The definitions of the T, N, and M categories correspond to the FIGO stages. Both systems are included for comparison. The classification applies only to primary carcinomas of the vulva. There should be histological confirmation of the disease. A carcinoma of the vulva that has extended to the vagina is classified as carcinoma of the vulva. The FIGO stages are based on surgical staging. TNM stages are based on clinical and/or pathological classification. The regional lymph nodes are the inguinofemoral (groin) nodes. Notes* **T3 is not used by FIGO. They label it T4. The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note
VULVA (ICD‐O‐3 C51)
Rules for Classification
Anatomical Subsites (Fig. 405)
Regional Lymph Nodes
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis
Carcinoma in situ (preinvasive carcinoma), intraepithelial neoplasia grade III (VIN III)
T1
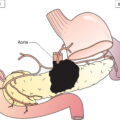
Tumour confined to vulva or vulva and perineum (Fig. 406c)
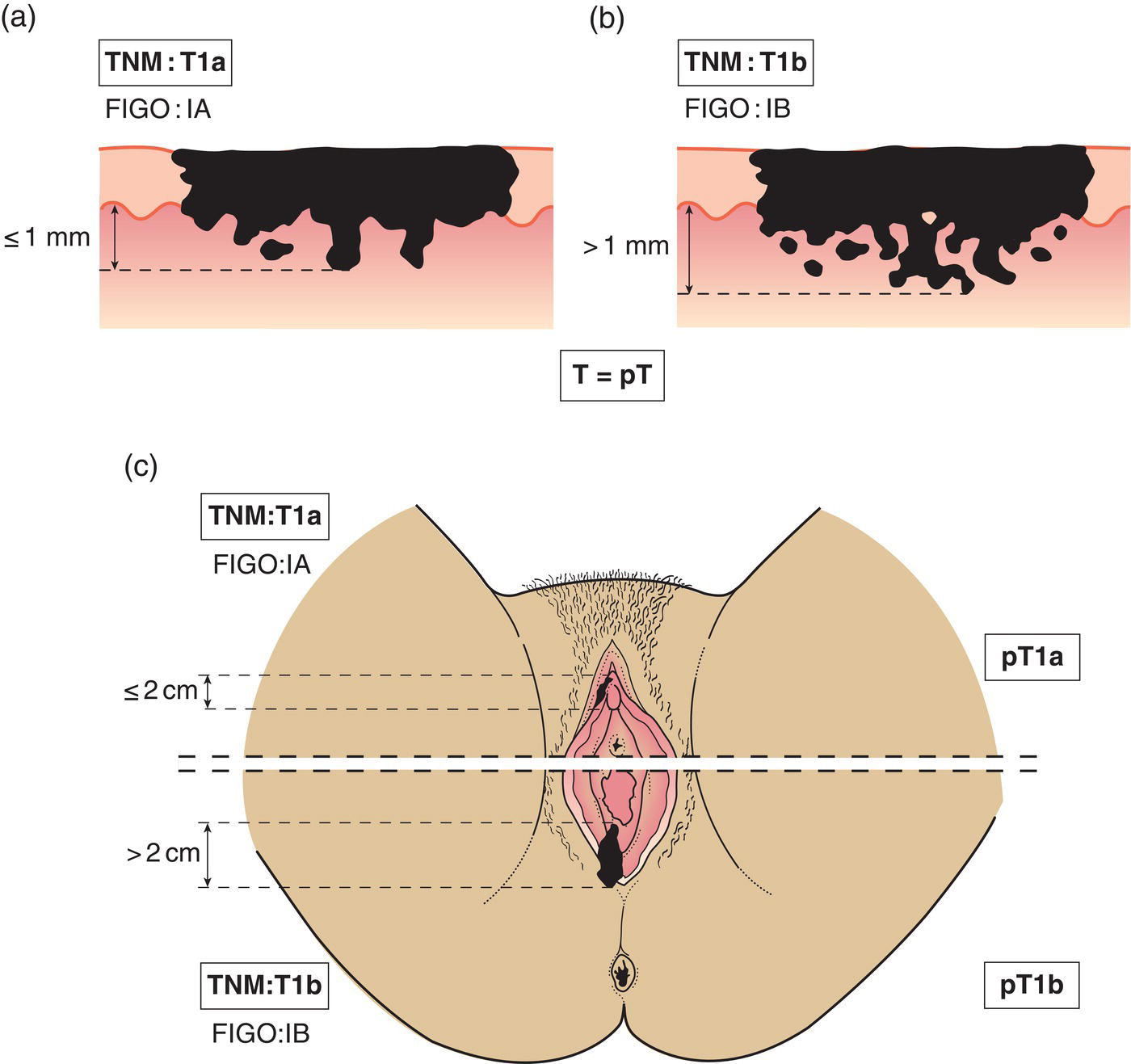
T1a
Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension and with stromal invasion no greater than 1.0 mm* (Fig. 406a)
T1b
Tumour greater than 2 cm or with stromal invasion greater than 1 mm* (Fig. 406b)
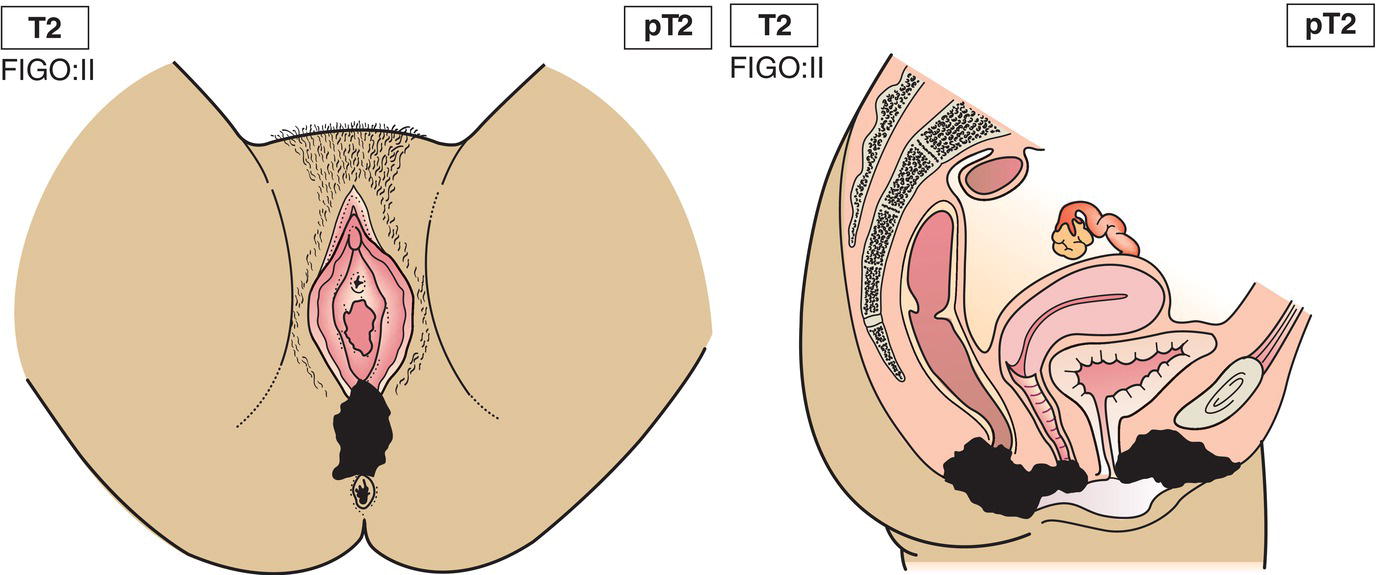
T2
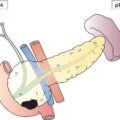
Tumour invades any of the following perineal structures: lower third urethra, lower third vagina, anus (Fig. 407)
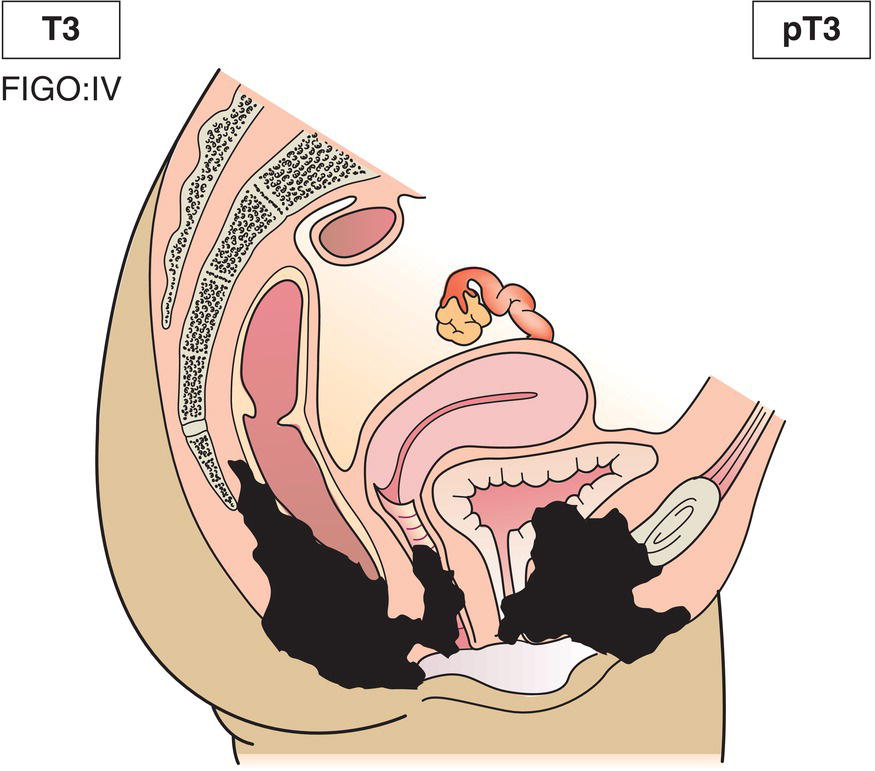
T3**
Tumour invades any of the following perineal structures: upper 2/3 urethra, upper 2/3 vagina, bladder mucosa, rectal mucosa; or fixed to pelvic bone (Fig. 408)
The depth of invasion is defined as the measurement of the tumour from the epithelial–stromal junction of the adjacent most superficial dermal papilla to the deepest point of invasion.
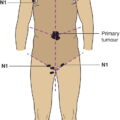
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis with the following features
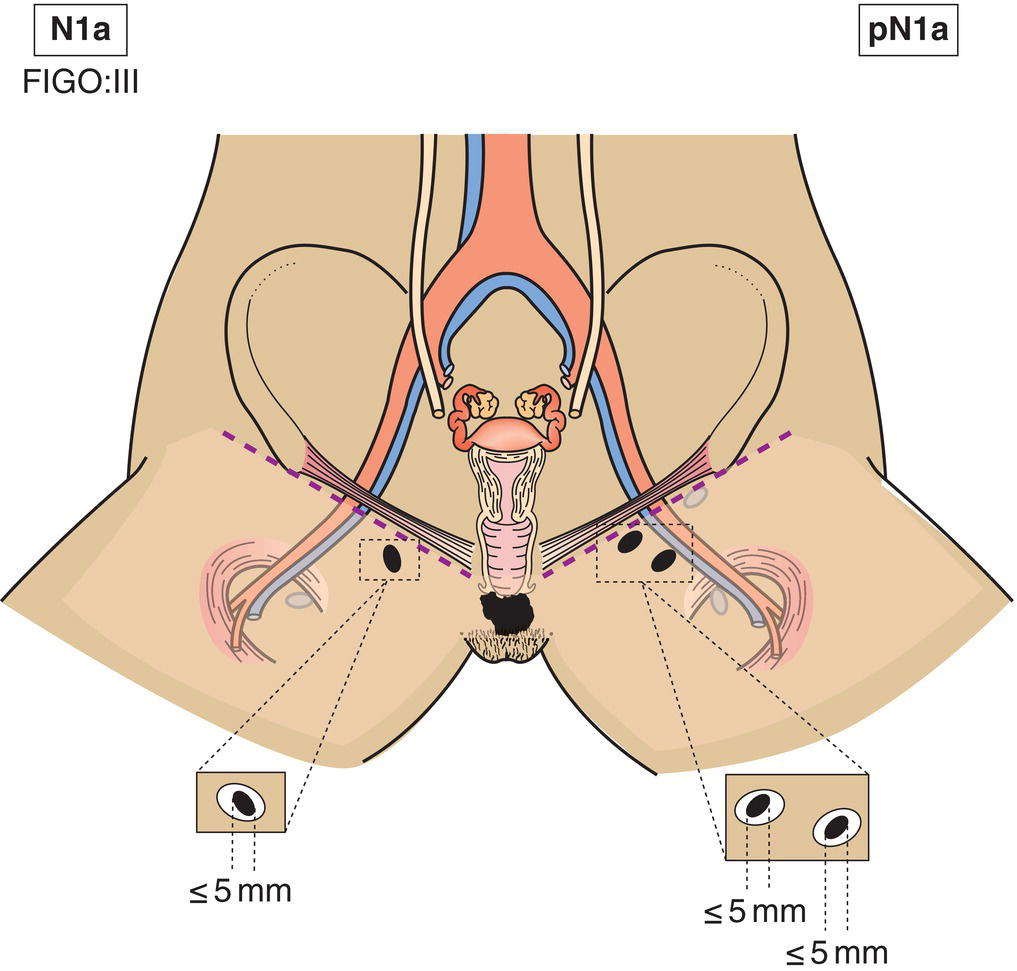
N1a
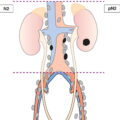
One or two lymph node metastasis less than 5 mm (Fig. 409)
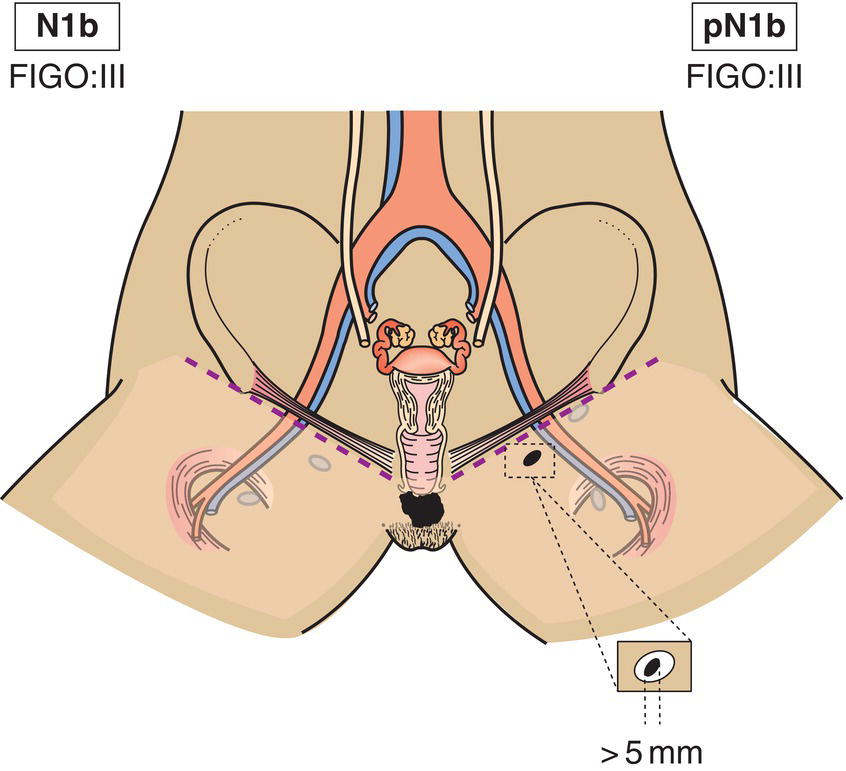
N1b
One lymph node metastases 5 mm or greater (Fig. 410)
N2
Regional lymph node metastasis with the following features:
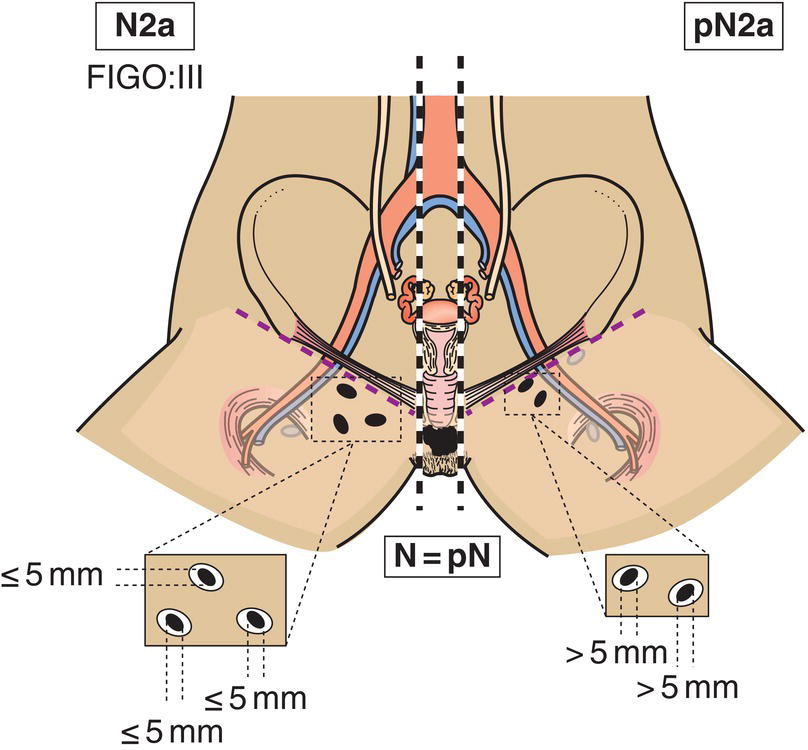
N2a
Three or more lymph node metastases each less than 5 mm (Fig. 411)
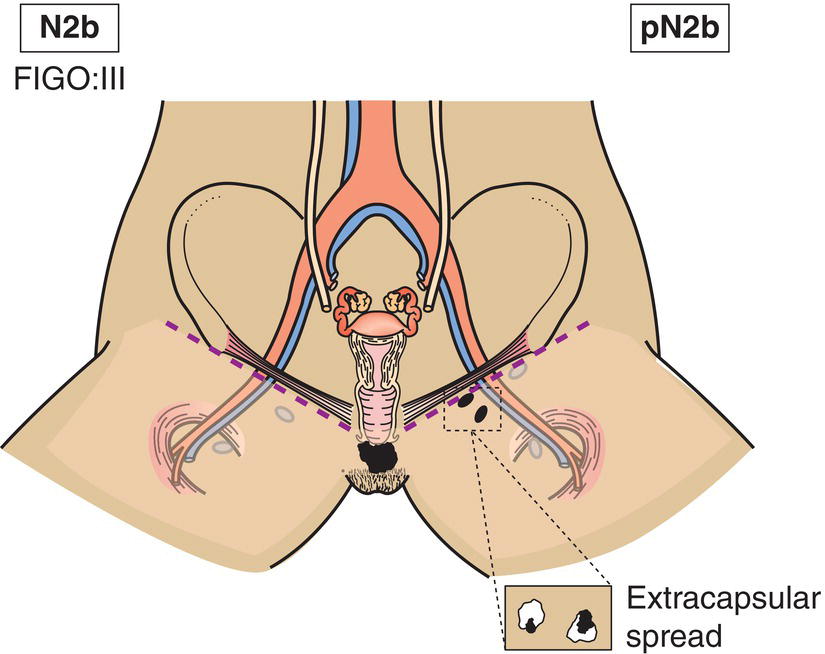
N2b
Two or more lymph node metastases 5 mm or greater (Fig. 412)
N2c
Lymph node metastasis with extracapsular spread
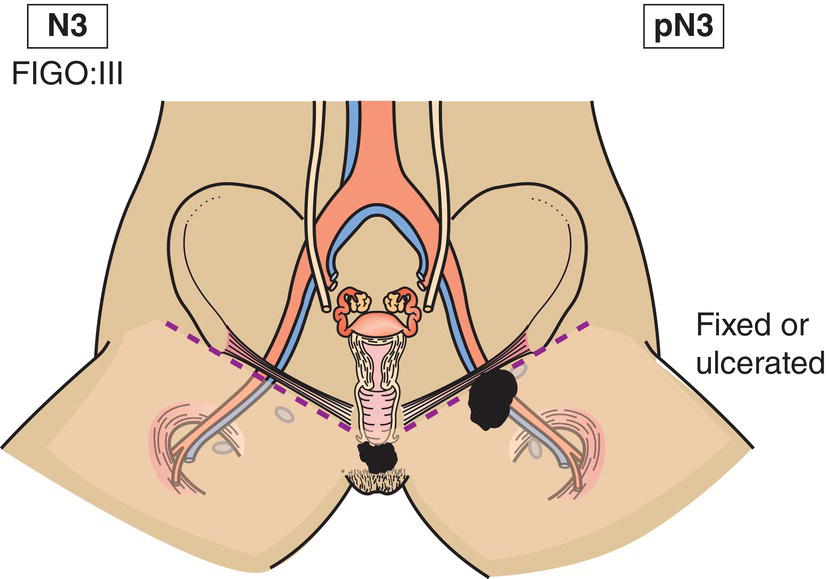
N3
Fixed or ulcerated regional lymph node metastasis (Fig. 413)
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
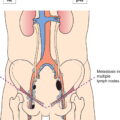
Distant metastasis (including pelvic lymph node metastasis)
pTN Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
pN0
Histological examination of an inguinofemoral lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 6 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree