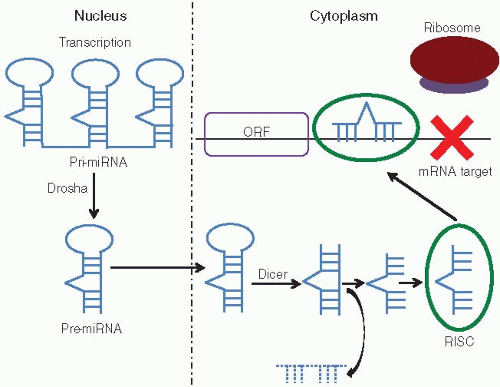
activity, and some miRNAs promote epigenetic methylation of cell cycle genes in mammalian cell lines.11 MicroRNAs also bind directly to DNA within promoter regions, thereby blocking transcription.12
of this pathway that promote constitutive activation of Wnt-mediated signaling.18 In the absence of functional APC, Wnt signaling leads to accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm, which is translocated to the nucleus where it facilitates transcription of protooncogenes, such as CMYC and cyclin D1.18 Biallelic APC inactivation usually results from mutations, but may also occur due to downregulation by miRNAs. For example, both miR-135a and miR-135b are complementary
to the 3’ UTR of APC mRNA. Colon cancers with high miR-135a and miR-135b levels also contain fewer APC mRNA transcripts, suggesting that miR-135a and miR-135b regulate Wnt signaling by promoting decay of APC mRNA.19
Table 13.1 Summary of the Literature Regarding Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Colon Cancer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Table 13.2 Regulatory MicroRNA Targets and Function in Colon Cancer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree