Chapter Outline
PEDIATRIC VERSUS ADULT CANCERS
CHILDHOOD ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA AS A MODEL OF CLONAL EVOLUTION
EVOLUTIONARY PENETRANCE OF DISEASE
“Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution” was Dobzhansky’s bold but persuasive claim, and nothing is as natural in biology as natural selection. It has been occurring for approximately 3 billion years whenever heritable traits vary in replicating populations, affecting the survival and reproductive fitness of molecules, unicellular or multicellular organisms, each in the face of environmental selective pressures.
When complex multicellular organisms evolved some 600 million years ago, the potential for individual cells to be selectable, or to clone, was suppressed or rendered subservient to the fitness of the entire individual. Two classic exceptions to this rule exist, however: the immune system and cancer. In the former, lymphoid cells genetically diversify their immunoglobulin heavy chain in B cells or T-cell receptor in T cells antigen recognition gene segments by recombinase-mediated rearrangement to produce more than 10 11 potentially selectable variants, collectively covering the recognition of essentially any infectious antigenic epitope. This naturally selected or adaptive system is under tight network control, although collapse of regulation can result in autoimmune disease or lymphoid cell cancers.
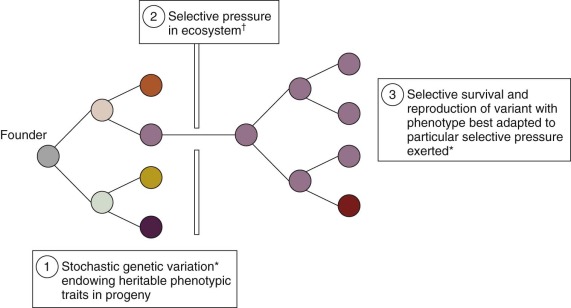
All pediatric and adult cancers are nonphysiologic, nonbeneficial clonal evolutions that follow the same rules of engagement as speciation in ecosystems ( Fig. 39-1 ). They are, in essence, breaking a 600-million-year-old covenant. It has been known for some time that cancer is a paradigmatic Darwinian, adaptive system. The implications for cancer risk, progression of disease, prognosis, drug resistance, and clinical response have only more recently been appreciated. Genomics has contributed significantly to this sharpness of focus, just as it has reinforced the underlying principles of evolutionary phylogeny and natural selection of species and variants. As in speciation, what emerges in cancer in terms of functionally important mutations (the so-called drivers ) or subclones is the consequence of selective pressures exercised via the tissue habitat or ecosystem ( Fig. 39-2 ), with outcome being heavily modulated both by variation in inherited susceptibility and by chance. Inherited susceptibility is a marked feature of pediatric cancers, both in terms of familial syndromes and in sporadic cases with little or no family history, as revealed by genomewide association studies. The element of chance applies in both cancer and evolution in general because mutations arise throughout the genome in a stochastic manner and independently of the functions encoded by particular genes. For mutations to have a functional impact in cancer requires that they occur in a manner that alters protein function (and consequently cell fitness) and in the appropriate context with respect to cell type and the presence (or absence) of other mutations with which they may be epistatic or interactive. The vast majority of mutations are neutral passengers of no consequence. The mutations we see recurrently are the result of natural or therapeutic selection.
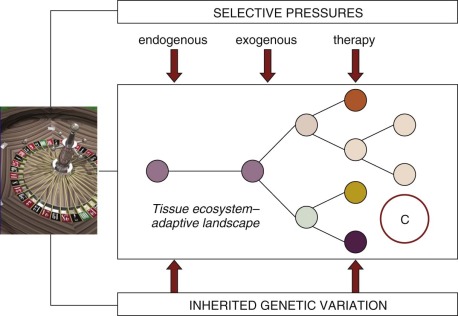
As clones evolve over time (within a few years for most pediatric cancers compared with decades for adult carcinomas) they also move in space or throughout tissue ecosystems, both within the primary site and to secondary sites. This characteristic has important implications for biopsy-based sampling, because anything other than the complete tumor will be a biased selection of subclones. This phenomenon has been well documented for adult cancers, and we assume that the same phenomenon must apply to most if not all pediatric solid tumors.
In evolutionary or Darwinian selection, it is the phenotype that is the focus of selectability—for example, a predator with sharp teeth, a thermoresistant bacteria, or a drug-resistant bacterium or cell. In addition, stable phenotypes are initiated and sustained by genotypic alterations that are either mutational or epigenetic. However, any evolutionary system must have a “unit of selection,” which is defined classically as any unit that replicates and in which a stable phenotype is linked to survival and/or reproductive success. For bacteria and protists, this unit is the single cell. For multicellular organisms, it is the entire individual. For cancer it will be somatic cells but probably not every cancer cell. The key attribute of any unit of selection is extensive replicative potential plus expression of the selectable phenotype. Extensive replication capacity, or self-renewal, is the key and exclusive feature of cancer stem cells. The numbers of stem cells vary greatly in individual cancers and are generally increased in frequency with progression of disease and clinical malignancy. In addition, the stem cell state may not be entirely stable, and under some circumstances (microenvironmental or mutational), non–stem cell progenitors can acquire or reacquire stem cell status. Despite these variables, it is likely that cancer stem cells are the units of selection that drive and sustain the evolution of cancer clones and are the repositories of drug resistance.
Pediatric Versus Adult Cancers
All cancers are consequences of stable variation in somatic cells that facilitate clonal escape. However, fundamental differences exist between pediatric and adult cancers ( Table 39-1 ). The most striking of these differences is the context of tissue or cell type involved, which in turn can be rationalized in terms of underlying risk factors. Most adult cancers are the consequences of protracted environmental or lifestyle exposures to epithelia. In contrast, most pediatric cancers can best be viewed as developmental accidents arising during very restricted windows of tissue morphogenesis in the embryo or fetus when particular stem or progenitor cells are proliferating. This view is supported by the finding that many of the inherited gene variants that contribute to the risk of pediatric cancer and many of the somatic mutations that are restricted to the cancer cells themselves are encoded by genes that are critical for the normal developmental biology and differentiation of the cells involved. Very few pediatric cancers are attributable to any known in utero external exposure (i.e., via the pregnant mother), despite an epidemiologic quest to find them lasting decades. This is not to say that pediatric cancers are not subject to variable risk factors. Aside from inherited variation in susceptibility, the numbers of cells at risk and proliferative stress may play a part. Higher birth weight is consistently associated with excess risk of pediatric cancer and may operate by simply increasing the number of proliferating “target” cells at risk. Patterns or timing of infection (especially in affluent, “hygienic” societies) may promote or trigger the clinical development of childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). This mechanism is likely to operate via proliferative stress on preleukemic clones that are generated in utero (rather than via specific viral transformation). Similarly, the striking peak of incidence of long bone osteosarcoma in adolescents might reflect the clinical emergence of a cancer initiated long before (prenatally) but promoted by the proliferative stress of the long bone growth spurt associated with puberty.
| Variable | Pediatric | Adult |
|---|---|---|
| Predominant lineage origins | Transient/developmental tissue progenitors in embryo and fetus Fetal blood | Epithelia Adult blood |
| Time frame of natural history | Months to 15 yr | 2-3 decades |
| Number of “driver” mutations required | 2 (?) | 5-8 (?) |
| Genetic instability | Rare | Common |
| Major risk factors | Endogenous proliferative stress (?) | Genotoxic exposures, persistent proliferative stress (hormonal), or infection |
| Cumulative risk | ~1 in 800 (0-15 yr) | ~1 in 3 (16-90 yr) |
| Age-associated incidence distribution | Defined, age-linked peak incidence in infancy or childhood | Increases as power of age * |
* Some exceptions are testicular cancer and Hodgkin lymphoma in young adults and choriocarcinoma.
A few types of cancer occur in both children and ageing adults, with acute leukemias and gliomas being clear examples. However, it is interesting that the genetics or mutational spectrum of these cancers, and probably their etiology, is very different according to age. Two nonexclusive “seed or soil” interpretations of this distinction have been proposed. One interpretation is that the mutations are different because the microenvironments and selective pressures are different, resulting in different mutant genes providing clonal advantage. A second interpretation is that the mutations are cell context–sensitive and that the cell type of origin is different and developmentally constrained. Evidence for the latter interpretation came from mouse modeling of the impact of GATA1 mutations, which revealed that the cellular targets that, with this mutation, lead to acute megakaryocytic leukemia in infants with Down syndrome, are developmentally restricted to the yolk sac and fetal liver.
The tissue distribution, composite phenotypes (or cell type), and gene expression profiles of pediatric cancers provide a strong indication of the possible lineage and cell type or origin, and this indication is endorsed by animal models ( Table 39-2 ). Subtypes of some cancers, such as medulloblastoma, may have distinct developmental origins. No unambiguous way exists to identify precisely when and where any childhood cancer is initiated by somatic mutations. Most mutations are assumed to originate prenatally either in the embryo or the developing fetus, possibly when the cell lineage stem or progenitor cell “targets” are under maximum risk from proliferation.
| 1. | Central nervous system | Gliomas | Glial precursor (different brain regions) |
| Ependymoma | Radial glial cells | ||
| Medulloblastoma * | |||
| (i) | Cerebellum (granule neuron precursor cells) | ||
| (ii) | Dorsal brain stem | ||
| 2. | Neuroblastoma | Embryonic neural crest cells | |
| 3. | Rhabdomyosarcoma | Muscle stem/progenitor cells (Satellite cells?) | |
| 4. | Hepatoblastoma | Embryonic liver precursor cells (?) | |
| 5. | Osteosarcoma | Bone progenitor cells | |
| 6. | Retinoblastoma | Embryonal retinoblasts | |
| 7. | Ewing sarcoma | Mesenchymal stem cells (?) | |
| 8. | Wilms tumor | Embryonic urogenital ridge (mesenchymal) progenitor/stem cells | |
| 9. | Acute leukemias | Fetal, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells | |
| (i) Childhood ALL | B (or T) progenitor cells (fetal liver or bone marrow) | ||
| (ii) Infant ALL | Fetal B/monocytic progenitor? | ||
| (iii) AML | Myeloid restricted stem/progenitor cells | ||
| (iv) Down syndrome AMKL | Fetal liver megakaryocytic erythroid progenitors |
* More distinctive subtypes in terms of cellular and anatomic origin probably exist than are listed here.
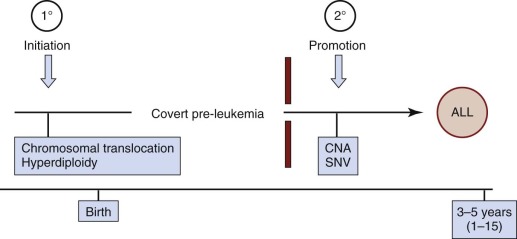
Childhood ALL as a Model of Clonal Evolution
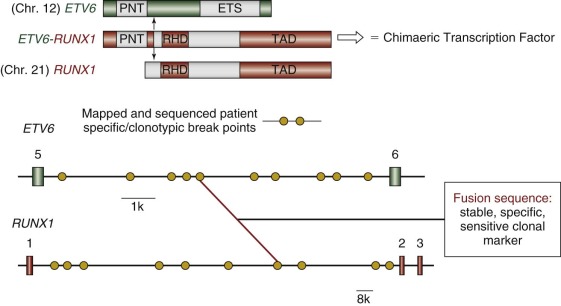
Childhood leukemias lend themselves to interrogation of their natural history more than any other pediatric cancer type. This situation occurs because, although it is initiated in tissue sites such as fetal liver, bone marrow, or thymus, the clone disseminates very readily into the accessible blood, including in the early stages of clinical covert natural history, such as at the birth of the child. Figure 39-3 illustrates a minimal two-stage model proposed for the development of the common form of B-cell precursor ALL in children. The challenge was to backtrack clonal history from the point of diagnosis when the genetic features of the clone were definable. For this task, chromosome translocation–generated chimeric gene fusion sequences are the ideal markers for clonal tracking, as illustrated in Figure 39-4 for the most frequent of such fusion genes, ETV6-RUNX1 (formerly TEL-AML1). Three tactics have been successfully adopted for backtracking clonal history in ALL ( Fig. 39-5 ), and collectively they have provided persuasive evidence for the in utero origin of disease and the two-step model that has been proposed. Formal proof of a prenatal origin of other pediatric cancers is not available, although the very young age of many patients at diagnosis and the embryonal phenotypes of some make a prenatal origin very likely. The oldest age at diagnosis of ALL to date with backtracking evidence for an in utero origin is 14 years. However, it is possible that some leukemias and other tumors in older children and even young adults are initiated prenatally with a protracted clinically silent latent period—for example, osteosarcoma in teenagers and testicular cancer in adults in their twenties and thirties. This scenario has yet to be formally assessed, however.