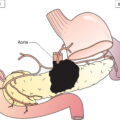
The classification applies only to carcinomas, including papillary, follicular, poorly differentiated, insular, anaplastic and medullary carcinomas. There should be microscopic confirmation of the disease and division of cases by histological type. The regional lymph nodes are the cervical and upper/superior mediastinal nodes The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. The four major histopathologic types are:
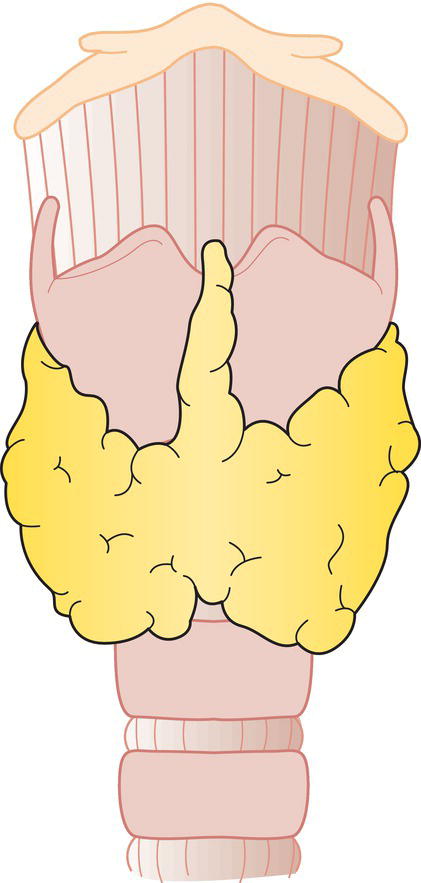
THYROID GLAND (ICD‐O C73) (FIG. 121)
Rules for Classification
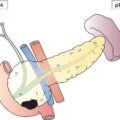
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 122)
TN Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
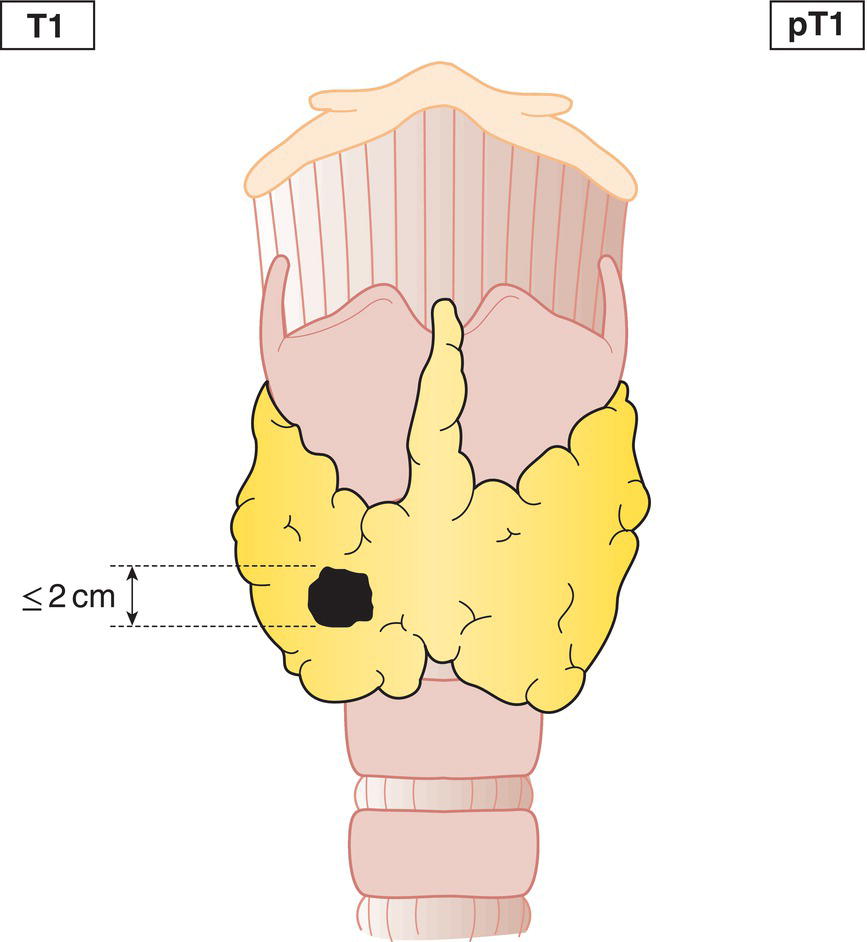
T1
Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid (Fig. 123)
T1a
Tumour 1 cm or less in greatest dimension, minimal extrathyroidal extension may be present
T1b
Tumour more than 1 cm but not more than 2 cm in greatest dimension, minimal extrathyroidal extension may be present
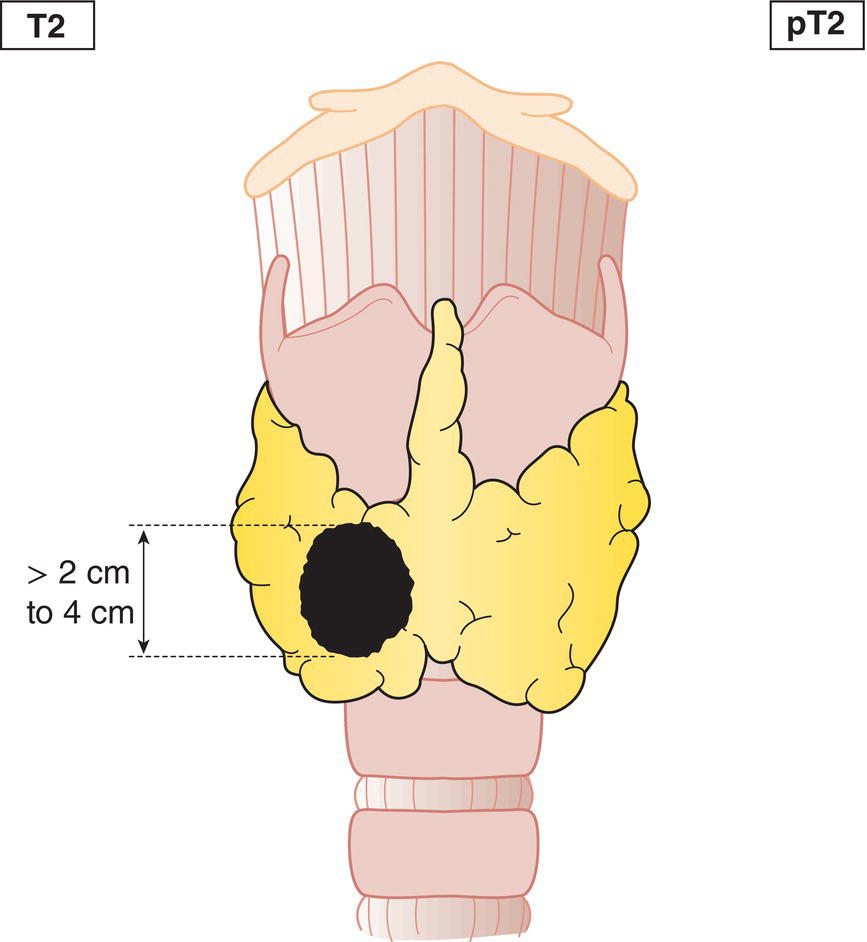
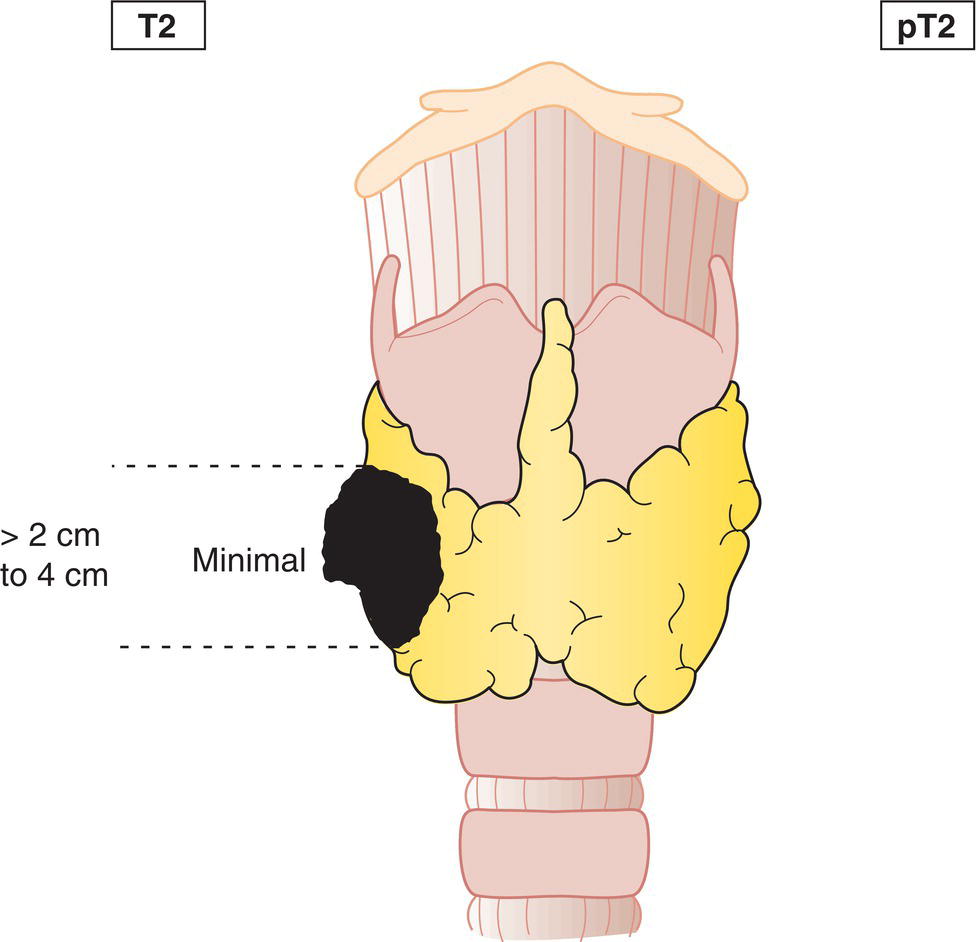
T2
Tumour more than 2 cm but not more than 4 cm in greatest dimension, minimal extrathyroidal extension may be present (Fig. 124, 125) 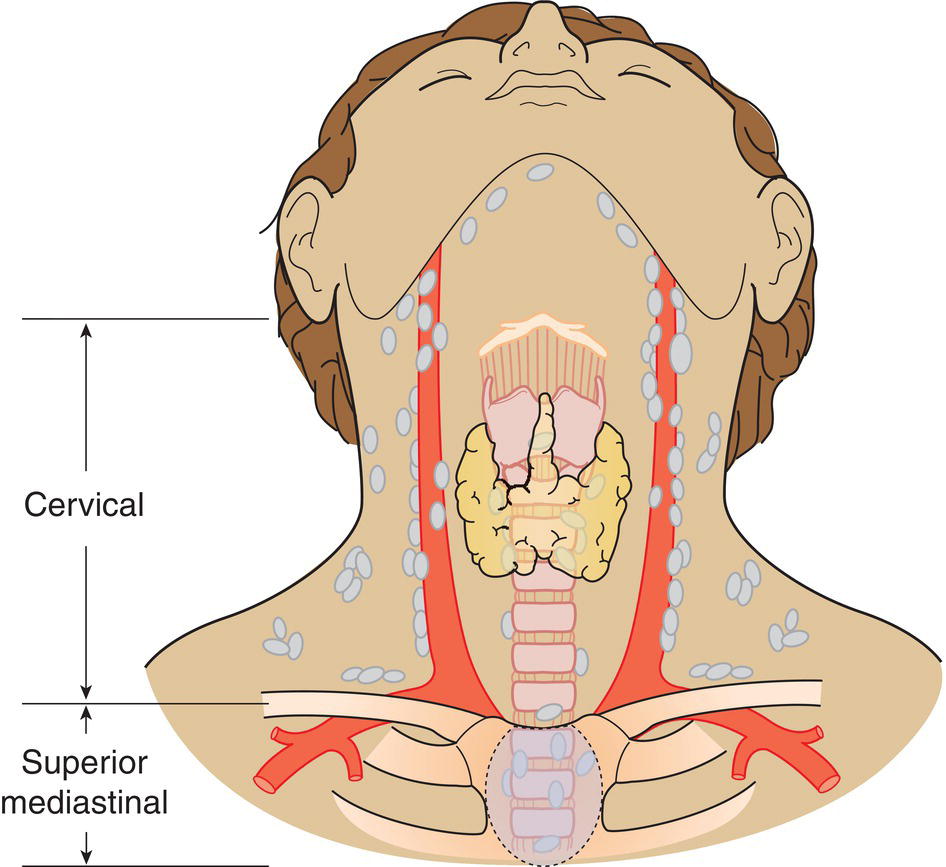
T3a
Tumour more than 4 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid or with minimal extrathyroid extension (Fig. 126)
T3b
Tumour of any size with gross extrathyroid extension invading the strap muscles (e.g., extension to sternohyoid, sternothyroid or omohyoid muscles)
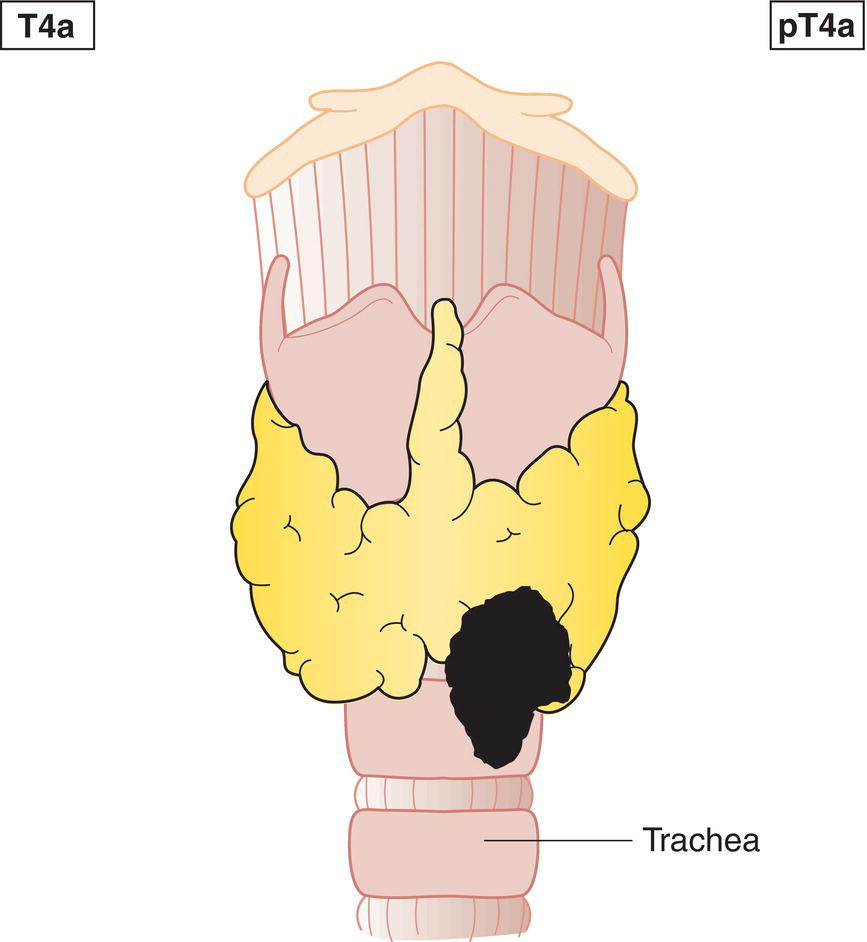
T4a
Tumour extends beyond the thyroid capsule and invades any of the following: subcutaneous soft tissues, larynx, trachea, oesophagus, recurrent laryngeal nerve (Figs. 127, 128)
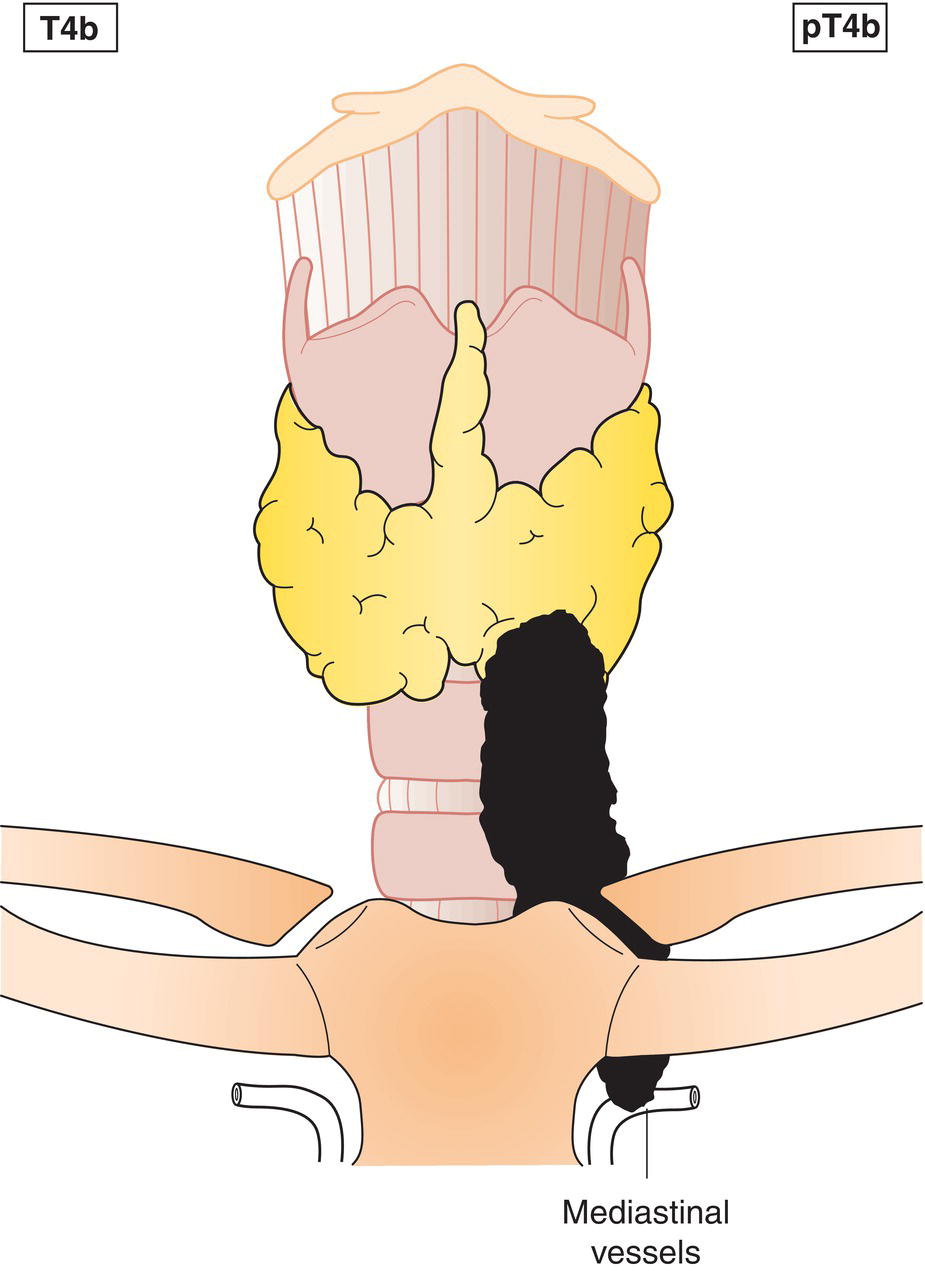
T4b
Tumour invades prevertebral fascia, mediastinal vessels, or encases carotid artery (Fig. 129) 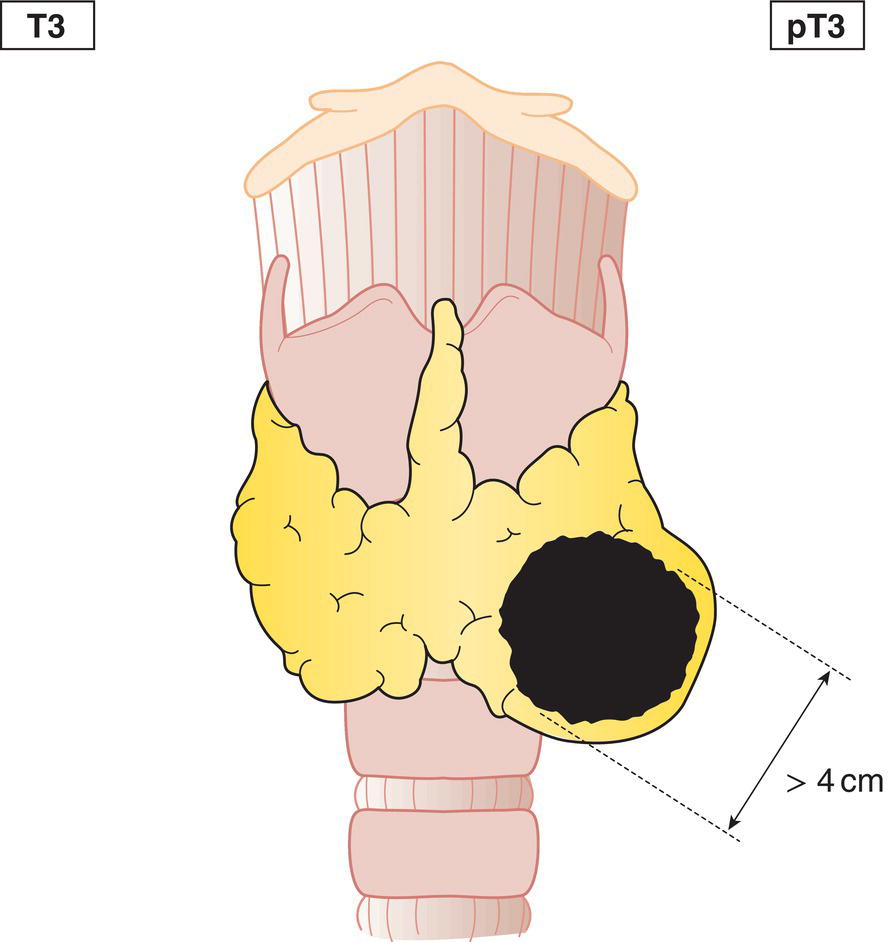
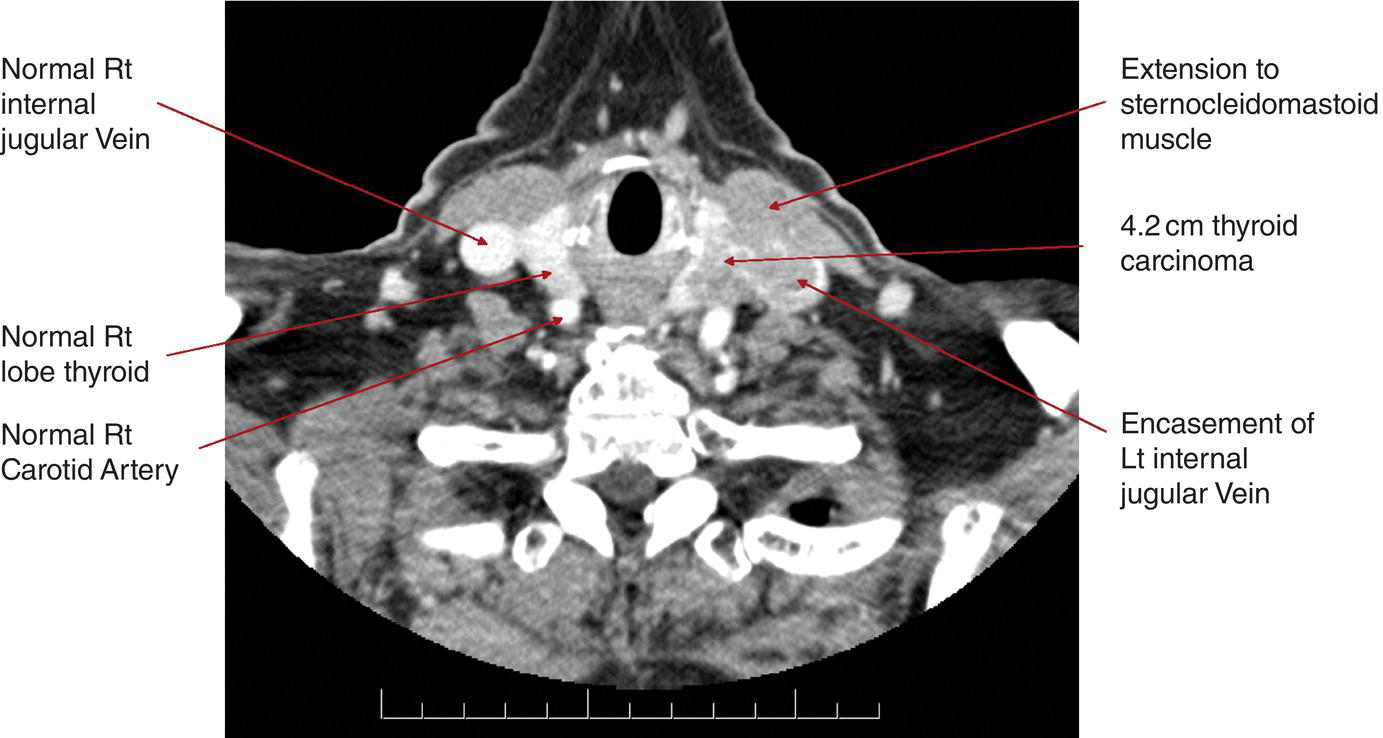
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
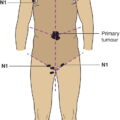
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis
N1a
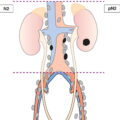
Metastasis in Level VI (pretracheal, paratracheal and prelaryngeal/Delphian lymph nodes) or upper/superior mediastinum (Fig. 130)
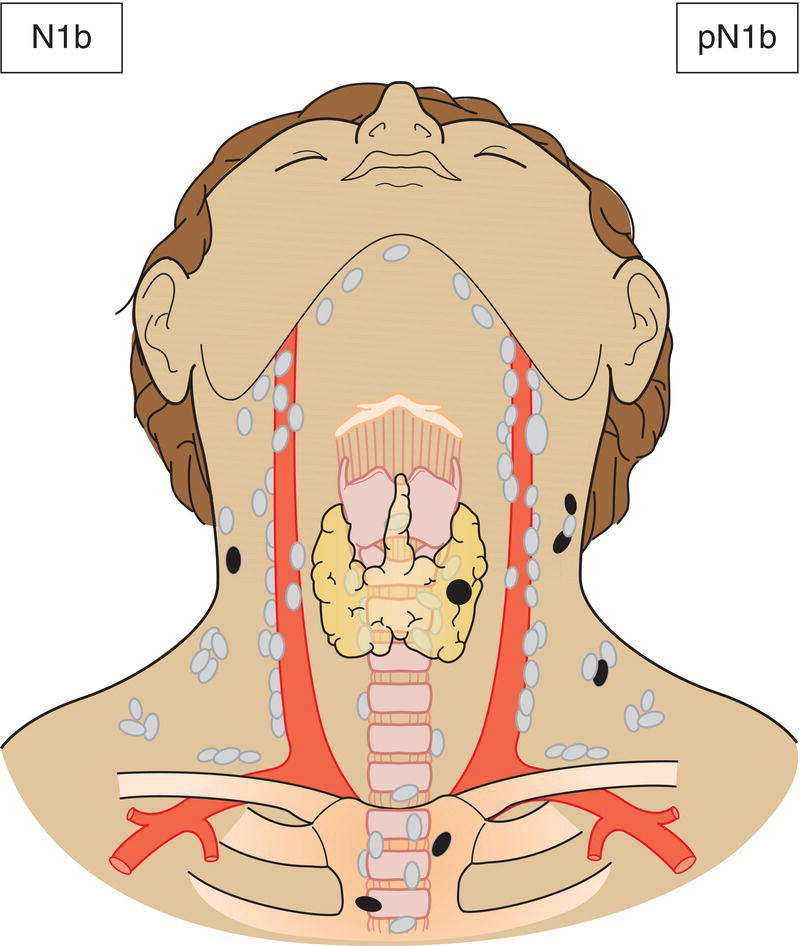
N1b
Metastasis in other unilateral, bilateral or contralateral cervical (Levels I, II, III, IV or V) or retropharyngeal (Fig. 131) 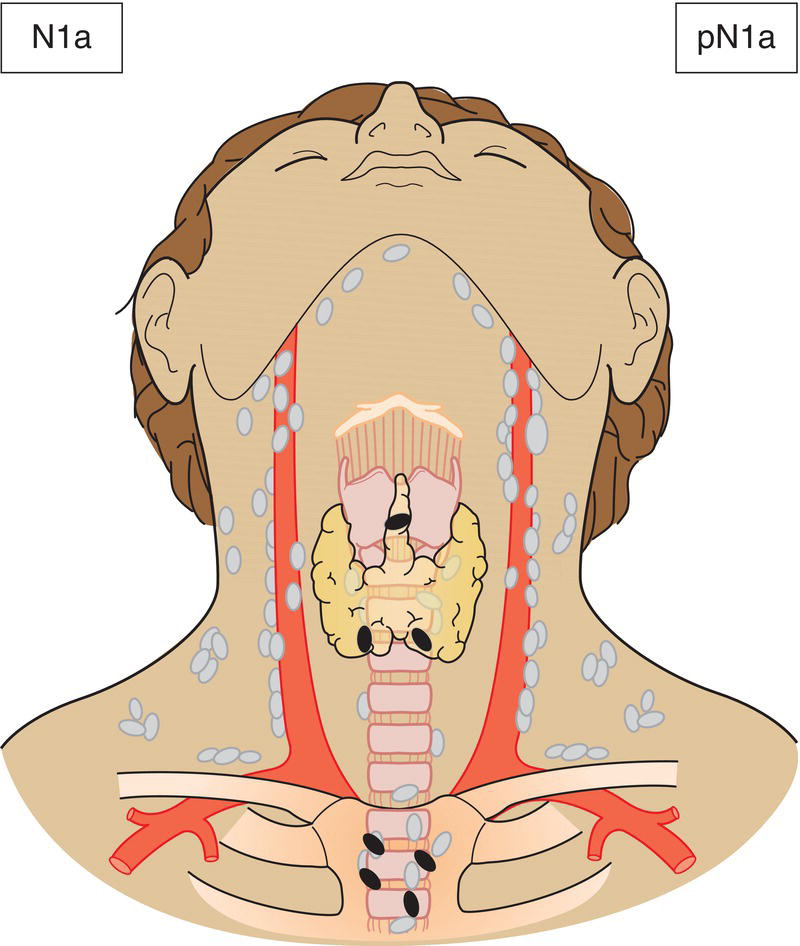
pTN Pathological Classification
Histopathologic Types
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree