SIDE EFFECTS OF ANDROGENS
Adverse effects of androgens may be caused by their androgenic actions or, if they are aromatizable, by their estrogenic effects.156 Other side effects are related to the particular androgen formulation (e.g., hepatotoxicity with 17α-alkylated androgens).
ANDROGENIC SIDE EFFECTS
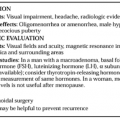
Complaints of excessive stimulation of libido and erections induced by androgen replacement therapy are uncommon. This complication usually occurs in young boys and men with long-standing, severe androgen deficiency. In these patients, symptoms usually resolve spontaneously or with a reduction in the dosage of testosterone. Contrary to popular belief, androgen administration in physiologic or moderately supraphysiologic dosages does not cause excessive aggressiveness or anger. Social aggressiveness, motivation, initiative, energy, and well-being improve, and anger and irritability are reduced with androgen replacement therapy in hypogonadal men.156,157 In normal men, short-term administration of moderately high dosages of testosterone (testosterone enanthate up to 600 mg per week) causes a slight increase in sexual arousal but no change in sexual activity and no increase in angry behavior.156,158 However, the appearance of normal sexual and aggressive behavior in hypogonadal men as a result of testosterone replacement may cause distress in patients and their partners, who may require careful counseling.
Acne and increased oiliness of the skin often develop in patients receiving androgen therapy for the induction of puberty and is usually treated satisfactorily with local skin measures, retinoic acid cream, and antibiotics. Acne nearly always resolves spontaneously with continued androgen treatment. Frontal balding or androgenic alopecia may develop in genetically predisposed individuals during androgen therapy.
Testosterone and its intraglandular conversion to DHT by 5α-reductase are important determinants of normal prostate growth. In hypogonadal men, testosterone replacement therapy increases prostate volume and PSA levels to values comparable to those of age-matched eugonadal men.159 Androgen therapy in elderly men has not been associated with a greater rate of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), but exposure times have been relatively short (2 to 3 years).119 Thus, the prudent course is to undertake androgen treatment in elderly men with great care, especially in those with enlarged prostate glands or symptoms of bladder outlet obstruction.
Although acute urinary retention may occur because of androgen-induced prostatic growth in patients with BPH, it is extremely uncommon in the absence of prostatic carcinoma.160 Because prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men and its growth is stimulated by androgens, older men (older than 45 years of age) treated with testosterone should have a digital rectal examination and serum PSA measurement at least yearly.
Although acute urinary retention may occur because of androgen-induced prostatic growth in patients with BPH, it is extremely uncommon in the absence of prostatic carcinoma.160 Because prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men and its growth is stimulated by androgens, older men (older than 45 years of age) treated with testosterone should have a digital rectal examination and serum PSA measurement at least yearly.
Androgen use may cause mild or moderate weight gain as a result of protein anabolic effects and sodium and water retention induced by these agents.56 Patients with underlying edematous states (e.g., congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis) may have worsening edema during androgen treatment.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree