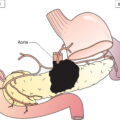
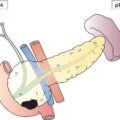
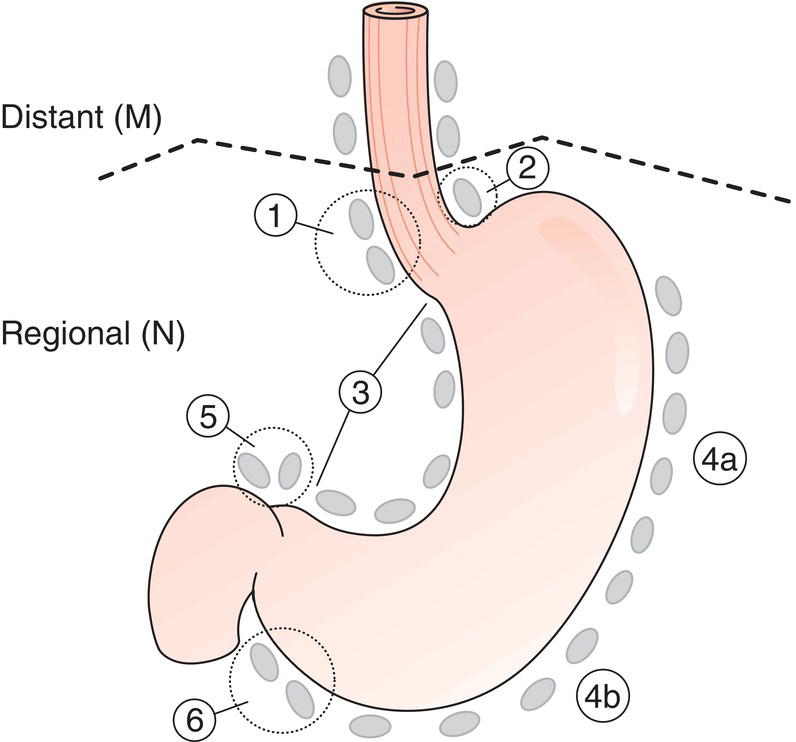
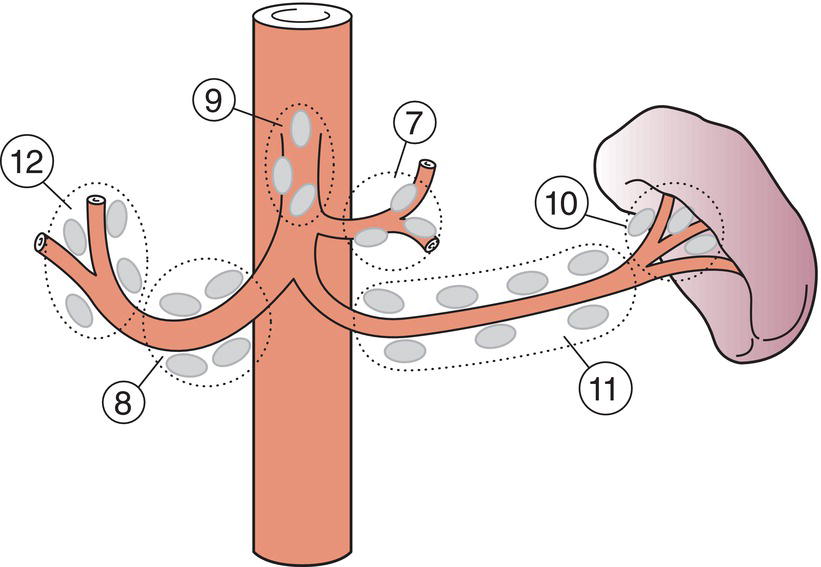
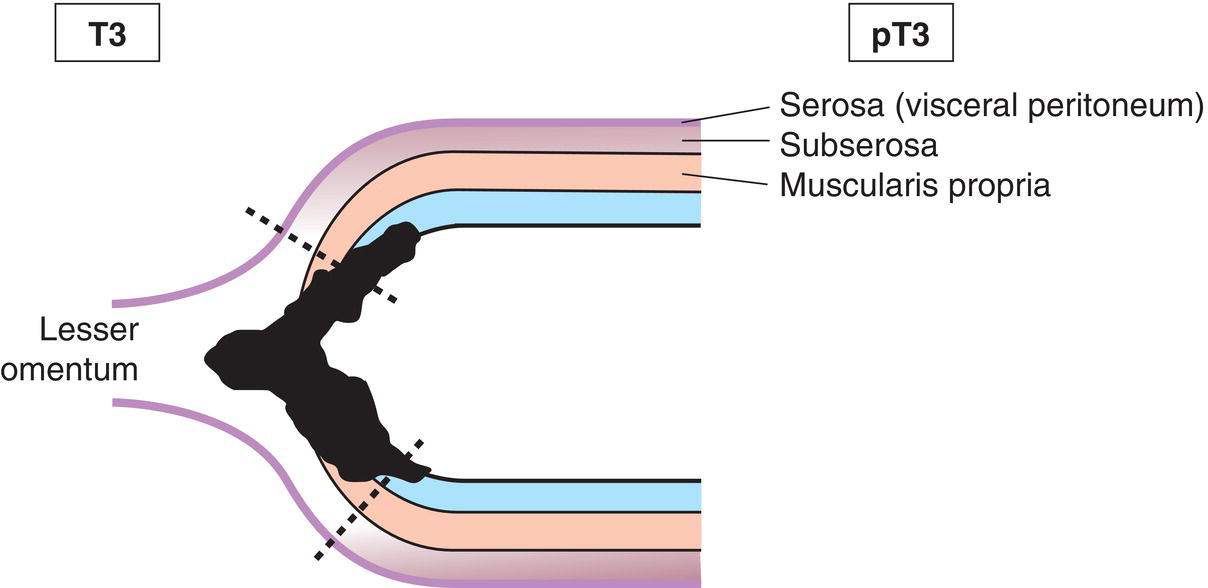
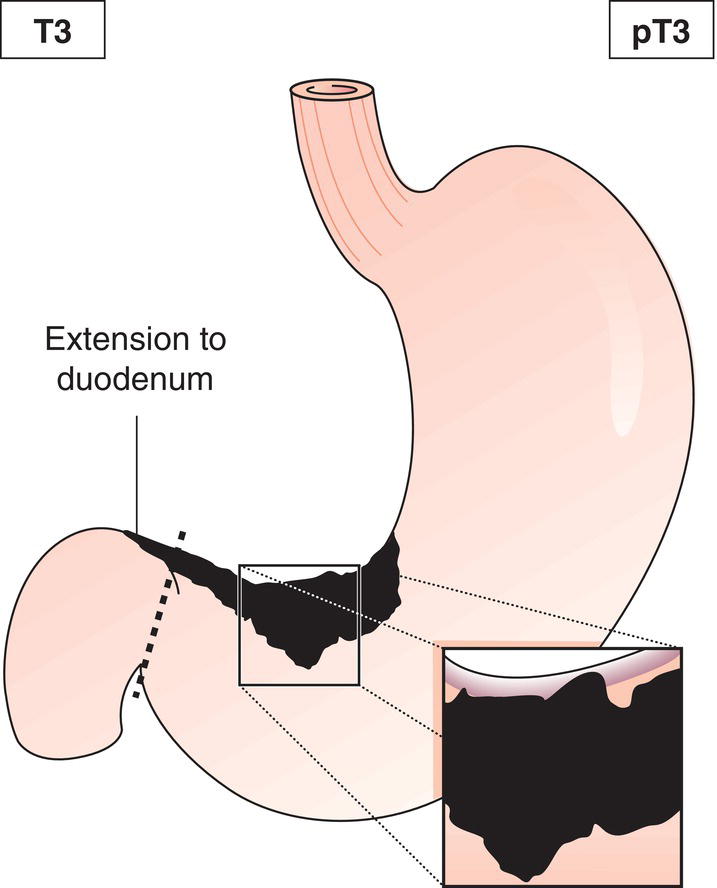
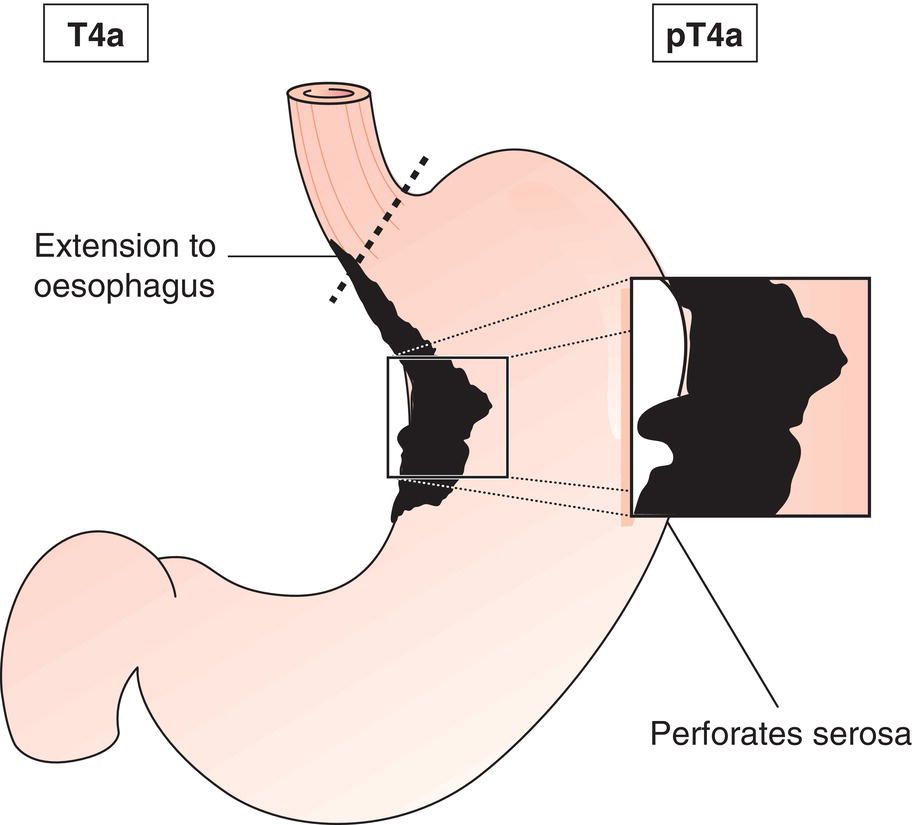
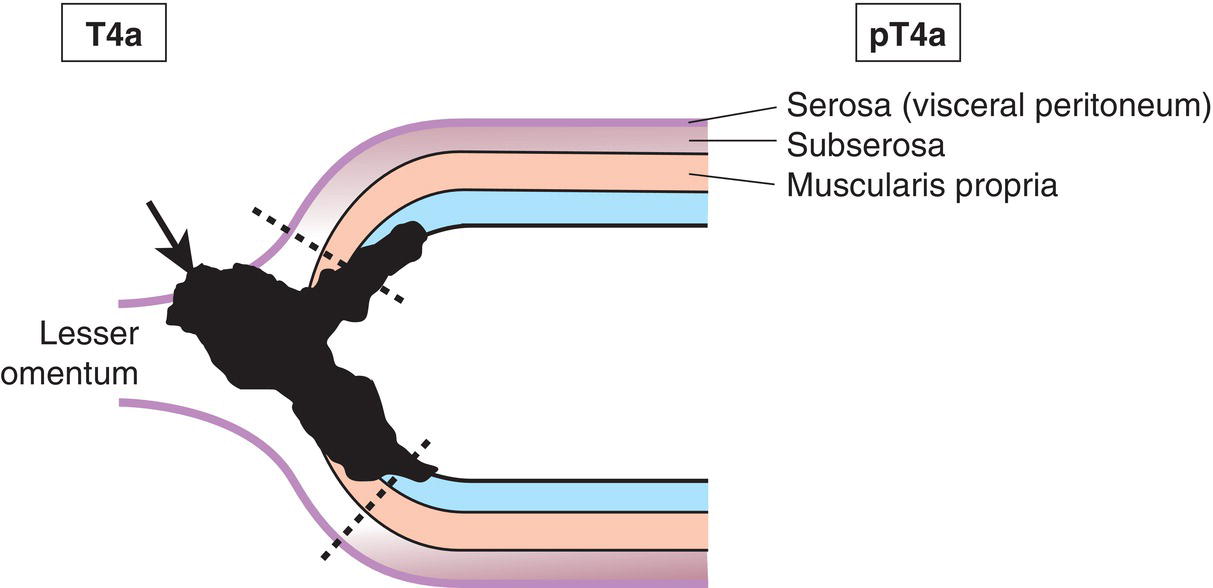
The classification applies only to carcinomas. There should be histological confirmation of the disease. Cancers involving the oesophagogastric junction whose epicentre is within the proximal 2 cm of the cardia (Siewert types I/II) are to be staged as oesophageal cancers. Cancers whose epicentre is more than 2 cm distal from the oesophagogastric junction will be staged using the Stomach Cancer TNM and Stage even if the oesophagogastric junction is involved. The regional lymph nodes of the stomach are the perigastric nodes along the lesser (1, 3, 5) and greater (2, 4a, 4b, 6) curvatures, the nodes along the left gastric (7), common hepatic (8), splenic (11) and coeliac arteries (9), and the hepatoduodenal nodes (12). Involvement of other intra‐abdominal lymph nodes such as retropancreatic, mesenteric and para‐aortic is classified as distant metastasis. Notes The adjacent structures of the stomach are the spleen, transverse colon, liver, diaphragm, pancreas, abdominal wall, adrenal gland, kidney, small intestine and retroperitoneum. Intramural extension to the duodenum or oesophagus is classified by the depth of greatest invasion in any of these sites including the stomach (Figs. 147, 149). Tumour that extends into gastrocolic or gastrohepatic ligaments or into greater or lesser omentum, without perforation of visceral peritoneum, is T3 (Fig. 150). Note Distant metastasis includes peritoneal seeding, positive peritoneal cytology, and omental tumour not part of continuous extension. The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
STOMACH (ICD‐O‐3 C16)
Rules for Classification
Anatomical Subsites (Fig. 142)
Regional Lymph Nodes (Figs. 143, 144)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Tis
Carcinoma in situ: intraepithelial tumour without invasion of the lamina propria, high‐grade dysplasia
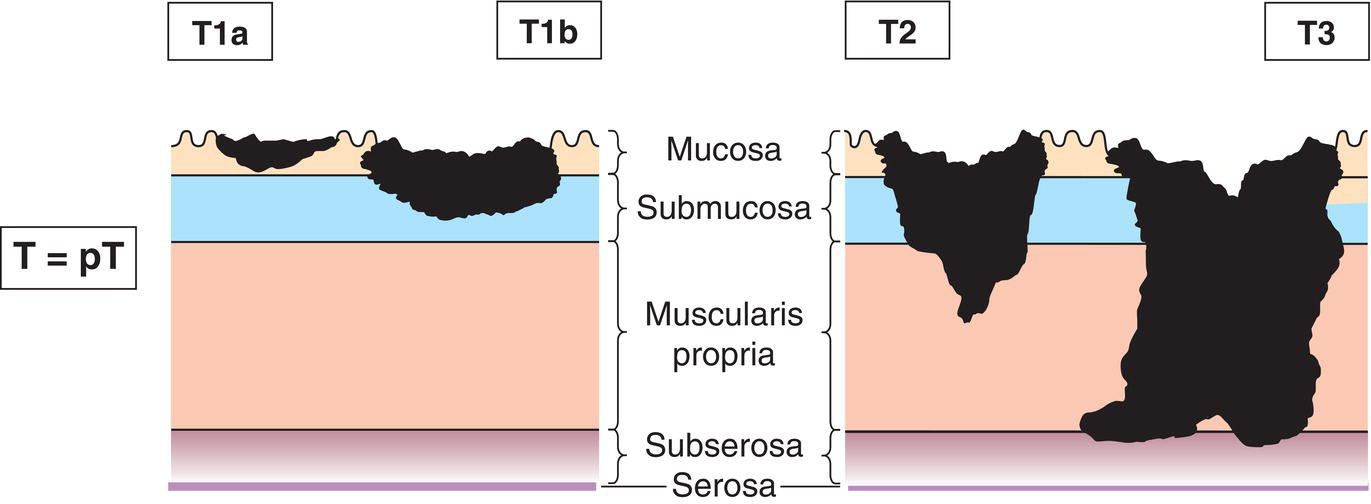
T1
Tumour invades lamina propria, muscularis mucosae or submucosa (Fig. 145)
T1a
Tumour invades lamina propria or muscularis mucosae
T1b
Tumour invades submucosa
T2
Tumour invades muscularis propria (Fig. 145)
T3
Tumour invades subserosa (Figs. 145, 146, 147)
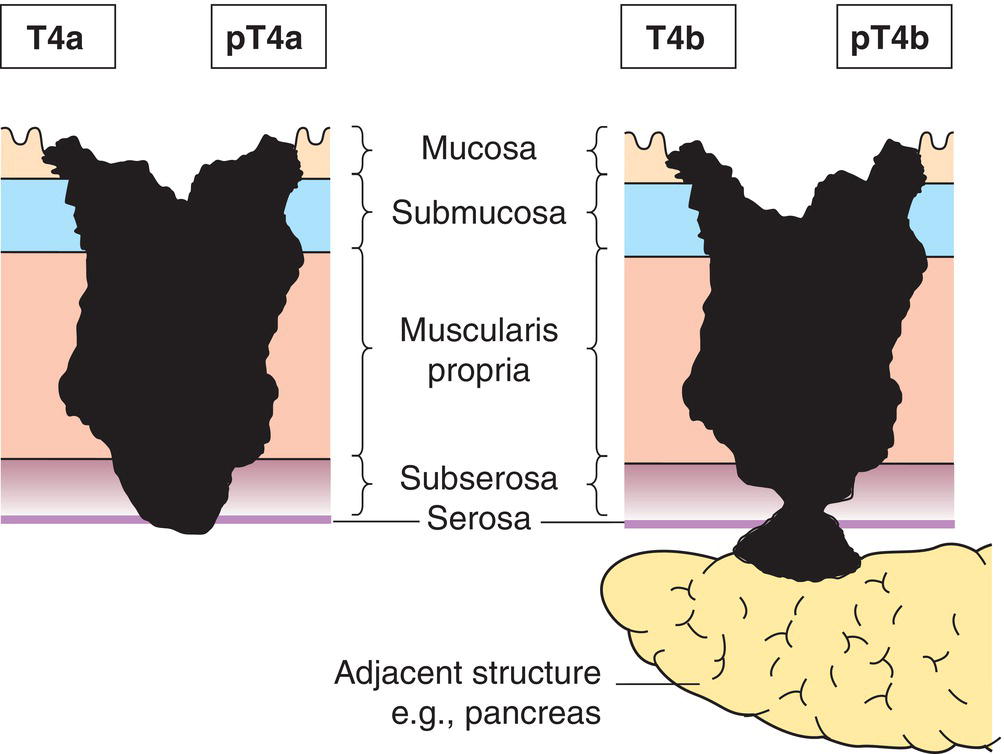
T4
Tumour perforates serosa (visceral peritoneum) or invades adjacent structures1,2,3
T4a
Tumour perforates serosa
T4b
Tumour invades adjacent structures2, 3 (Fig. 148) 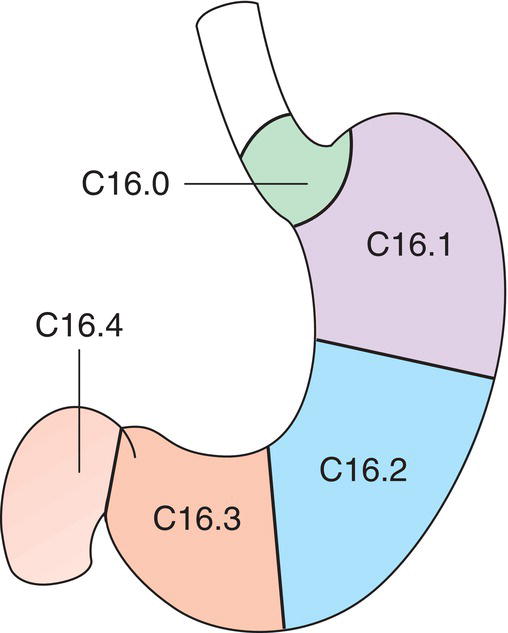
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
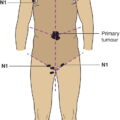
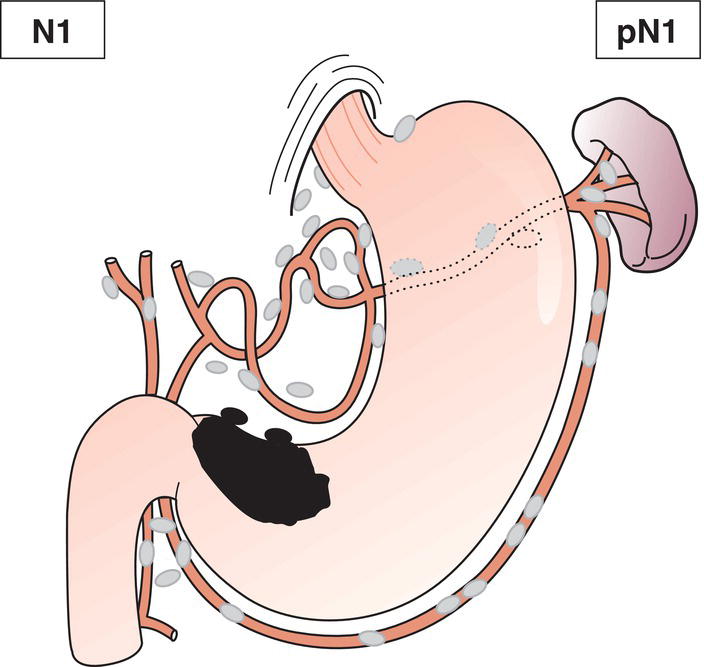
N1
Metastasis in 1 to 2 regional lymph nodes (Fig. 151)
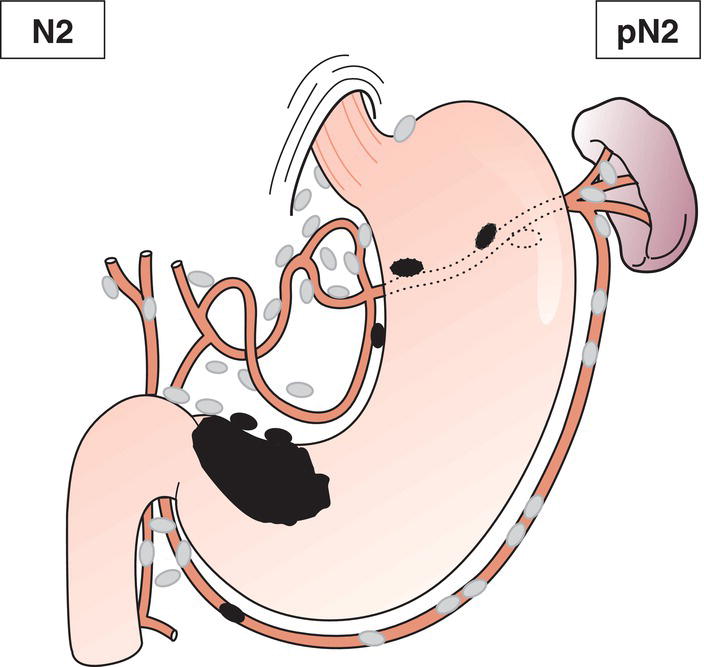
N2
Metastasis in 3 to 6 regional lymph nodes (Fig. 152)
N3
Metastasis in 7 or more regional lymph nodes
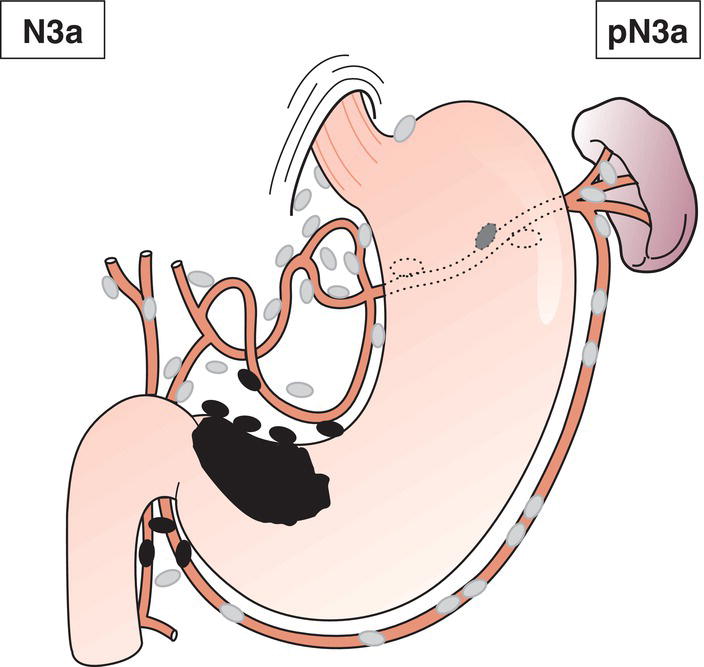
N3a
Metastasis in 7 to 15 regional lymph nodes (Fig. 153)
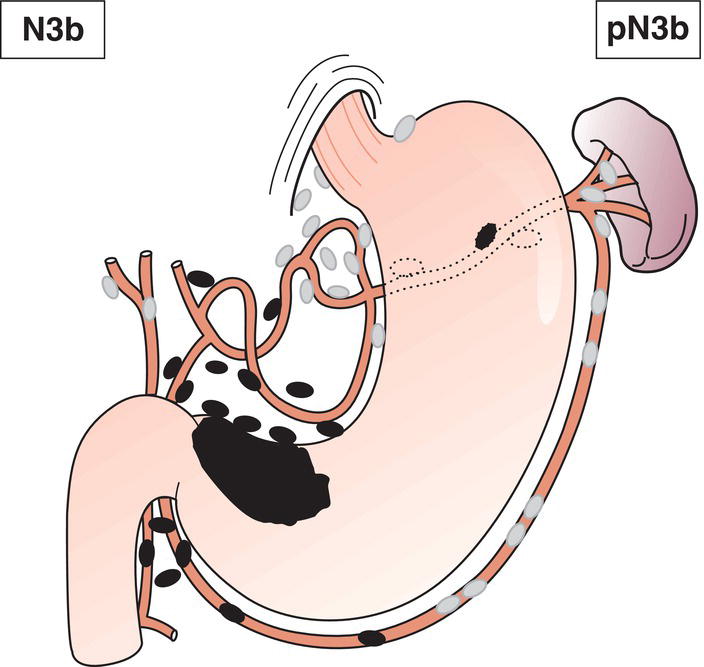
N3b
Metastasis in 16 or more regional lymph nodes (Fig. 154)
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
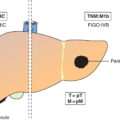
M1
Distant metastasis (Fig. 154)
pTNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pN0
Histological examination of a regional lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 16 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree