Applicant’s side
Consultant’s side
Activity
Example
Name of act
Patient ± medical ± paramedical staff
Medical staff ± paramedical staff
Examination
Stroke diagnosis
Consultation
Patient + medical or paramedical staff
Medical staff ± paramedical staff
Care or diagnosis procedure by local staff with remote guidance
Wound dressing
Medical assistance
Patient + medical or paramedical staff
Paramedical staff
Care or evaluation by local staff with remote guidance or support
Dementia diagnosis with a local psychologist
Paramedical assistance
Medical ± paramedical staff
Medical ± paramedical staff
Discussion on medical records and decision
Rehabilitation during palliative care
Synchronous expertise, staff, multidisciplinary meeting
Medical ± paramedical staff
Medical
Answer on medical records and advice
Adapting anti-thrombotic treatment in a patient already known to the consultant
Asynchronous expertise
Patient ± paramedical staff
Rehabilitation staff
Rehabilitation
Speech therapy with no speech therapist available on site
Rehabilitation
Information from a medical device “with” patient
Medical staff
Remote follow-up of a parameter or vital sign
Monitoring of weight in heart failure patient
Monitoring
20.5 The Process of a Telemedicine Act
A telemedicine act is a sequence of actions. We will describe the process that was implemented at Gérontopôle Toulouse (France) for patients from nursing home partners of the telemedicine project (Fig. 20.1).
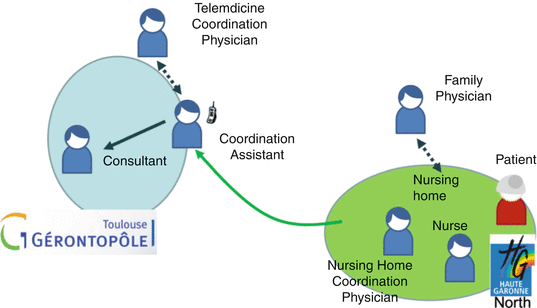

Fig. 20.1
UML diagram of actors for the provision of telemedicine for nursing homes in the north of Haute Garonne by Gérontopôle. Full arrows are showing compulsory participations, dotted arrows are showing conditional participations
The nursing home asks for a telemedicine appointment during the follow-up of a patient of Gérontopôle or as a first time expertise. The patient may be referred by the nursing home (i.e., by the nursing staff with the agreement of the patient’s family physician and in collaboration with the coordination physician in case of chronic wounds, behavior problems, etc.) or by the patient’s physician (in case of difficult diagnosis). The applicant contacts the coordination assistant (CA) by phone or secure email. The CA organizes for all the actors to be available, checks records are properly transmitted, organizes the availability of the “meeting room,” and emails the date of the appointment and the directions to get connected. If advice is required on the most adequate consultant for the case, the CA will refer to the physician in charge of coordinating the telemedicine activity for proper choice.
At the said time, the actors connect. All, but only, the persons relevant to the case of the patient are present. Being in time is most important. Both sides check they can see and hear one another (PiP), everybody greets each other, patient first if present. The consultant notes all the persons attending with their profession or role. The act proper starts. This may include discussion of films, pictures, or X-rays presented during the act. When an agreement is reached by the participants on the diagnosis and treatments, the consultant writes a report on the telemedicine medical records (TMR), as an answer to the request form from the applicant. The applicant gets the report on the TMR and adds it to the patient’s records.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree