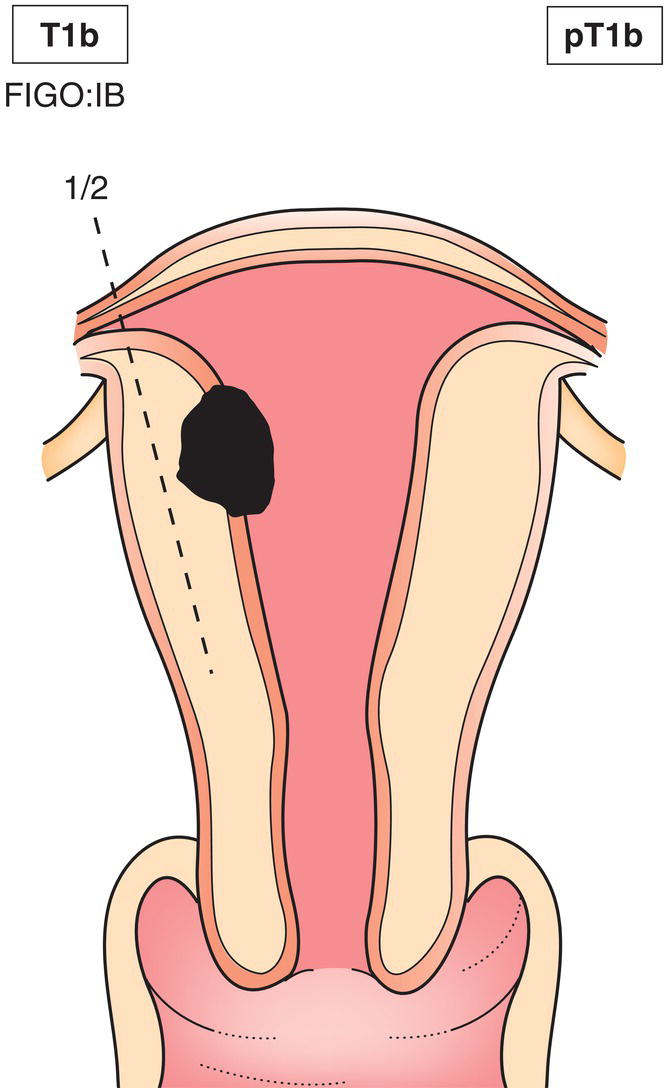
ΌT1b
ΌIB
ΌTumour invades to less than half of the myometrium (Fig. 450)
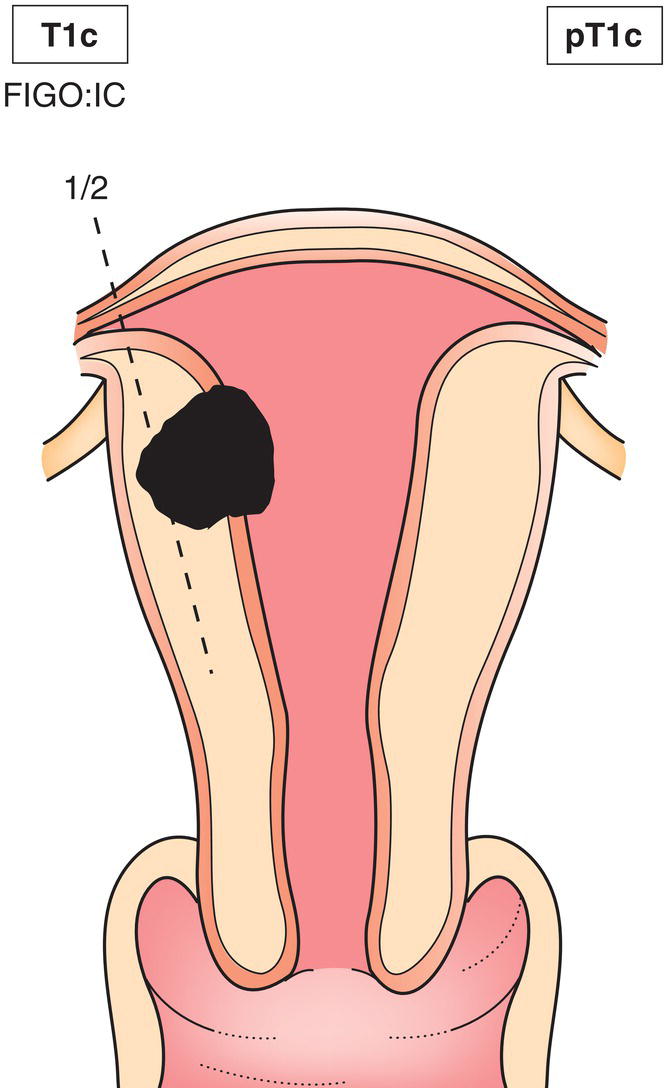
ΌT1c
ΌIC
ΌTumour invades more than half of the myometrium (Fig. 451)
T2
II
Tumour extends beyond the uterus, within the pelvis
ΌT2a
ΌIIA
ΌTumour involves adnexa (Fig. 444)
ΌT2b
ΌIIB
ΌTumour involves other pelvic tissues (Fig. 445)
T3
III
Tumour involves abdominal tissues
ΌT3a
ΌIIIA
ΌOne site (Fig. 446)
ΌT3b
ΌIIIB
ΌMore than one site (Fig. 447)
N1
IIIC
Metastasis to regional lymph nodes
T4
IVA
Tumour invades bladder or rectum (Fig. 448)
M1
IVB
Distant metastasis
Simultaneous tumours of the uterine corpus and ovary/pelvis in association with ovarian/pelvic endometriosis should be classified as independent primary tumours.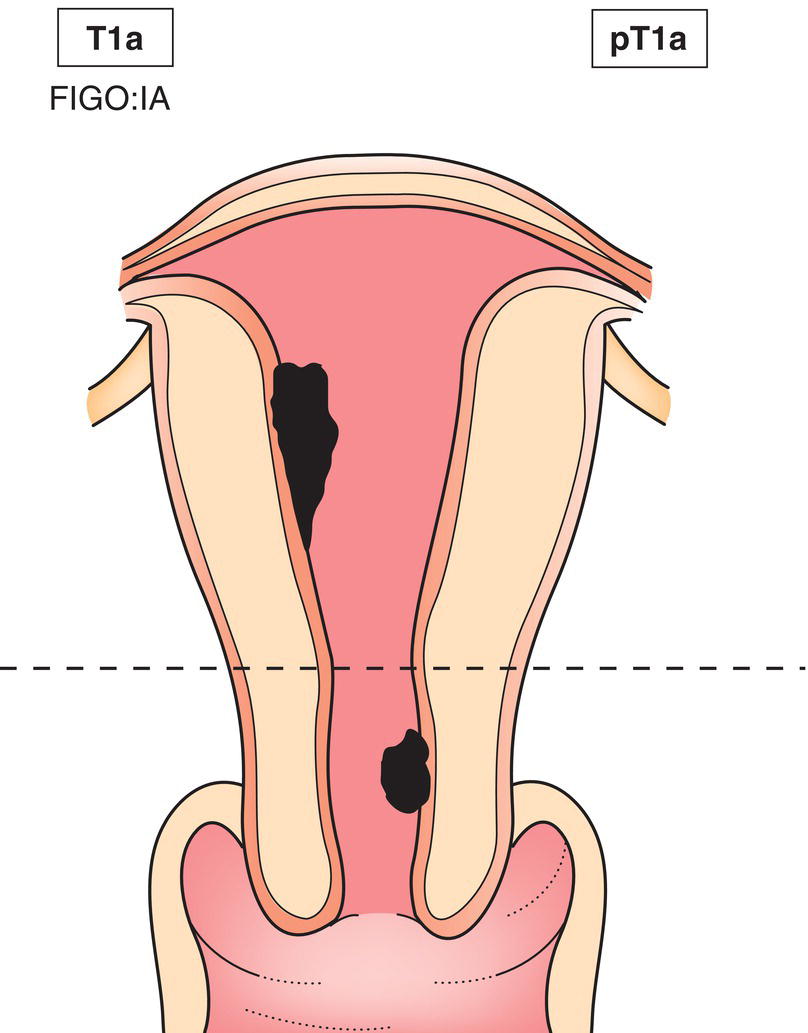
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis (excluding adnexa, pelvic and abdominal tissues)
pTNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree