Pulmonary Blastoma
Sanja Dacic
Pulmonary blastoma is a rare biphasic tumor composed of primitive malignant glands resembling well-differentiated fetal adenocarcinoma and immature, embryonic-type sarcomatous stroma.1
PULMONARY BLASTOMA, CYTOLOGY
Pulmonary blastomas are rare tumors that are not typically diagnosed cytologically. Cytologic features include malignant glandular cells or malignant mesenchymal spindle cells, or both.
PULMONARY BLASTOMA, GROSS FEATURES
Pulmonary blastomas typically are large, well-circumscribed masses that have a tan to tan-yellow fleshy cut surface (Figs. 15-1 and 15-2). They often have satellite lesions and associated pleural effusions.
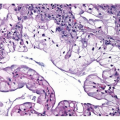
PULMONARY BLASTOMA, HISTOPATHOLOGY
The glycogen-rich tubules and primitive stroma resemble fetal lung between 10 and 16 weeks gestation (“pseudoglandular stage”). The tubules are lined by pseudostratified, nonciliated columnar cells with clear or lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm. Subnuclear or supranuclear vacuoles containing glycogen are producing an endometrioid appearance ( Figs. 15-3,15-4,15-5,15-6,15-7 and 15-8). A small amount of mucin within the glandular lumens may be present, but intracellular mucin is unusual. Similar to fetal adenocarcinomas, morular structures composed of squamous nests can be seen. Stomal cells have blastema-like configuration and have a similar appearance to Wilms tumor of the kidney. Stromal cells may be round, oval, or spindlelike. Foci of differentiated sarcomatous elements such as rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, or chondrosarcoma may be found.2,3
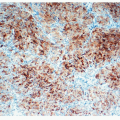
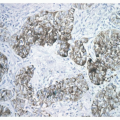
PULMONARY BLASTOMA, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY
The epithelial component, including glands and morules, is diffusely positive for epithelial markers such as cytokeratin 7, AE1/AE3, EMA, CEA, and TTF-1. Neuroendocrine markers such as chromogranin A and synaptophysin, Clara cell antigen, and polypeptide hormones (calcitonin, ACTH, serotonin, L-enkephalin) are focally positive. The sarcomatous stroma is diffusely immunoreactive for vimentin and muscle- specific actin. Focal cytokeratin AE1/AE3 positivity may be present. Desmin, myoglobin, and S100 protein can be expressed if specific muscle or cartilage mesenchymal differentiation is present.4,5 and 6
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree