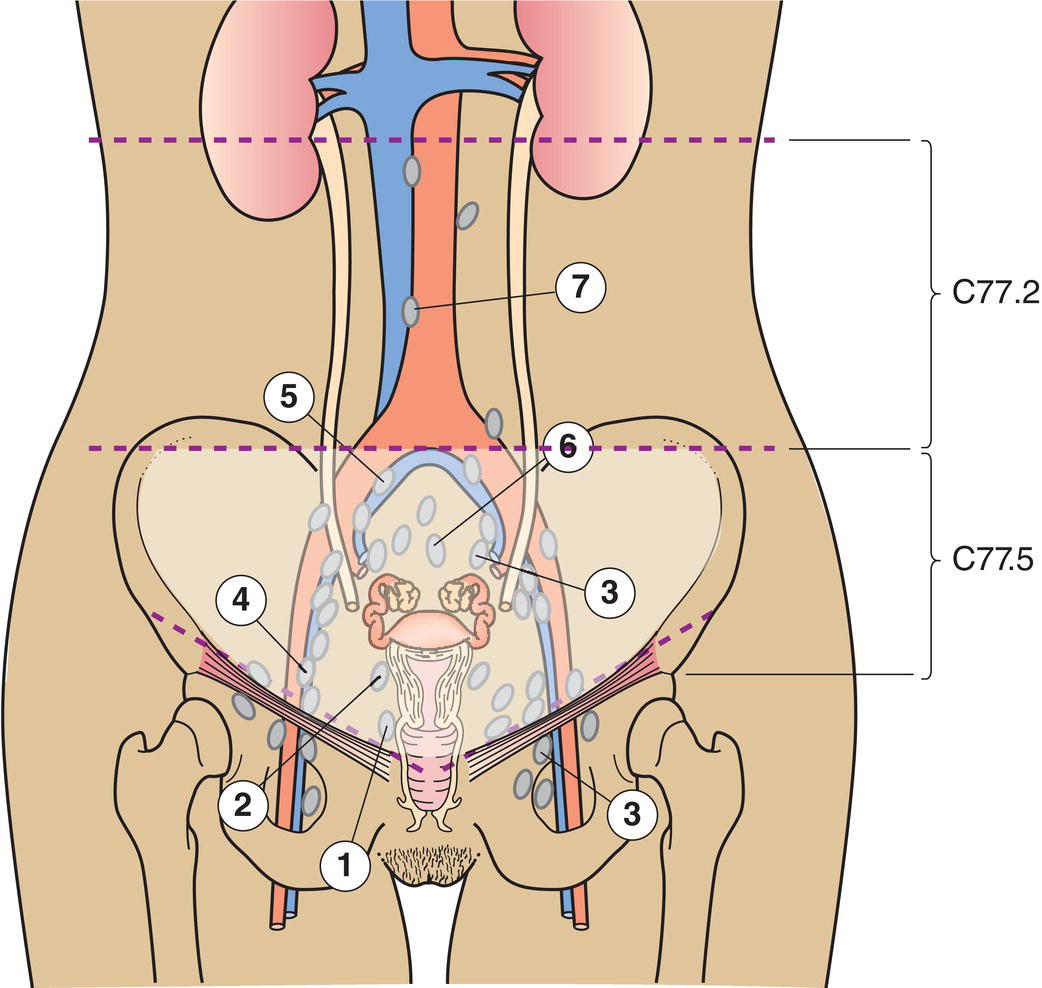
The definitions of the T and M categories correspond to the FIGO stages. Both systems are included for comparison. The classification applies only to carcinomas. There should be histological confirmation of the disease. FIGO staging of cervical carcinoma was updated in 2018 (ref: DOI: 10.1002/ijgo.12611) and has significant differences to TNM. Please note a new version of TNM staging for cervix is proposed which aligns with the new version of FIGO (see https://www.uicc.org/resources/tnm/publications‐resources for details) The regional lymph nodes are the paracervical (1), parametrial (2), hypogastric (internal iliac, obturator) (3), common (5) and external iliac (4), presacral (6), lateral sacral nodes (7) and para‐aortic nodes (8). Note Note 2The depth of invasion should be taken from the base of the epithelium, either surface or glandular, from which it originates. The depth of invasion is defined as the measurement of the tumour from the epithelial–stromal junction of the adjacent most superficial papillae to the deepest point of invasion. 3Vascular space involvement, venous or lymphatic, does not affect classification. 4FIGO does not consider horizontal extent in definition of IA1 or IA2. Note 2 FIGO defines IB2 as Invasive carcinoma ≥ 2.0 cm and > 4.0 cm in greatest dimension. FIGO has an additional category of IB3: Invasive carcinoma ≥ 4.0 cm in greatest dimension. Notes Note The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note
CERVIX UTERI (ICD‐O‐3 C53)
Rules for Classification
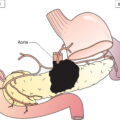
Anatomical Subsites (Fig. 424)
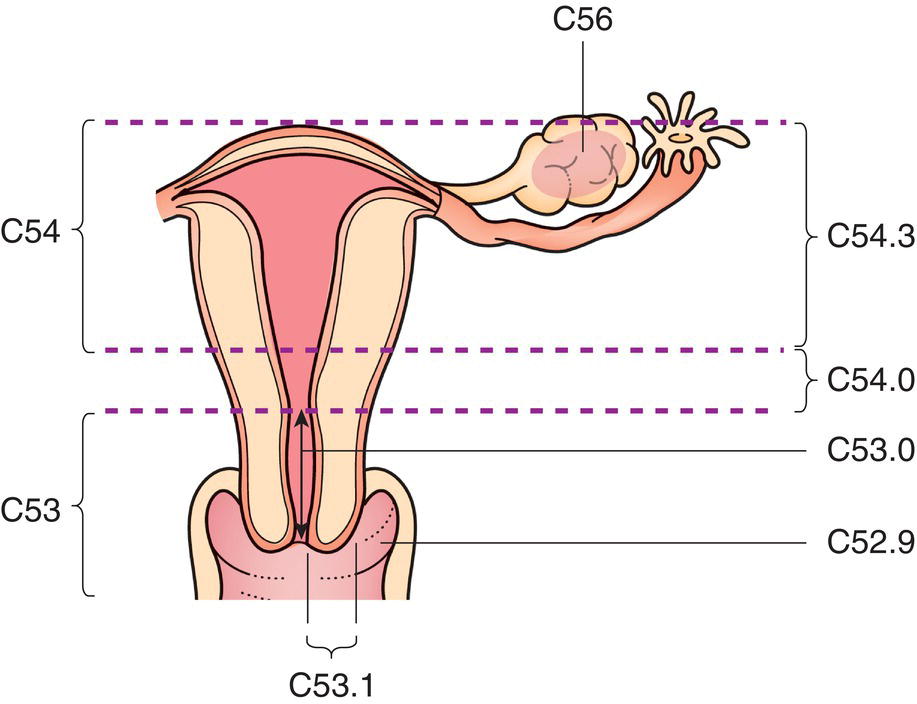
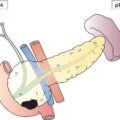
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 425)
In the 7th edition the para‐aortic nodes were considered to be distant metastatic, but to be consistent with advice from FIGO the para‐aortic nodes are now classified as regional.
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TNM Categories
Definition
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis1
Carcinoma in situ (preinvasive carcinoma)
T1
Tumour confined to the cervix (extension to corpus should be disregarded)2
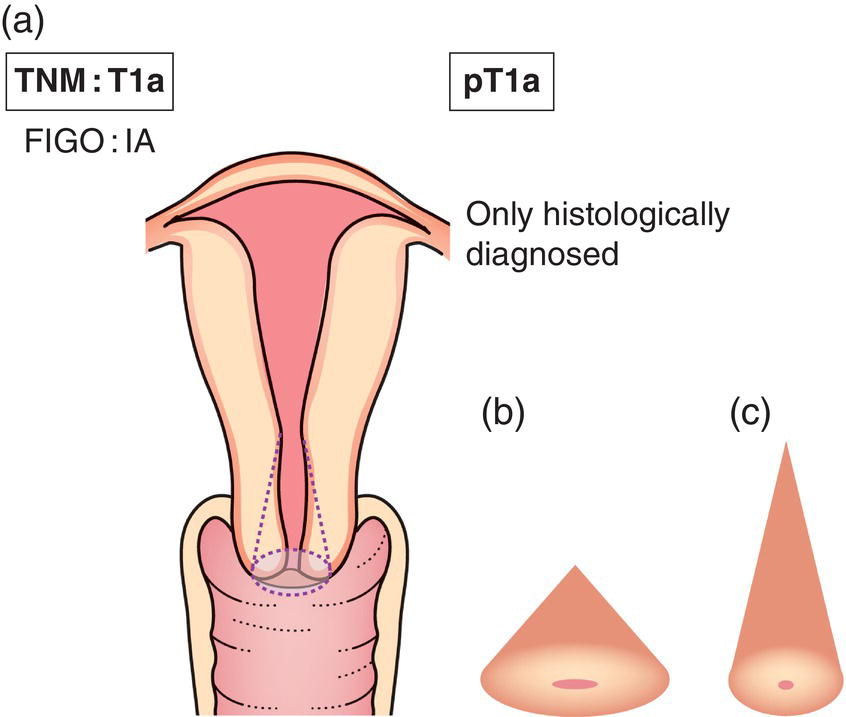
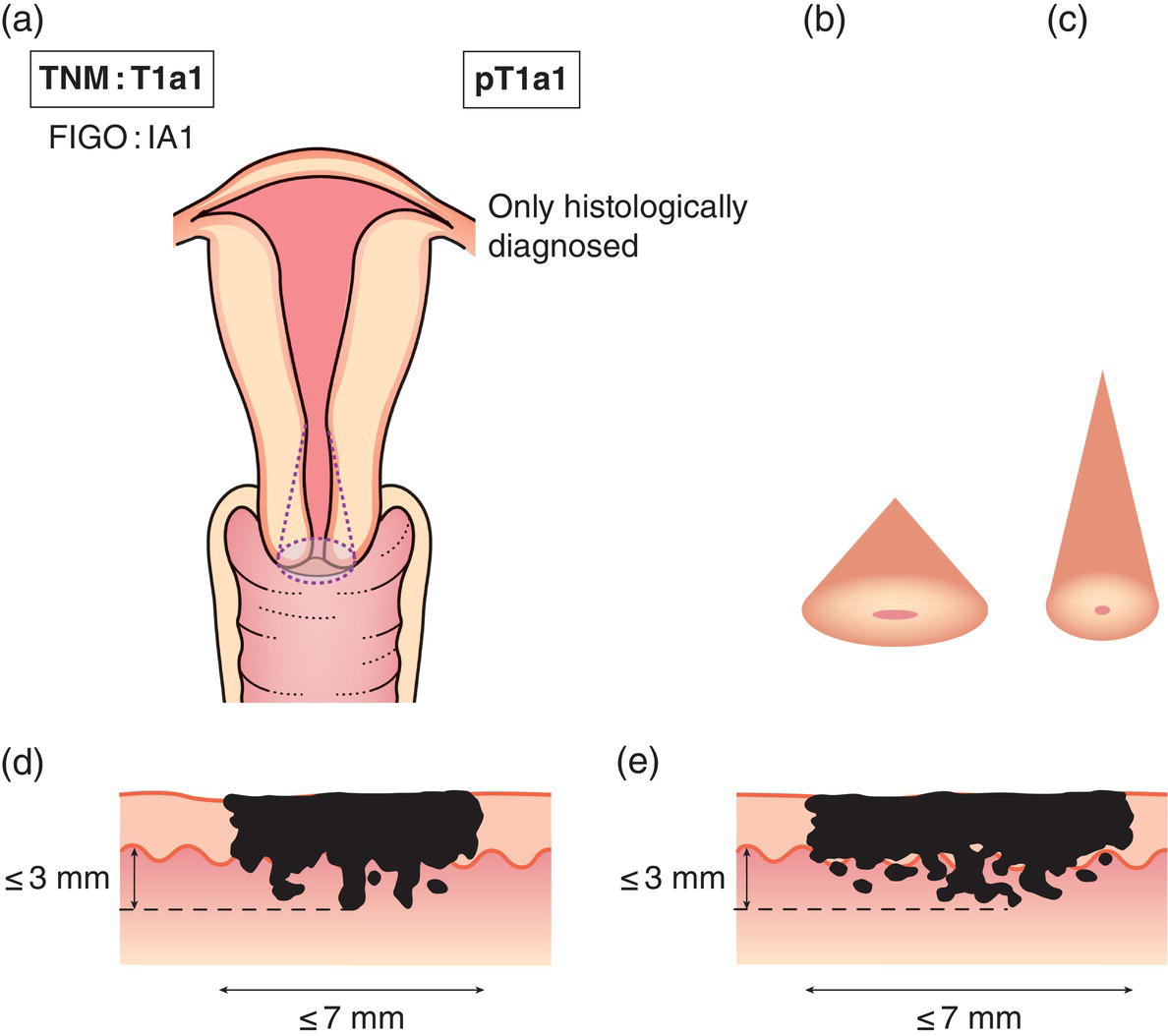
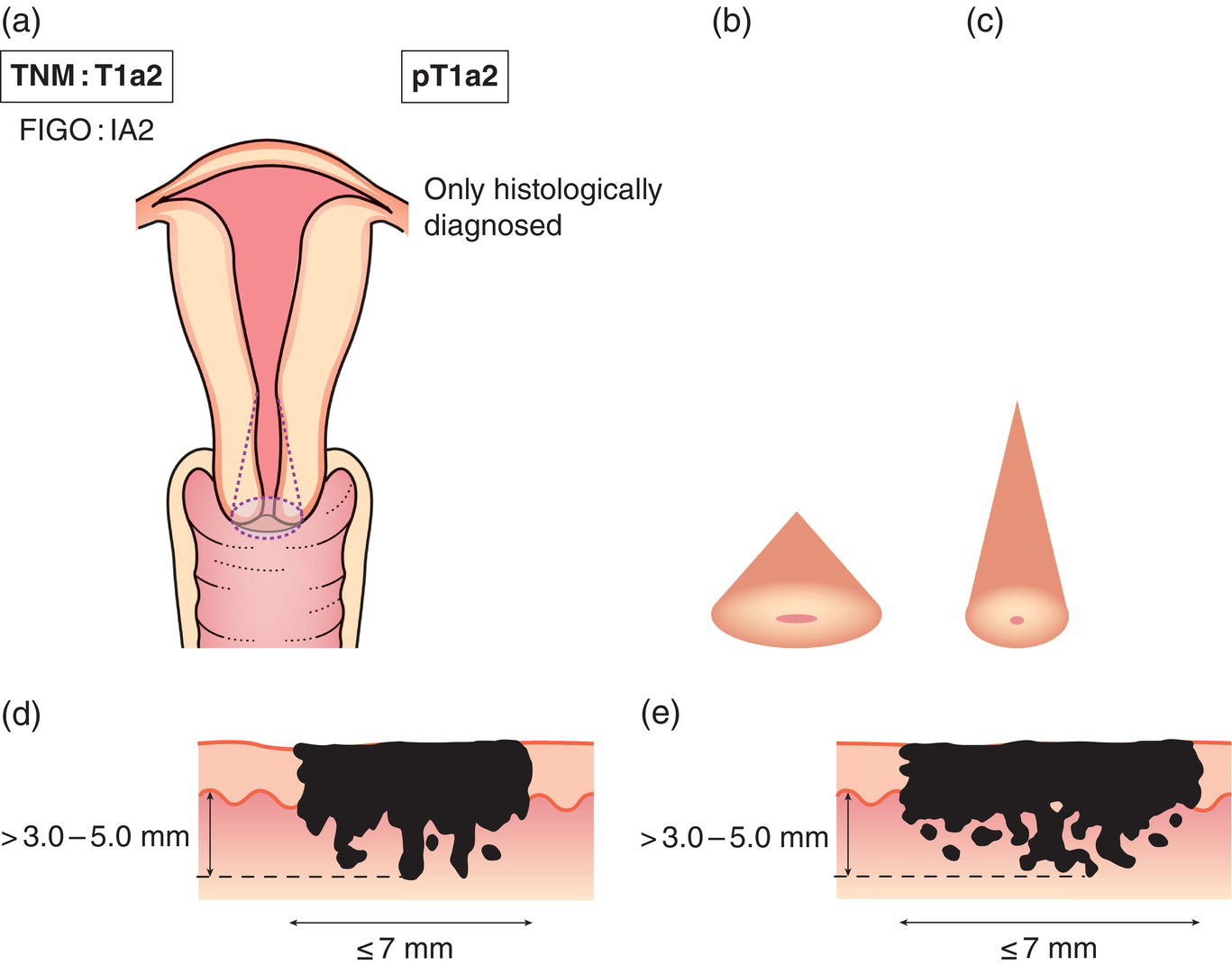
T1a3,4
Invasive carcinoma diagnosed only by microscopy (Fig. 426). Stromal invasion with a maximal depth of 5.0 mm measured from the base of the epithelium and a horizontal spread of 7.0 mm or less2 (Fig. 427)
T1a1
Measured stromal invasion 3.0 mm or less in depth and 7.0 mm or less in horizontal spread
T1a2
Measured stromal invasion more than 3.0 mm and not more
than than 5.0 mm with a horizontal spread of 7.0 mm or less (Fig. 428)
1FIGO no longer include Stage 0 (Tis)
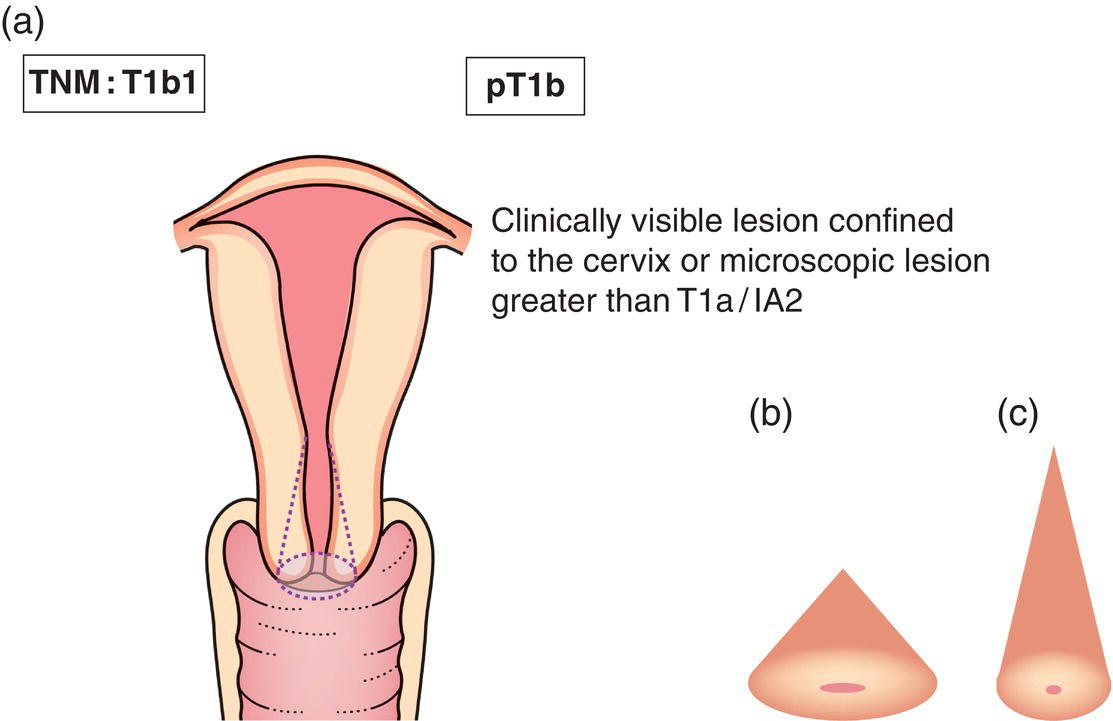
T1b
Clinically visible lesion confined to the cervix (Figs. 429, 431 ) or microscopic lesion greater than T1a/IA2 (Fig. 430)
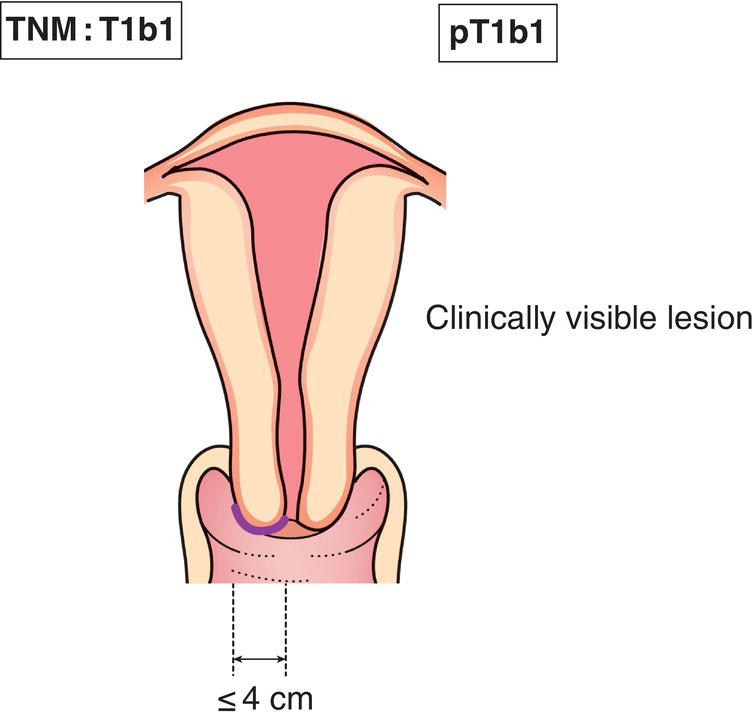
T1b1
Clinically visible lesion 4.0 cm or less in greatest dimension1 (Fig. 429)
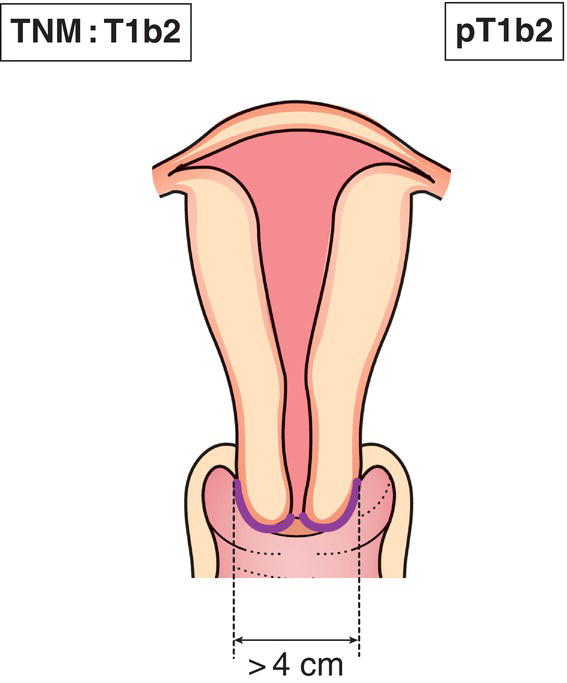
T1b2
Clinically visible lesion more than 4.0 cm in greatest dimension2 (Fig. 431)
1 FIGO defines IB1 as Invasive carcinoma ≥ 5.0 mm depth of invasion and < 2.0 cm in greatest dimension.
T2
Tumour invades beyond uterus but not to pelvic wall or to lower third of vagina (Fig. 432)
T2a
Tumour without parametrial invasion
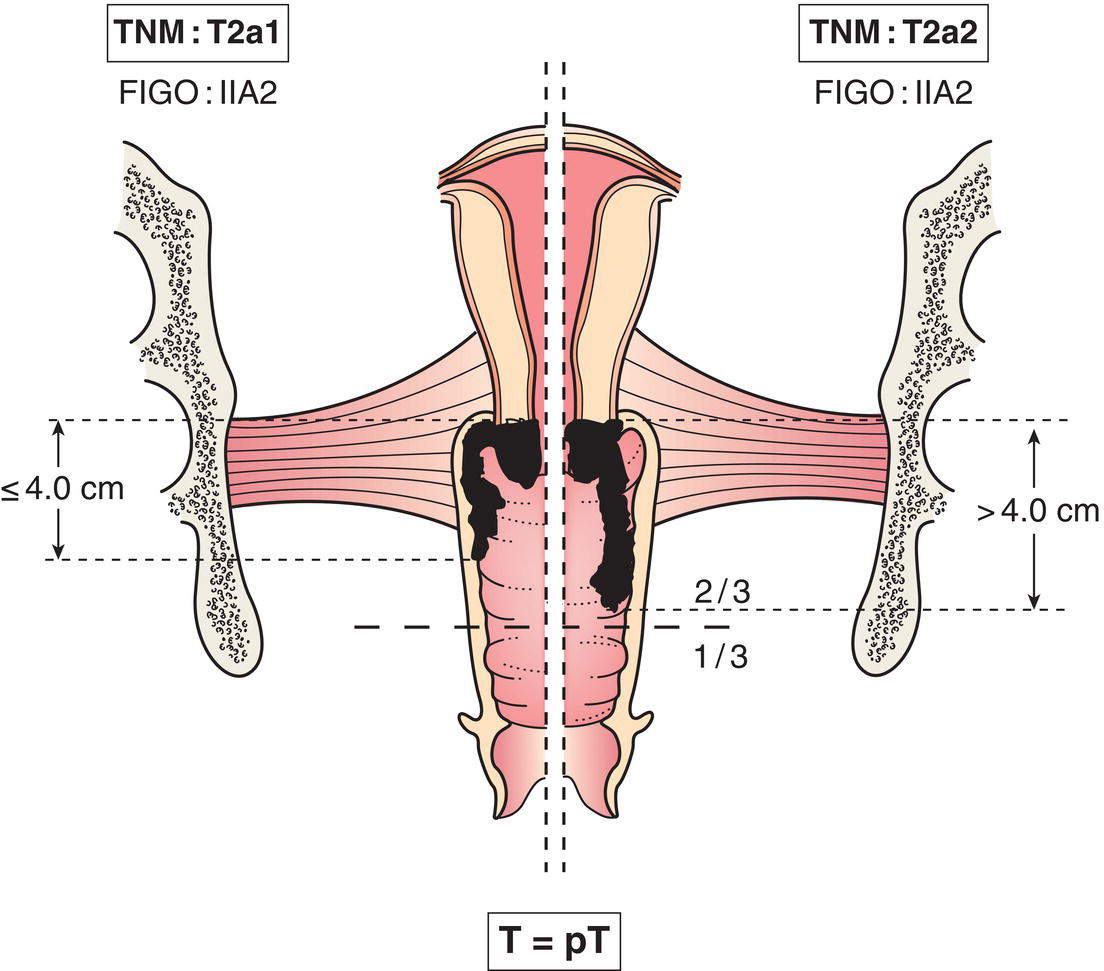
T2a1
Clinically visible lesion 4.0 cm or less in greatest dimension
T2a2
Clinically visible lesion more than 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
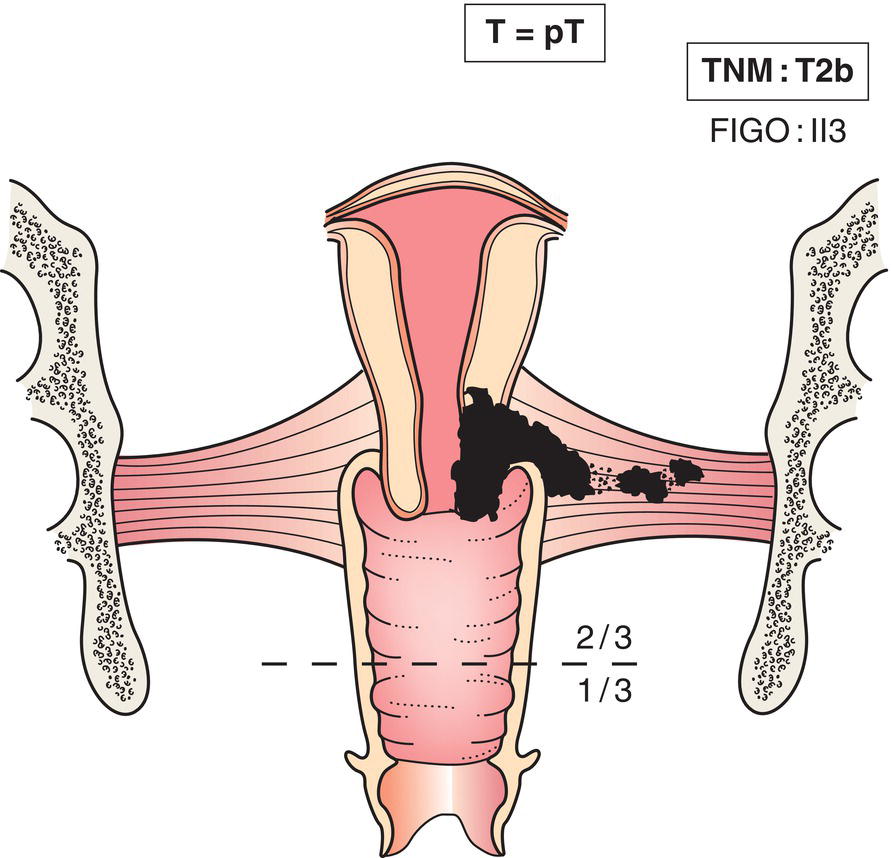
T2b
Tumour with parametrial invasion (Fig. 433)
T3
Tumour extends to pelvic wall, involves lower third of vagina, causes hydronephrosis or non‐functioning kidney (Fig. 434)
T3a
Tumour involves lower third of vagina
T3b
Tumour extends to pelvic wall, causes hydronephrosis or nonfunctioning kidney
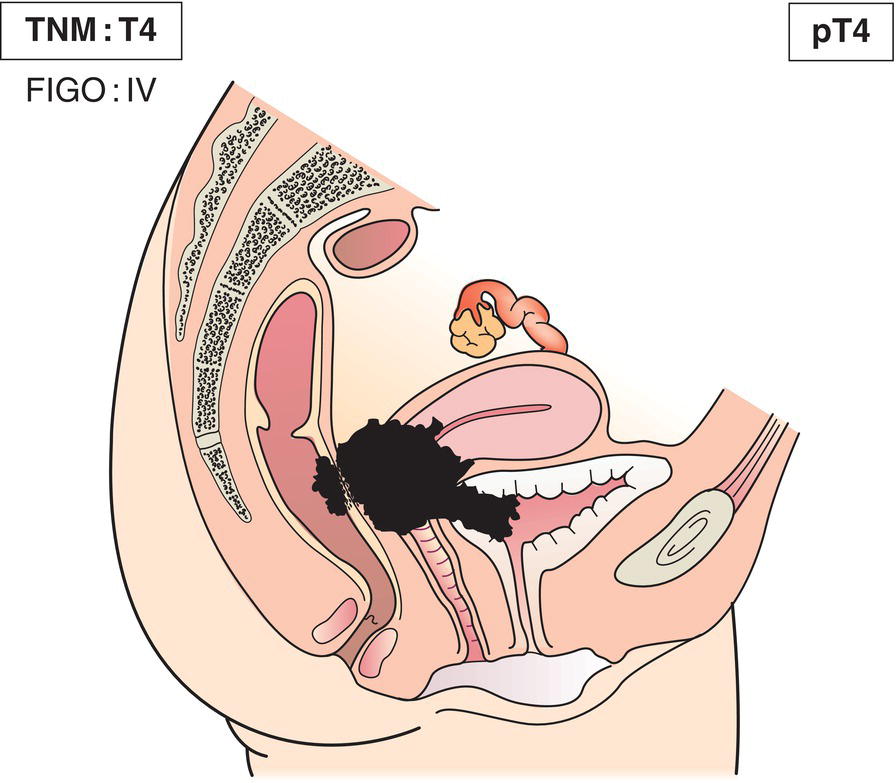
T4
Tumour invades mucosa of the bladder or rectum, or extends beyond true pelvis1 (Fig. 435)
M1
Distant metastasis
1Bullous oedema is not sufficient to classify a tumour as T4.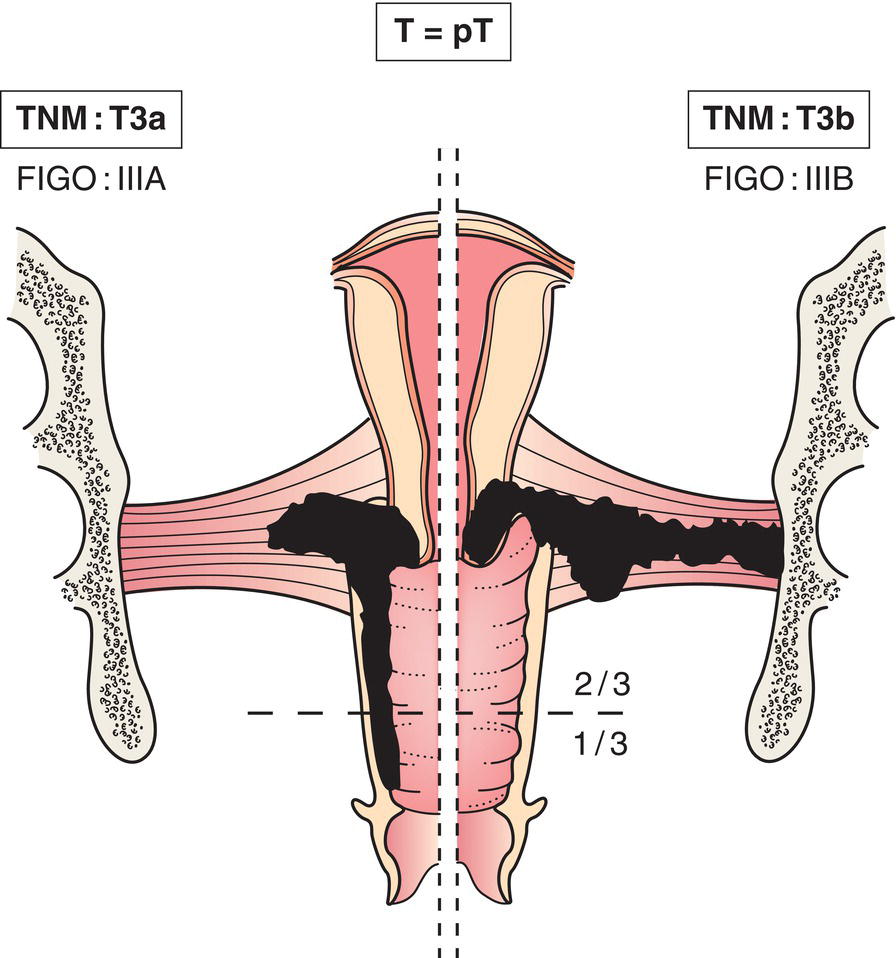
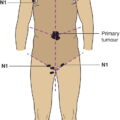
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
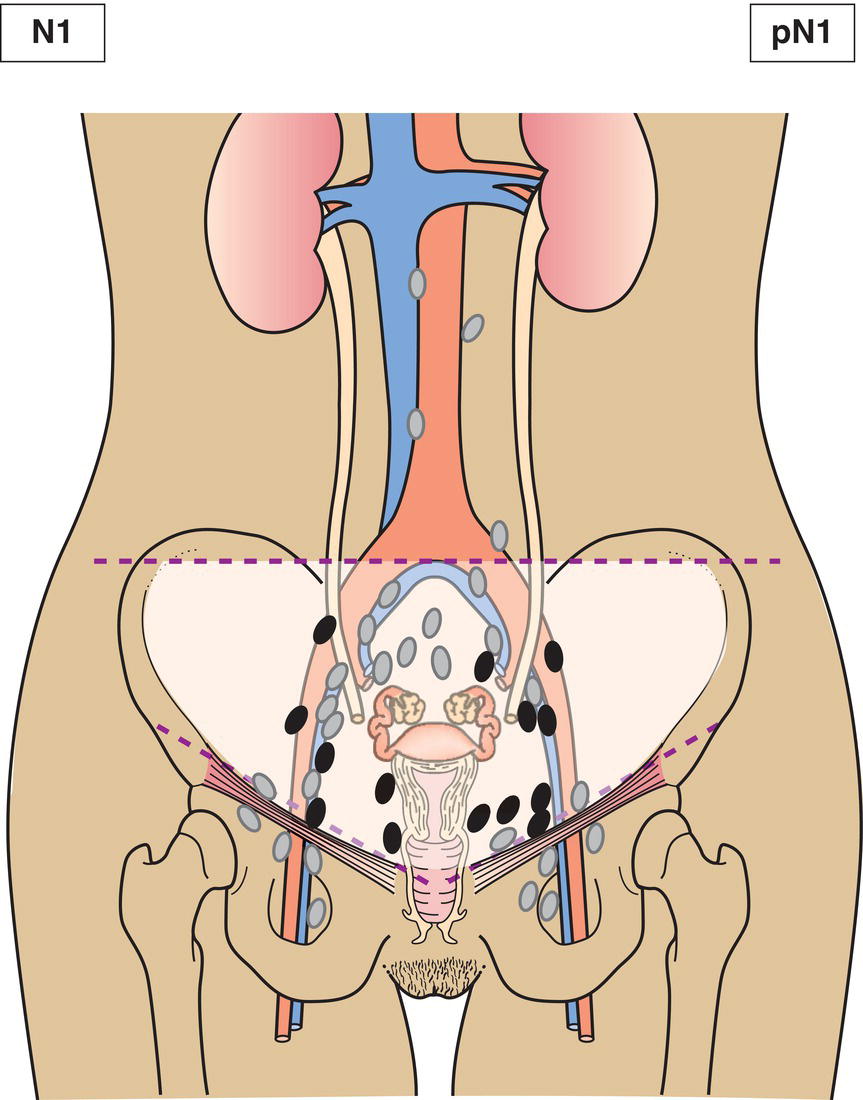
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis* (Fig. 436)
FIGO now includes regional lymph nodes in staging of cervical carcinoma. IIIC1 pelvic lymph node metastasis only. IIIC2 para‐aortic lymph node metastasis.
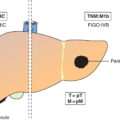
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis (includes inguinal lymph nodes and intraperitoneal disease). It excludes metastasis to para‐aortic lymph nodes, vagina, pelvic serosa, and adnexa
pTNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
pN0
Histological examination of a pelvic lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 10 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree