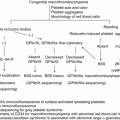
International consensus report
ASH
BSCH
Japan
First-line
Prednisone/prednisolone (10–20 mg/day)
IVIG (dose not specified)
IV anti-D
Prednisone/prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day)
IVIG (1 g/kg for 2 days)
Prednisone/prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day)
IVIG (0.4 g/kg/day for 5 days or 1 g/kg/day for 2 days)
Prednisolone (10–20 mg/day) * 0.5–1 mg/kg/day can be also considered for severe cases.
IVIG (0.4 g/kg/day for 3–5 days)
Second-line
High-dose IV methyl-prednisolone (1000 mg) ± IVIG or azathioprine
Splenectomy (second trimester)
Corticosteroids and IVIG
Splenectomy (second trimester)
High-dose IV methylprednisolone (1000 mg) ± IVIG
Azathioprine
Splenectomy (second trimester)
Splenectomy should be avoided
Third-line
Cyclosporine, dapsone, TPO-R agonists, rituximab (not recommended but use in pregnancy described)
As far as the choice of corticosteroids is concerned, prednisone or prednisolone is preferred to dexamethasone, which crosses the placenta more readily [3]. While the ASH guideline recommends a starting dose of prednisone 1 mg/kg daily, there is no evidence that a higher starting dose is better than a lower dose [3]. Therefore, other experts recommend a starting dose of 0.25–0.5 mg/kg daily. In fact, the Japanese consensus report recommends 10–20 mg/day as a starting dose [5] since a Japanese nationwide study revealed that prednisolone dose of 15 mg/day or more might be associated with premature delivery, preeclampsia, or congenital abnormalities [6]. The international consensus report also recommends this lower starting dose [2].
The conventional dose of IVIG is 0.4 g/kg/day for 5 days, which is recommended in Japanese consensus report [5]. Alternatively, 1 g/kg/day for 2 days can be considered according to ASH and BSCH guidelines [3, 4]. The duration of response to IVIG is usually 2–3 weeks [2], and therefore after an initial response, repeat infusions might be required to prevent bleeding symptoms and keep an adequate platelet count if the patient should be managed only with IVIG.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree