Fig. 6.1
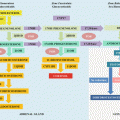
Diagnosis of hyperprolactinemia algorithm
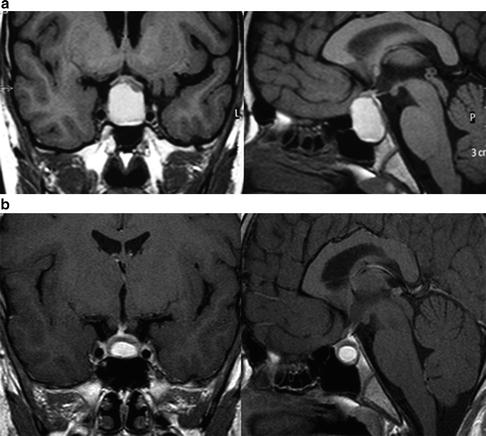
Fig. 6.2
(a) Before treatment. Sellar T1-weighted MRI after gadolinium enhancement, coronal (left) and sagittal (right) depicted a sellar mass impinging optic chiasma. (b) After 1 year of treatment with CAB. Sellar T1-weighted MRI after gadolinium enhancement, coronal (left) and sagittal (right) depicted an important reduction of tumor dimensions, with optic chiasma free of compression
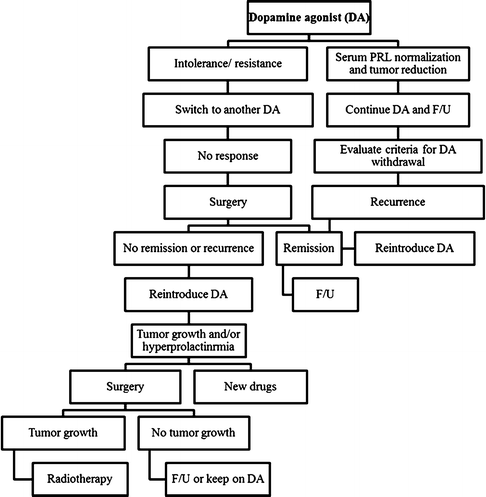
Fig. 6.3
Prolactinoma treatment algorithm
A sellar MRI was performed in a 11-year-old male patient complaining of headache and a sellar mass was depicted (Fig. 6.2a). Serum PRL level was 1,130 ng/ml. The patient also had pubertal impairment development. Neurophthalmologic evaluation was normal. After 4 years of treatment with BRC, there was tumoral reduction without normalization of serum PRL levels. In our department, BRC was substituted for CAB and dosage was gradually augmented until 3.5 mg a week. After 1 year of treatment with CAB, serum PRL levels were normal and an additional tumoral reduction occurred (Fig. 6.2b).
References
1.
Bronstein MD. Disorders of prolactin secretion and prolactinomas. In: DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL, editors. Endocrinology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2010. p. 333–57.
2.
3.
Batrinos ML, Panitsa-Faflia C, Tsiganou E, Pitoulis G, Liapi C. Contribution to the problem of hyperprolactinaemia: experience with 4,199 prolactin assays and 117 prolactinomas. Int J Fertil Menopausal Stud. 1994;39(2):120–7.PubMed
4.
5.
6.
7.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Glezer A, Soares CR, Vieira JG, Giannella-Neto D, Ribela MT, Goffin V, Bronstein MD. Human macroprolactin displays low biological activity via its homologous receptor in a new sensitive bioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(3):1048–55.PubMedCrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree