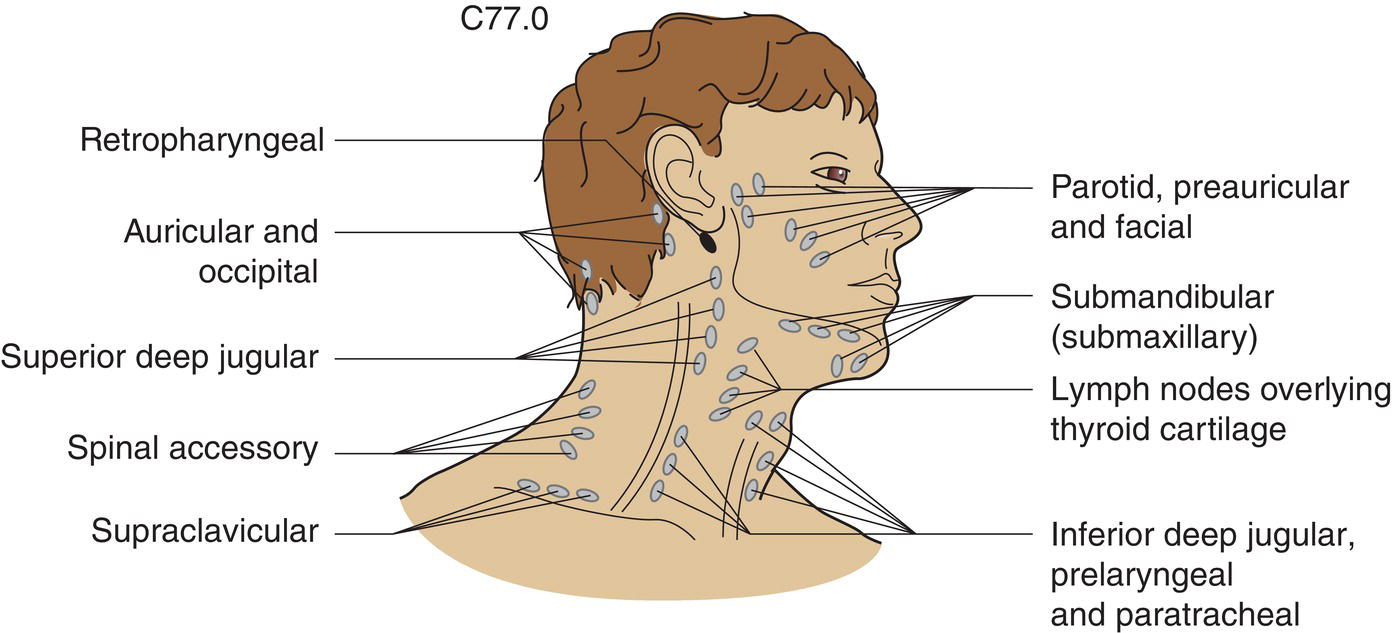
The classification applies only to carcinomas, excluding Merkel cell carcinoma. There should be histological confirmation of the disease and division of cases by histological type. The following sites are identified by ICD‐O‐3 topography rubrics (see Fig. 334): The regional lymph nodes are Ipsilateral preauricular, submandibular, cervical and supraclavicular lymph nodes (see Fig. 335). Note Note The pT categories correspond to the T categories Histological examination of a selective neck dissection specimen will ordinarily include 10 or more lymph nodes. Histological examination of a radical or modified radical neck dissection specimen will ordinarily include 15 or more lymph nodes. Note
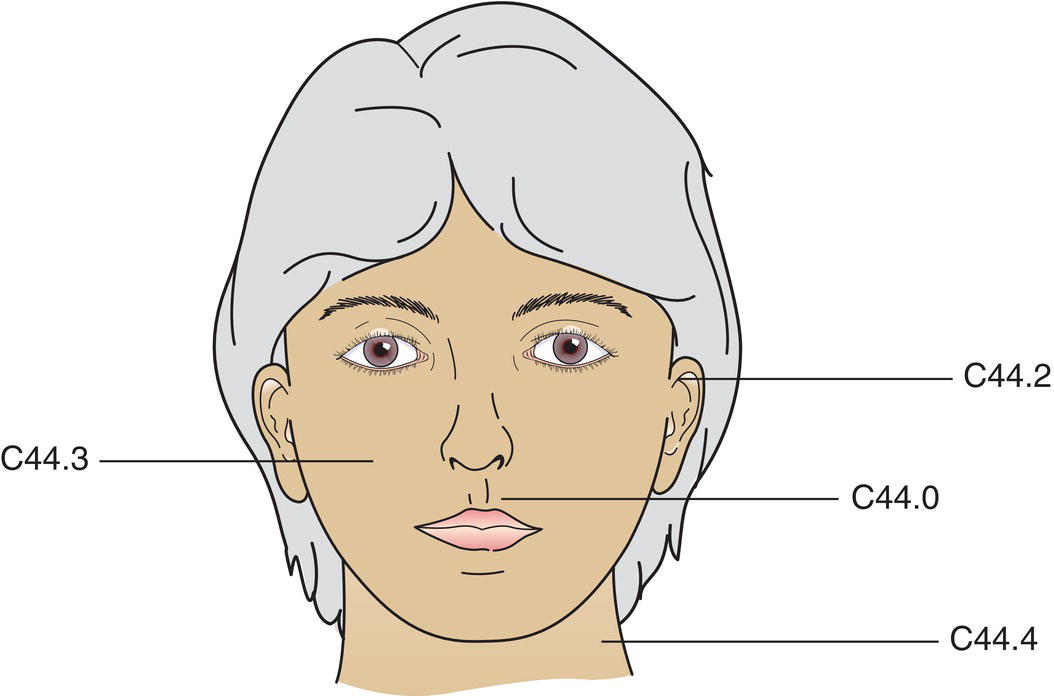
CARCINOMA OF SKIN OF THE HEAD AND NECK (ICD‐O‐3 C44.0, C44.2–4)
Rules for Classification
Anatomical Sites and Subsites
Regional Lymph Nodes
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
Tx
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis
Carcinoma in situ (Fig. 336)
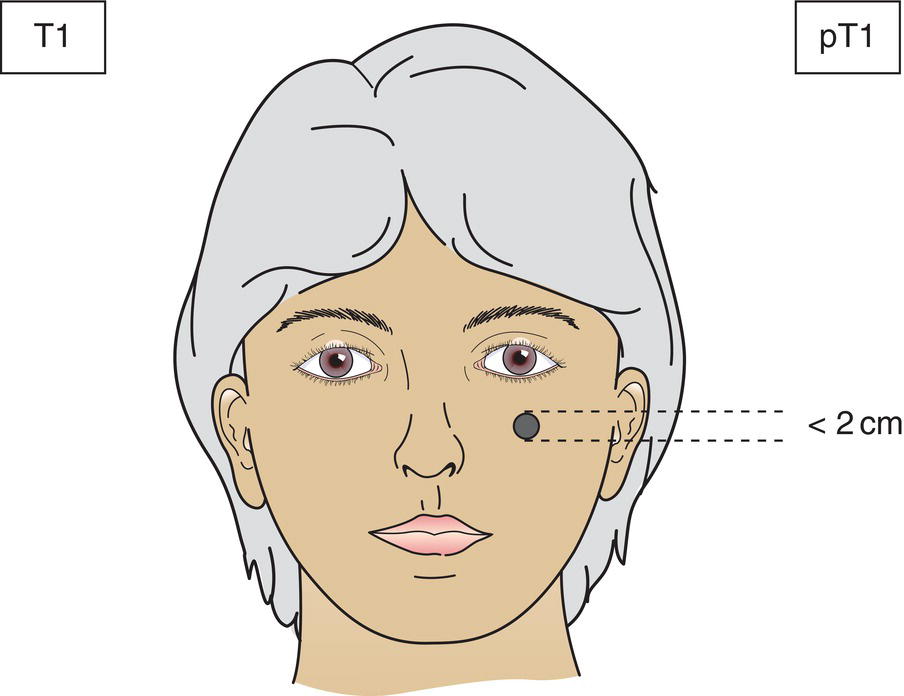
T1
Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension (Fig. 337)
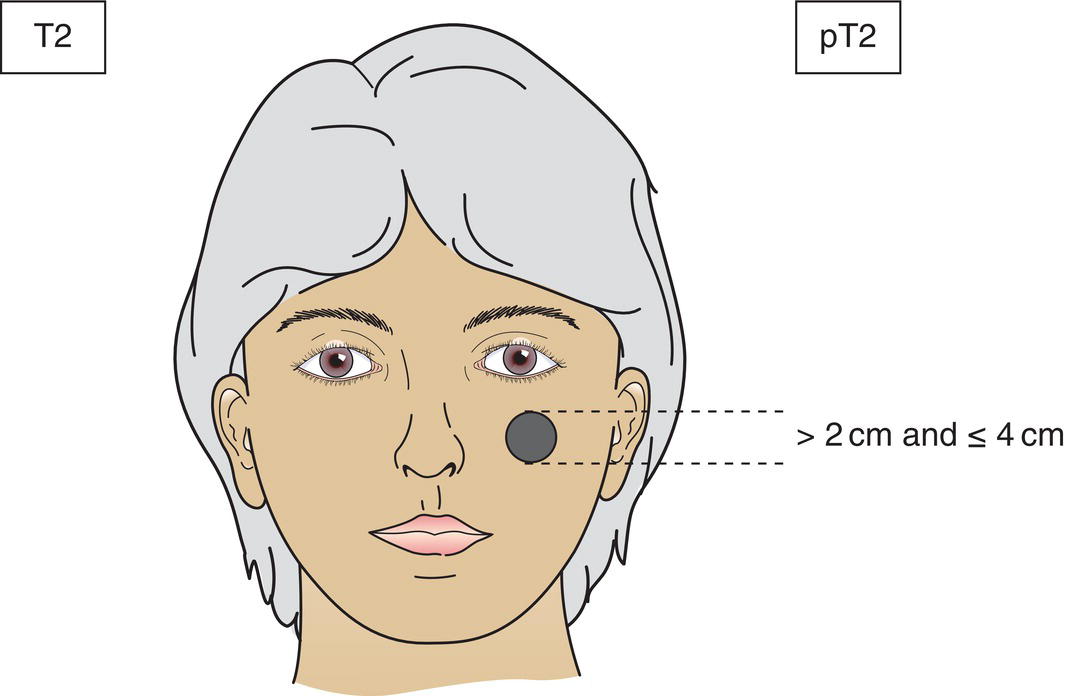
T2
Tumour > 2 cm and ≤ 4 cm in greatest dimension (Fig. 338)
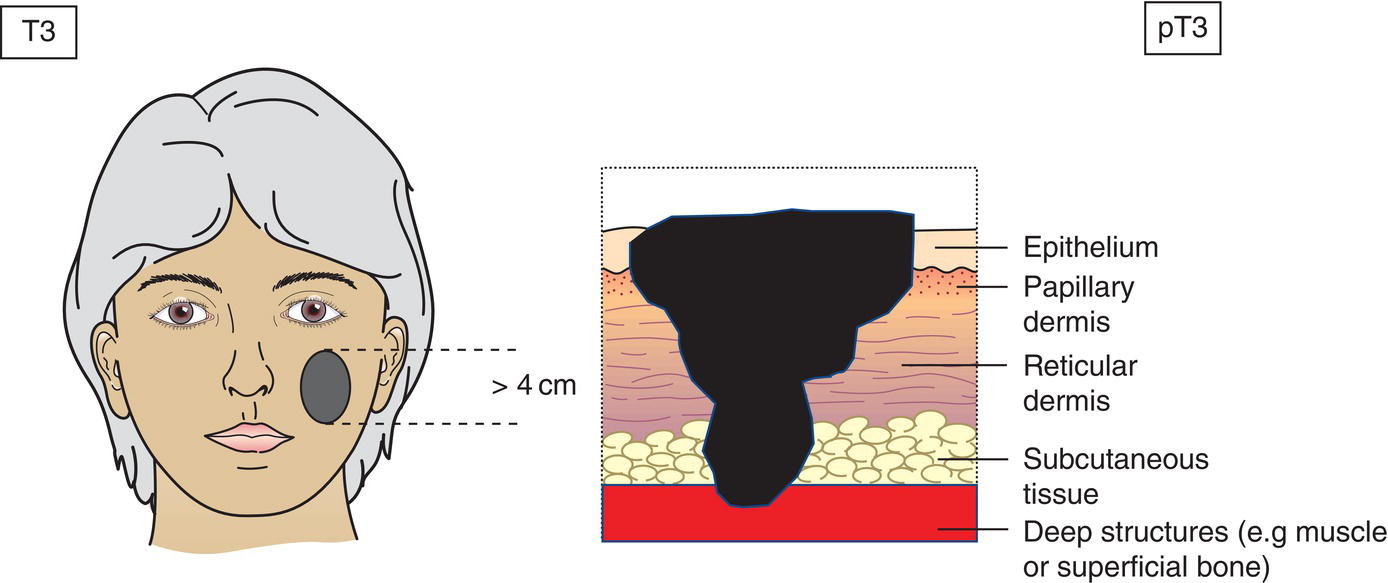
T3
Tumour > 4 cm in maximum dimension or minor bone erosion or perineural invasion or deep invasion* (Fig. 339)
T4a
Tumour with gross cortical bone/marrow invasion
T4b
Tumour with skull base or axial skeleton invasion including foraminal involvement and/or vertebral foramen involvement to the epidural space
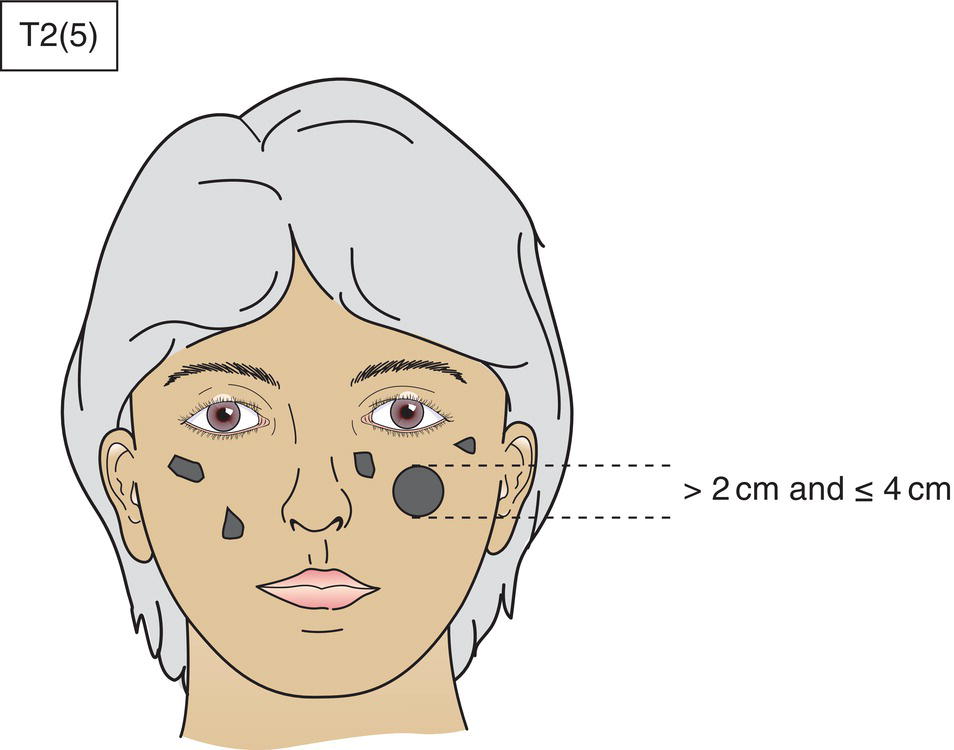
*In the case of multiple simultaneous tumours, the tumour with the highest T category is classified and the number of separate tumours is indicated in parentheses, e.g., T2(5) (Fig. 340)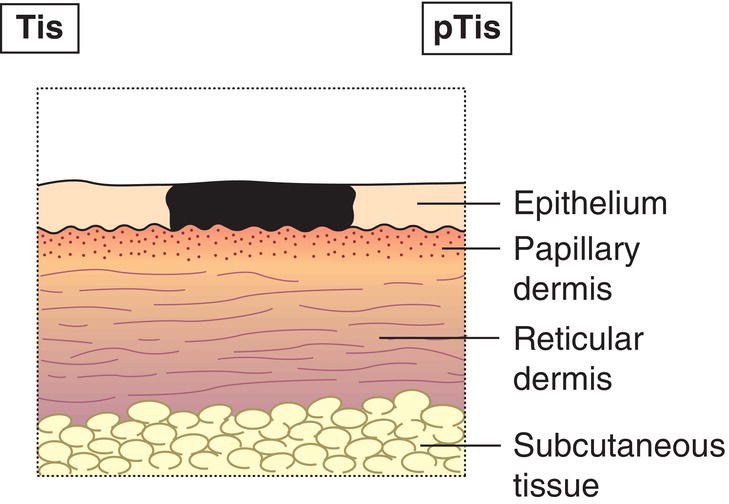
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
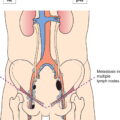
Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in greatest dimension without extranodal extension (Fig. 341)
N2
Metastasis as described below:
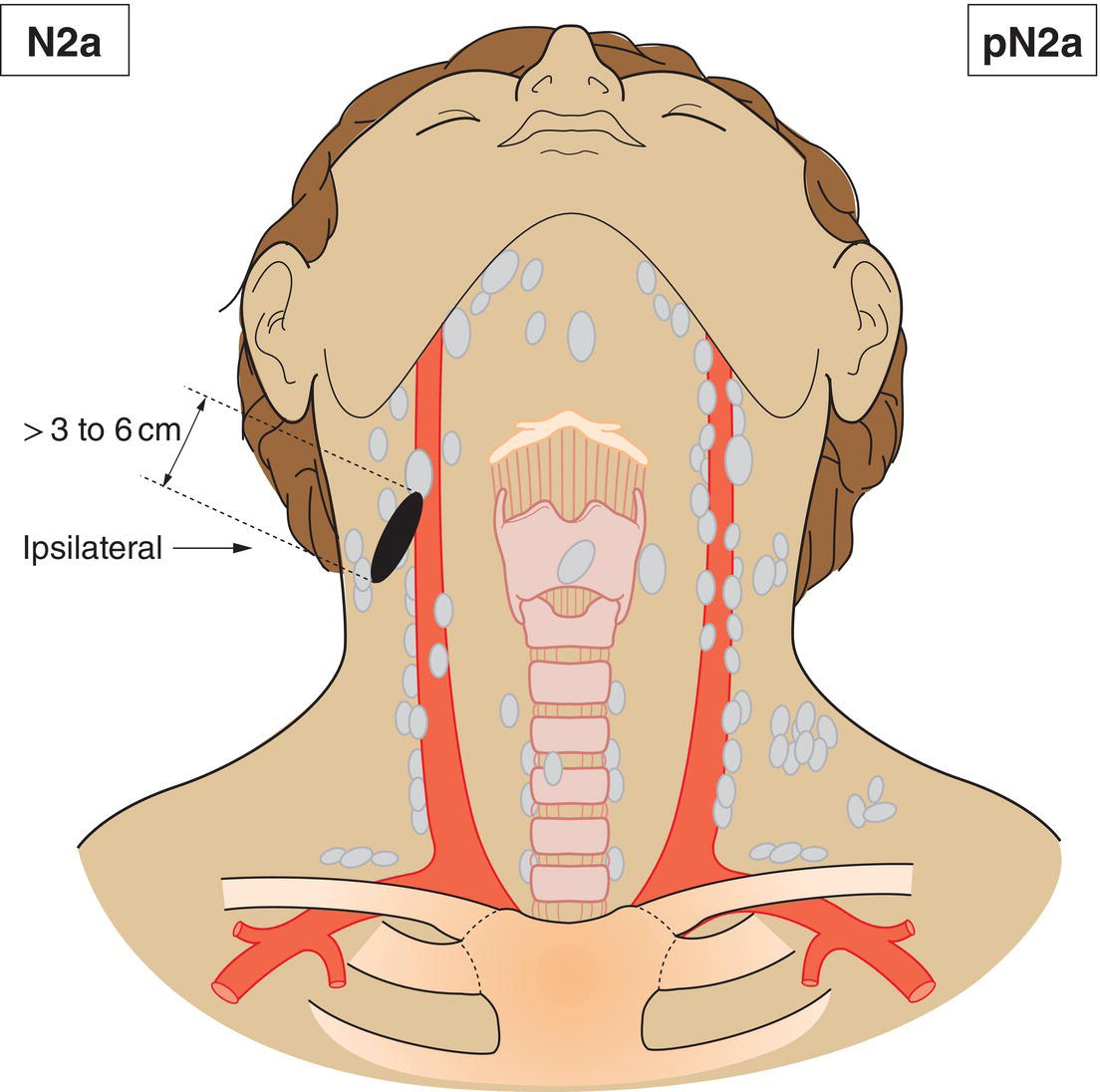
N2a
Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node more than 3 cm but not more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension (Fig. 342)
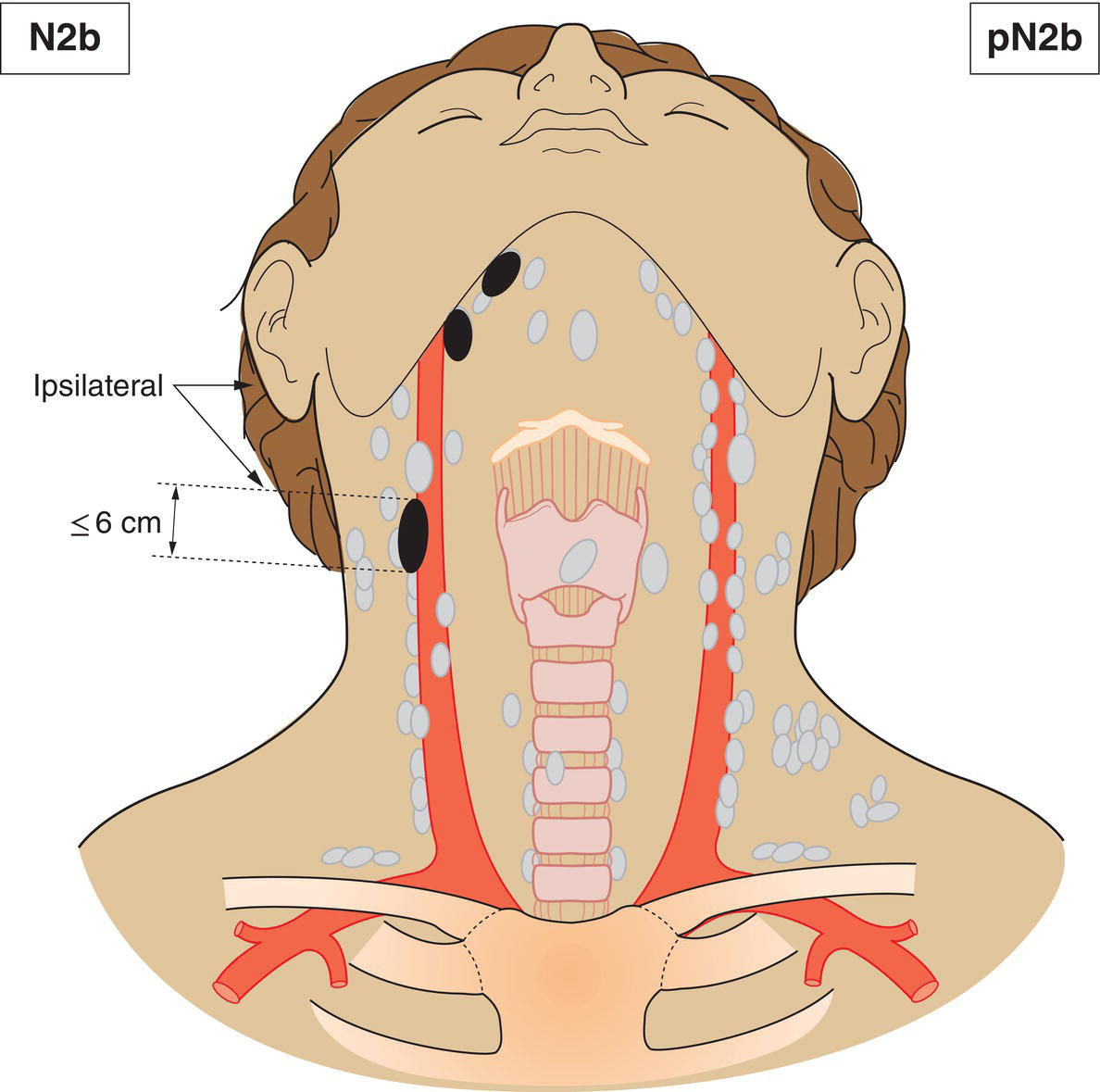
N2b
Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension, without extranodal extension (Fig. 343)
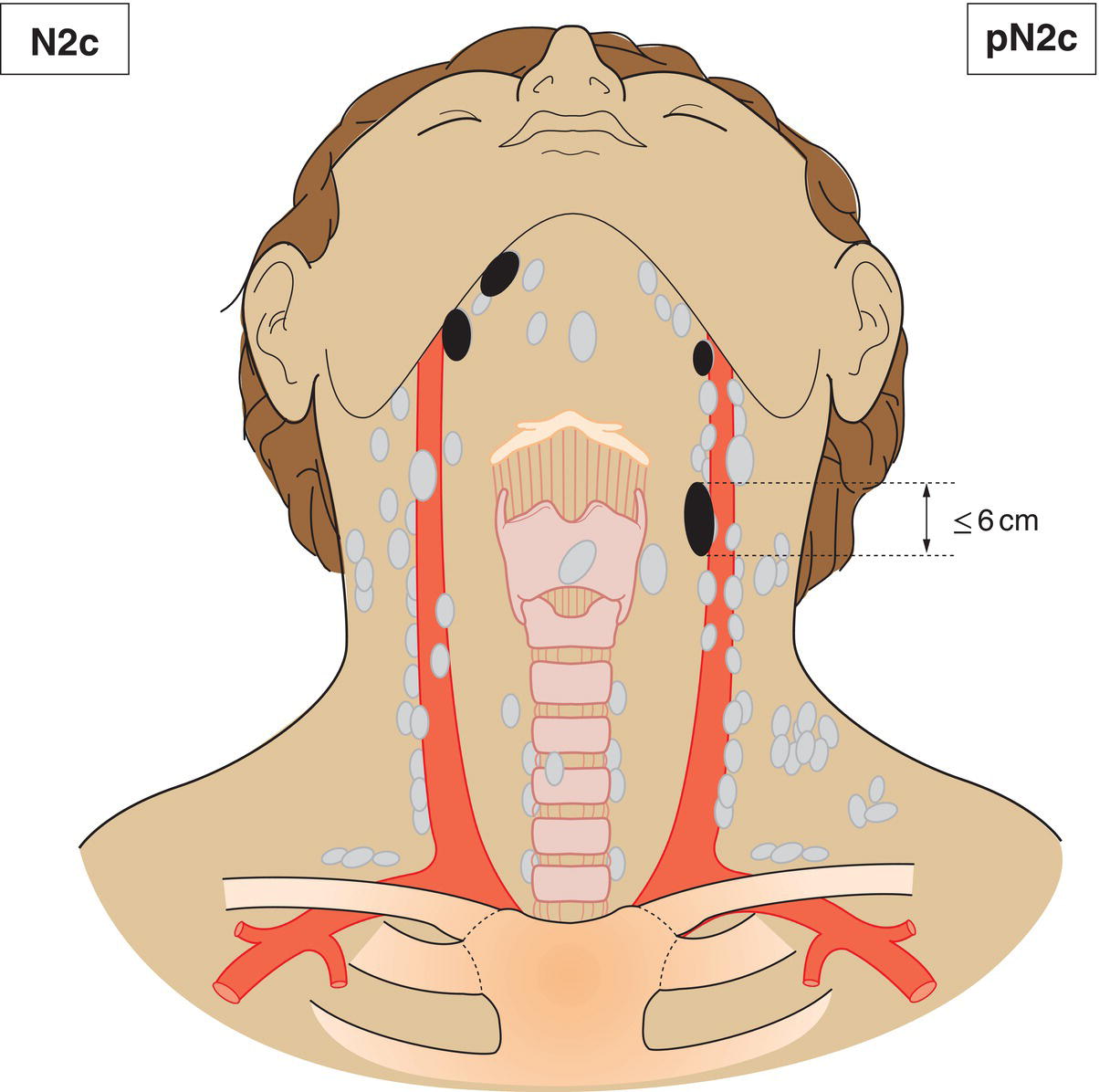
N2c
Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension, without extranodal extension (Fig. 344)
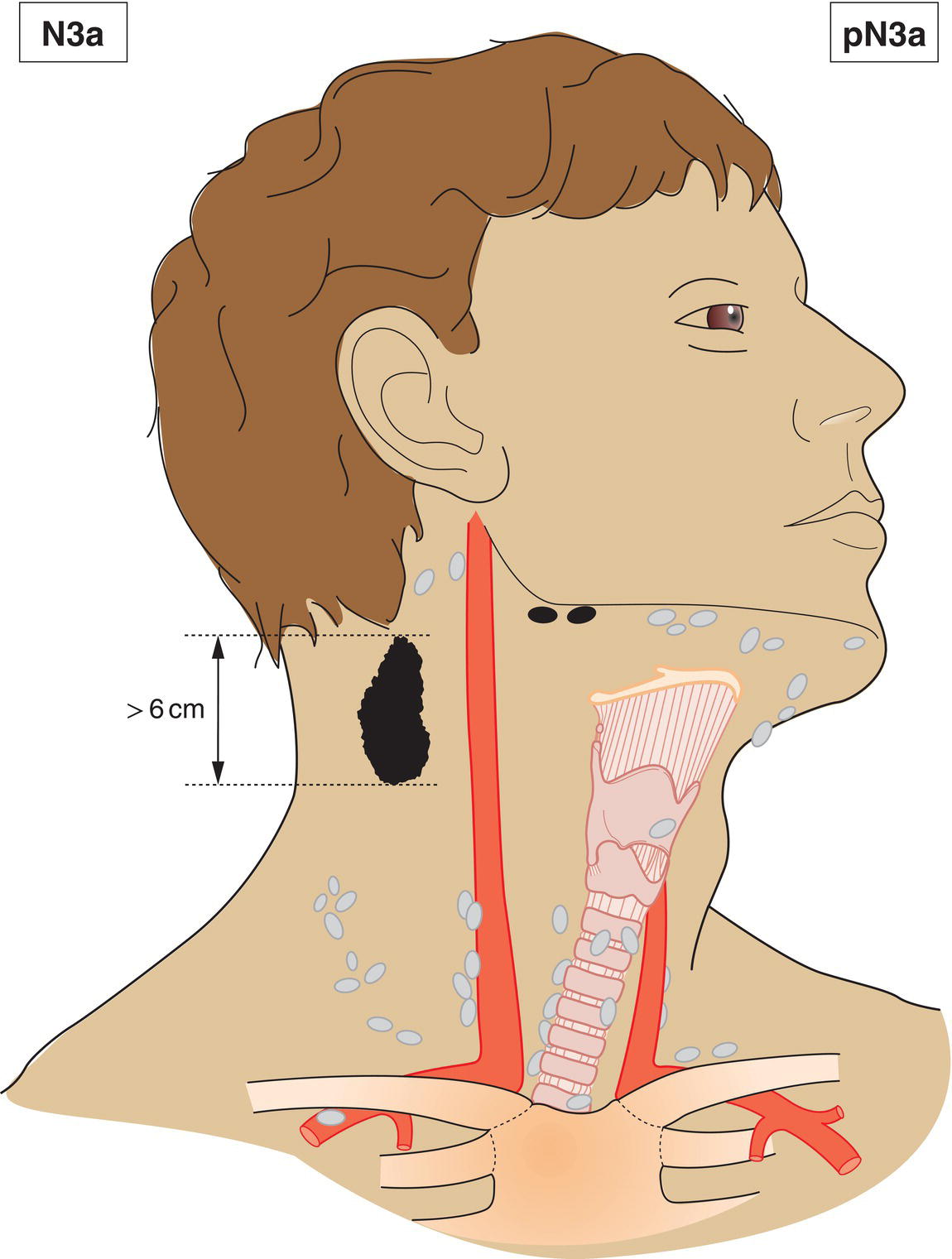
N3a
Metastasis in a lymph node more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension (Fig. 345)
N3b
Metastasis in single or multiple lymph nodes with clinical extranodal extension
*The presence of skin involvement or soft tissue invasion with deep fixation/tethering to underlying muscle or adjacent structures or clinical signs of nerve involvement is classified as clinical extranodal extension.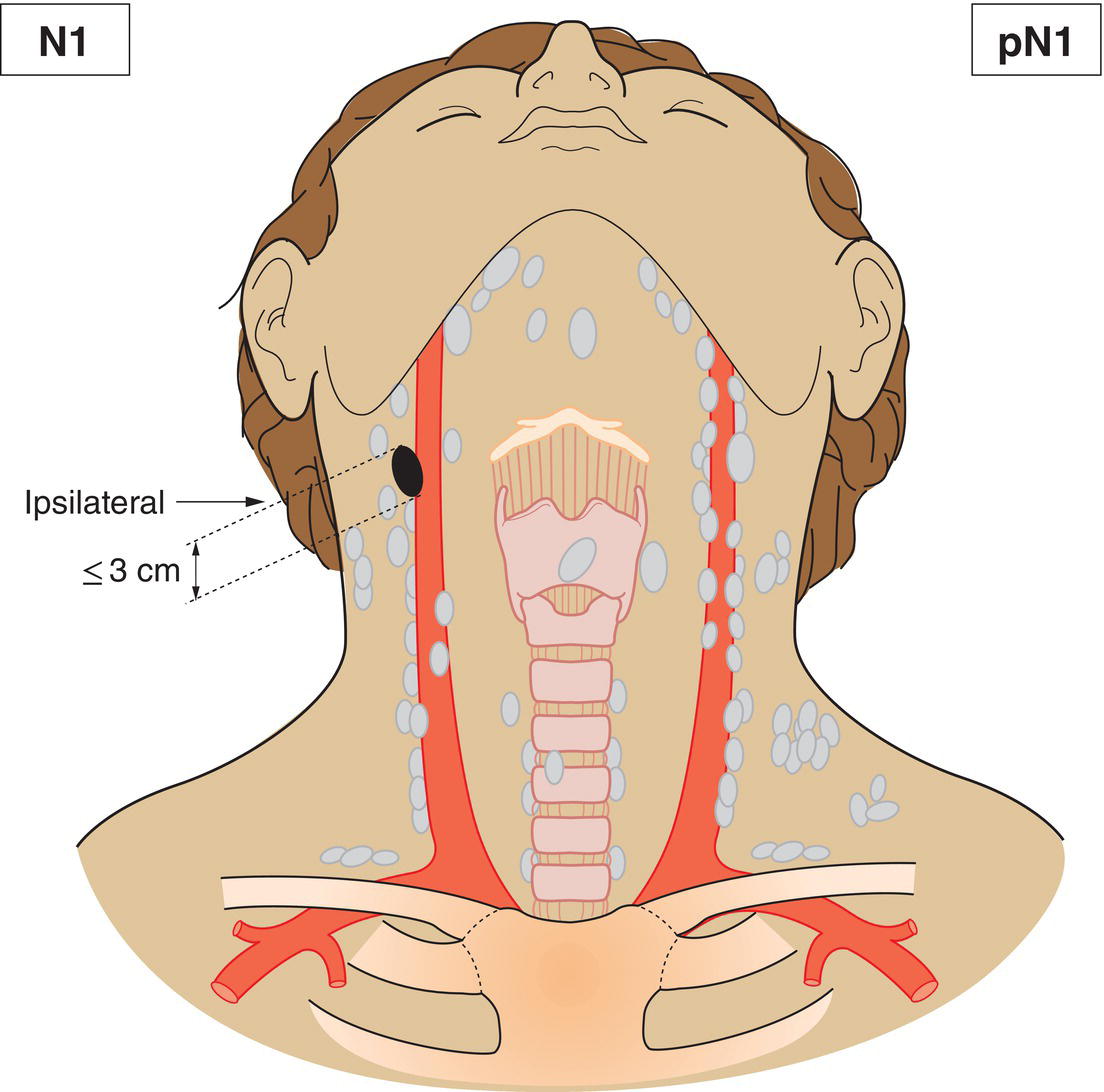
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
pTNM Pathological Classification
pN – Regional Lymph Nodes
pNX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
pN0
No regional lymph node metastasis
pN1
Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in greatest dimension without extranodal extension
pN2
Metastasis as described below:
pN2a
Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3 cm in greatest dimension with extranodal extension, or more than 3 cm but not more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension
pN2b
Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension
pN2c
Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension
pN3a
Metastasis in a lymph node more than 6 cm in greatest dimension without extranodal extension
pN3b
Metastasis in a lymph node more than 3 cm in greatest dimension with extranodal extension, or multiple ipsilateral, contralateral or bilateral, with extranodal extension
pM – Distant metastasis
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMx are not categories
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree