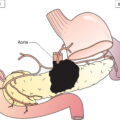
The definitions of the T, N, and M categories correspond to the FIGO stages. Both systems are included for comparison. The classification applies to malignant ovarian neoplasms of both epithelial and stromal origin, including those of borderline malignancy or of low malignant potential corresponding to “common epithelial tumours” of the earlier terminology. The classification also applies to carcinoma of the Fallopian tubes and to carcinomas of the peritoneum (Müllerian origin). There should be histological confirmation of the disease and division of cases by histological type. The FIGO stages are based on surgical staging. TNM stages are based on clinical and/or pathological classification. The regional lymph nodes are the hypogastric (obturator and internal iliac) (1), common iliac (2), external iliac (3), lateral sacral (4) and para‐aortic (5). Note bLiver parenchymal metastasis M1/stage IV. The pT and pN categories correspond to the T and N categories. Note
OVARIAN, FALLOPIAN TUBE AND PRIMARY PERITONEAL CARCINOMA (ICD‐O‐3 C56, C57, C48.1, C48.2)
Rules for Classification
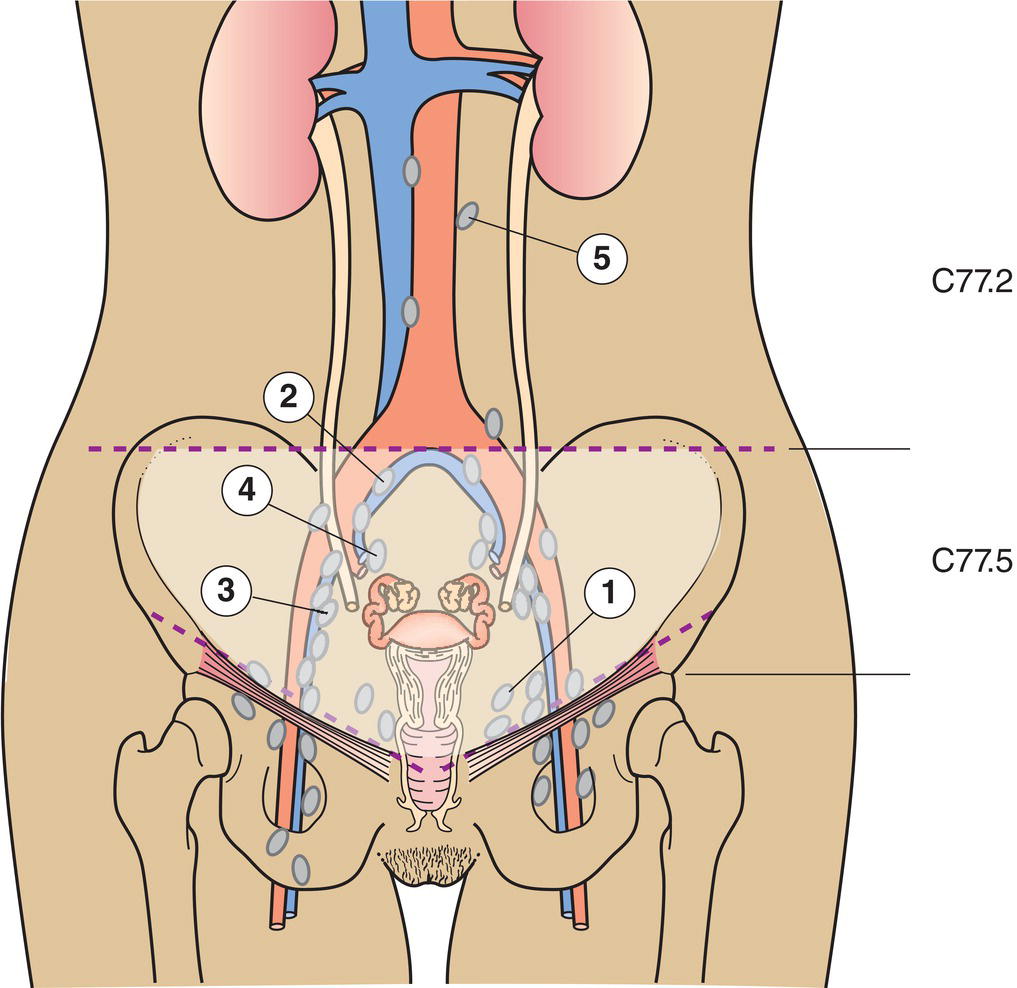
Regional Lymph Nodes (Fig. 452)
TNM Clinical Classification
T – Primary Tumour
TNM Categories
FIGO Stages
Definition
TX
Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
T1
I
Tumour confined to the ovaries (one or both) or fallopian tube(s)
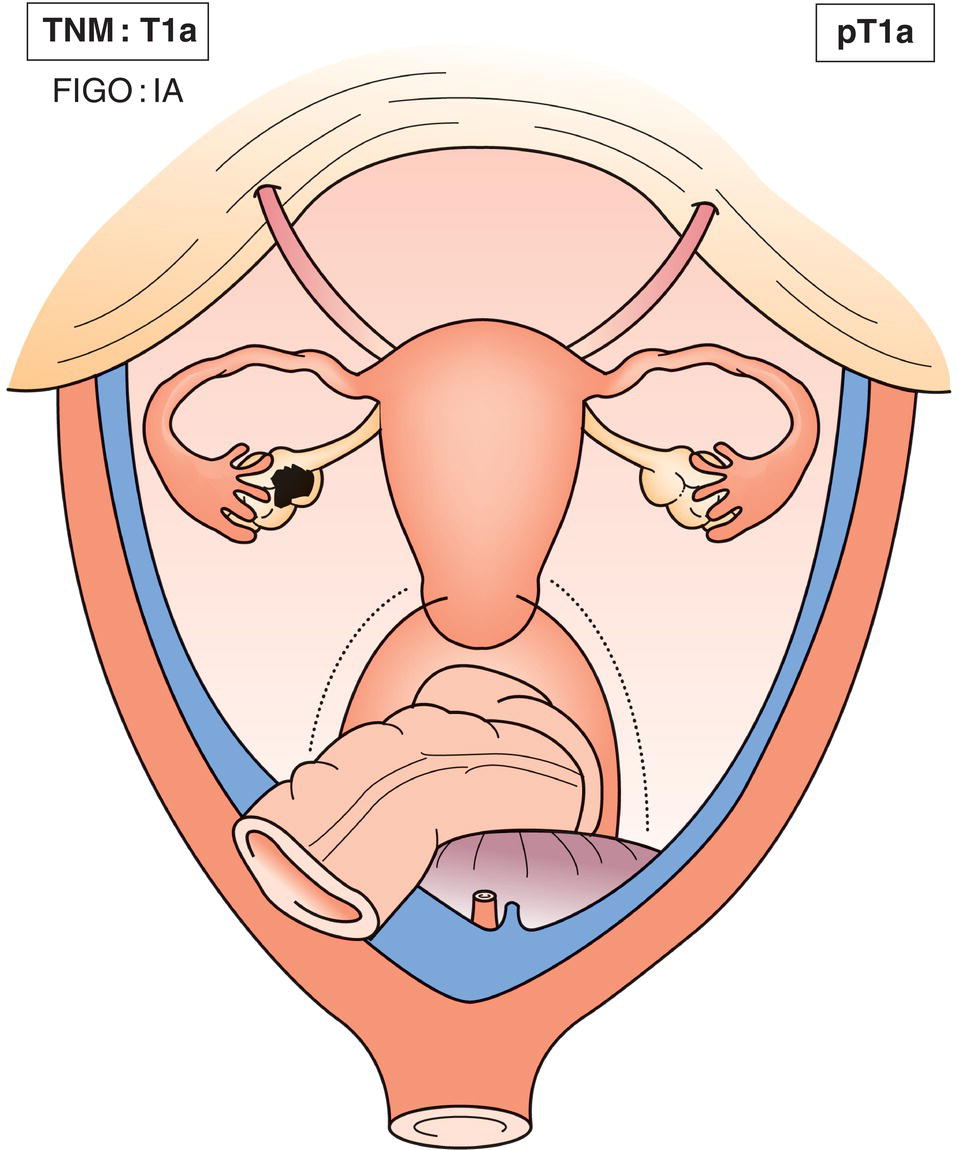
T1a
IA
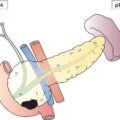
Tumour limited to one ovary (capsule intact) or fallopian tube; no tumour on ovarian or fallopian tube surface, no malignant cells in ascites or peritoneal washings (Fig. 453)
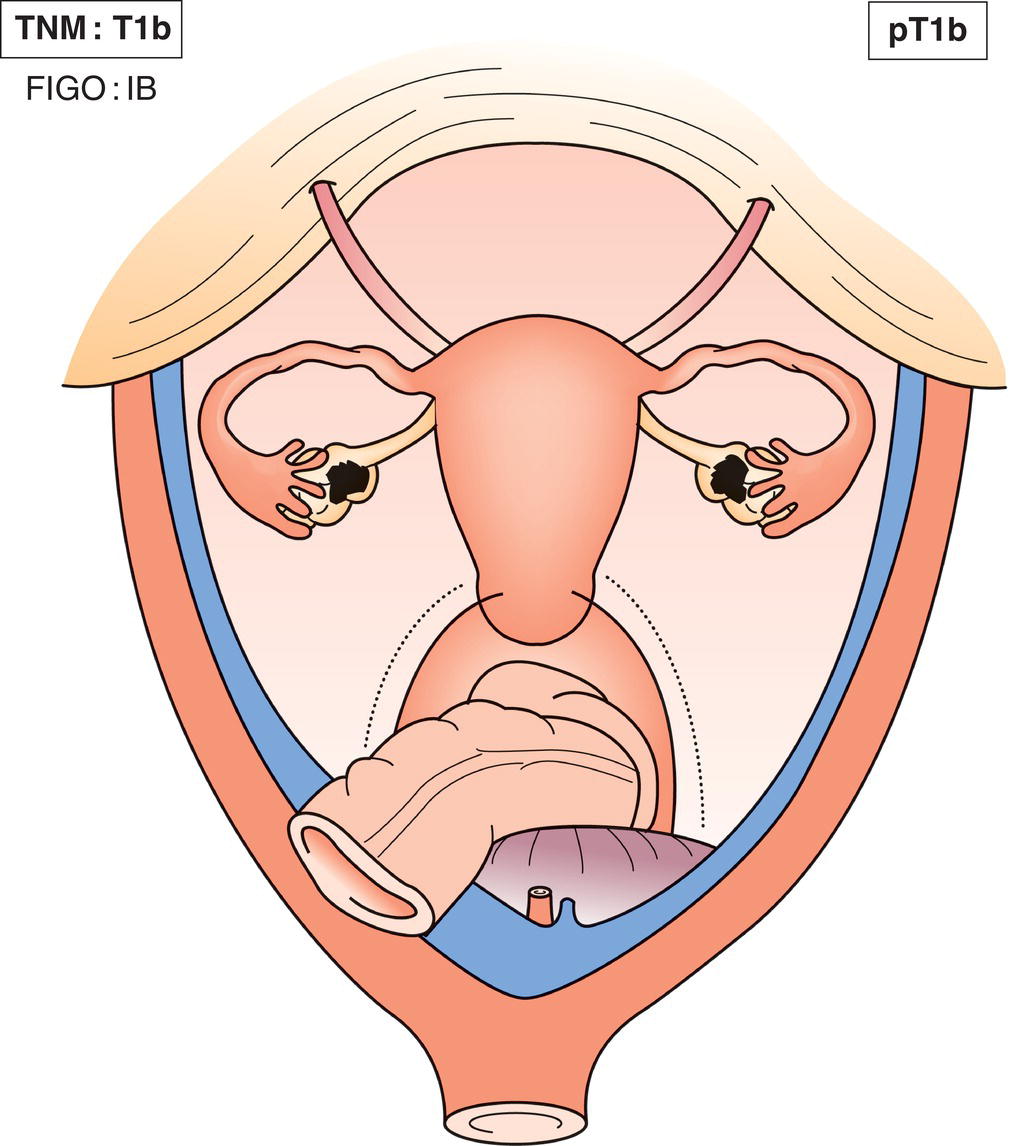
T1b
IB
Tumour limited to both ovaries or fallopian tubes (Fig. 454)
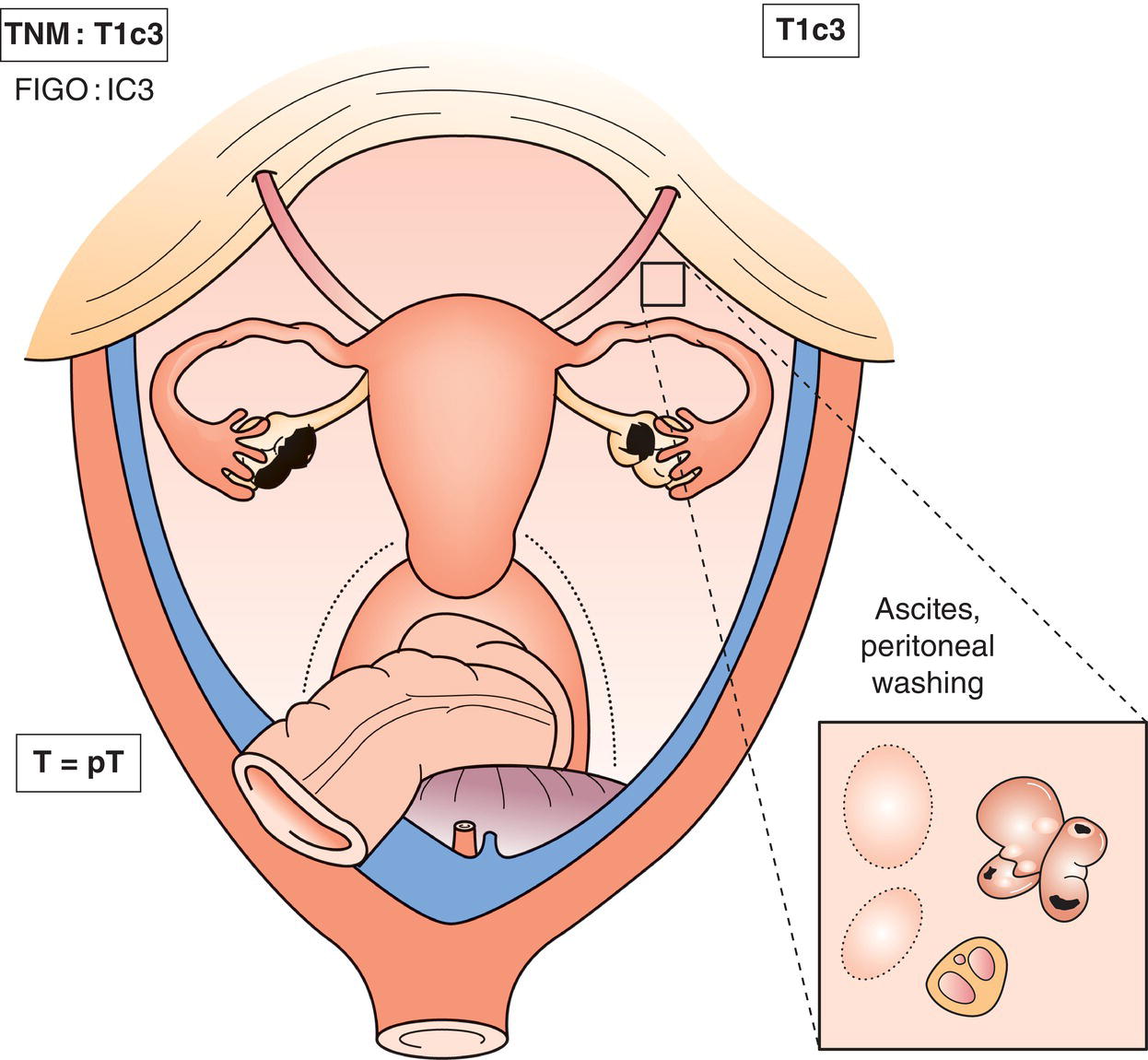
T1c
IC
Tumour limited to one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes with any of the following:
T1c1
Surgical spill
T1c2
Capsule ruptured before surgery or tumour on ovarian or fallopian tube surface
T1c3
Malignant cells in ascites or peritoneal washings (Fig. 455)
T2
II
Tumour involves one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes with pelvic extension (below the pelvic brim) or primary peritoneal cancer
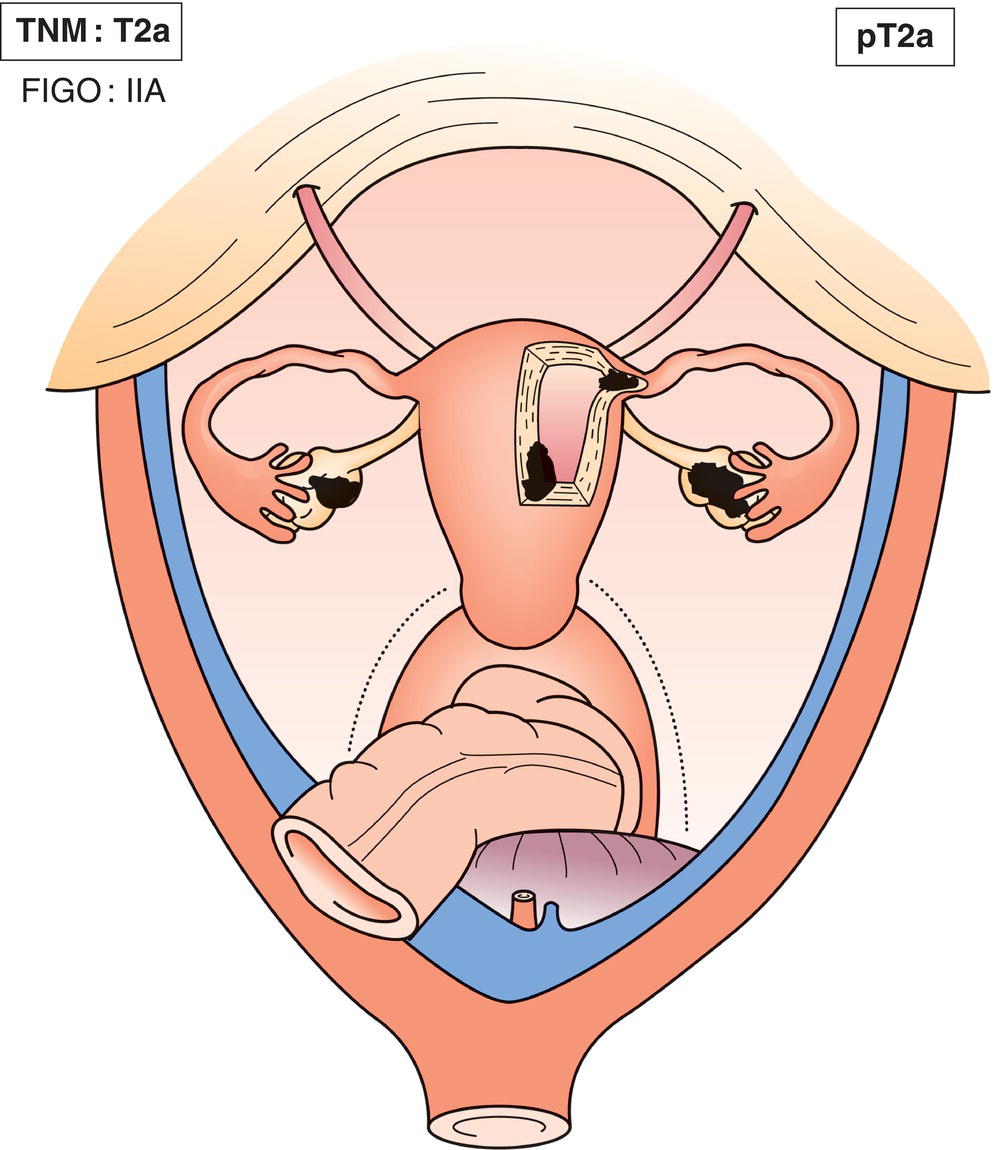
T2a
IIA
Extension and/or implants on uterus and/or fallopian tube(s) and or ovary(ies) (Fig. 456)
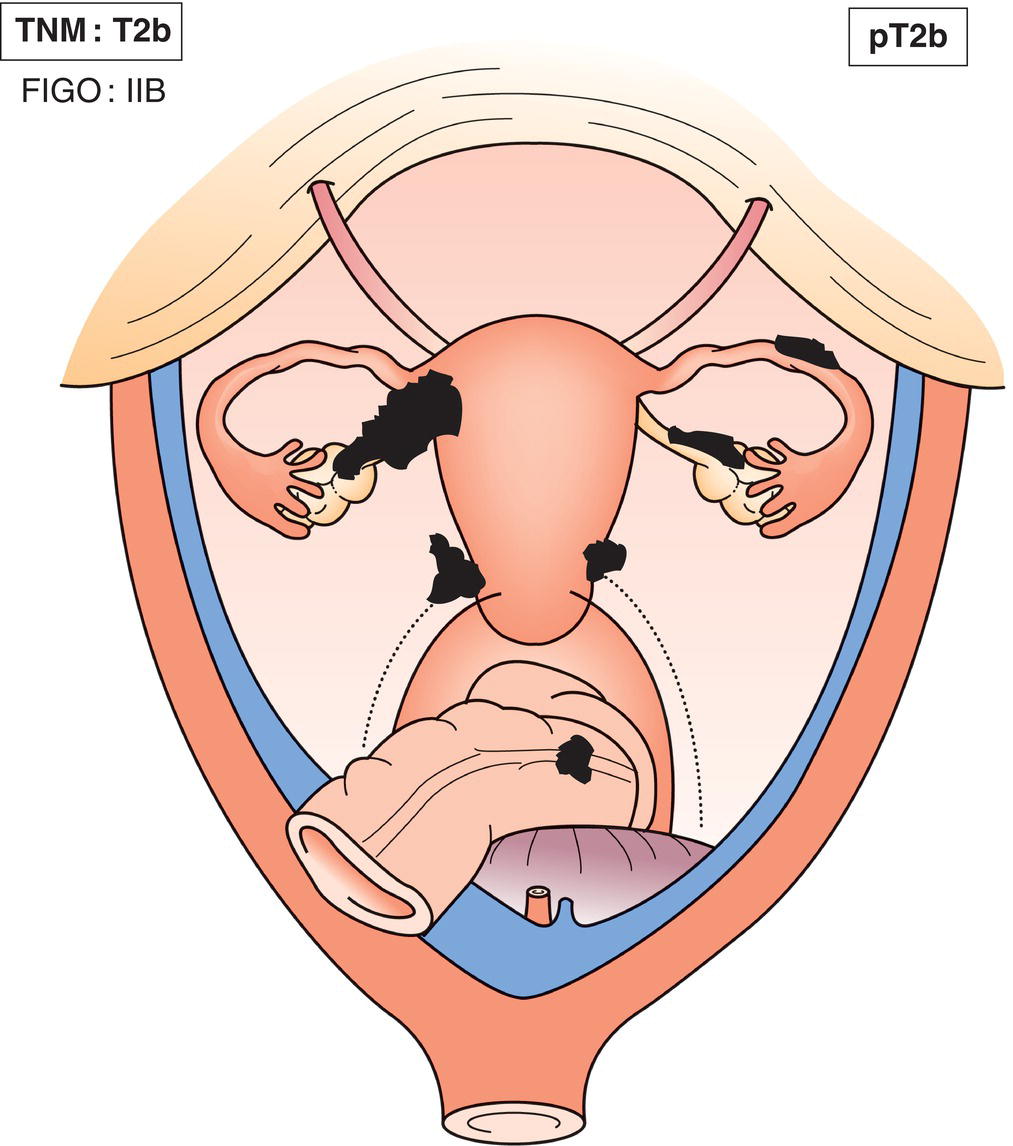
T2b
IIB
Extension to other pelvic tissues, including bowel within the pelvis (Fig. 457)
T3 and/or N1
IIIa
Tumour involves one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes or primary peritoneal carcinoma with cytologically or histologically confirmed spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis and/or metastasis to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes
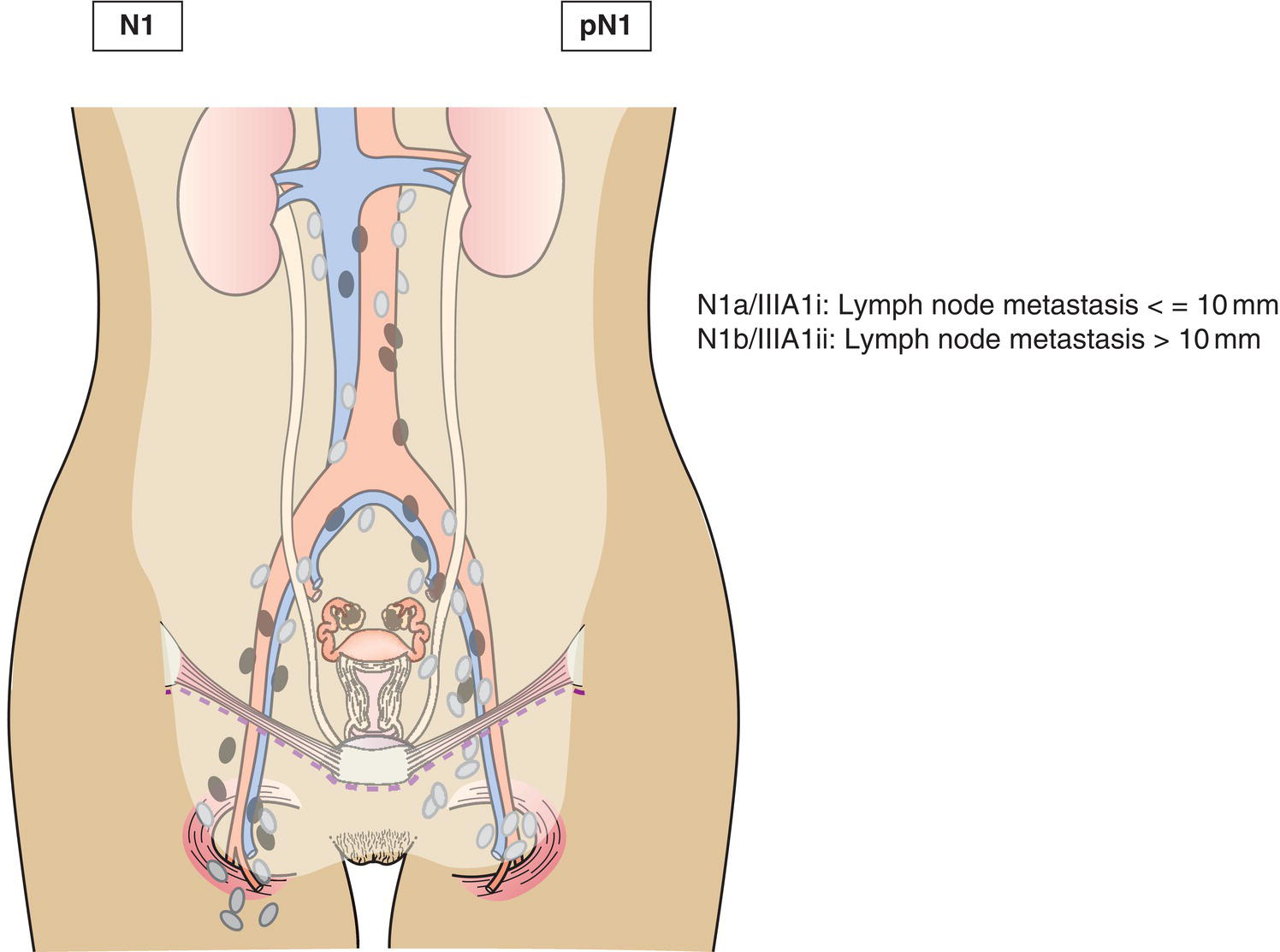
N1
Retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis only
N1a
IIIA1i
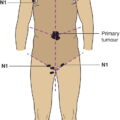
Lymph node metastasis not more than 10 mm in greatest dimension (Fig. 458)
N1b
IIIA1ii
Lymph node metastasis more than 10 mm in greatest dimension (Fig. 458)
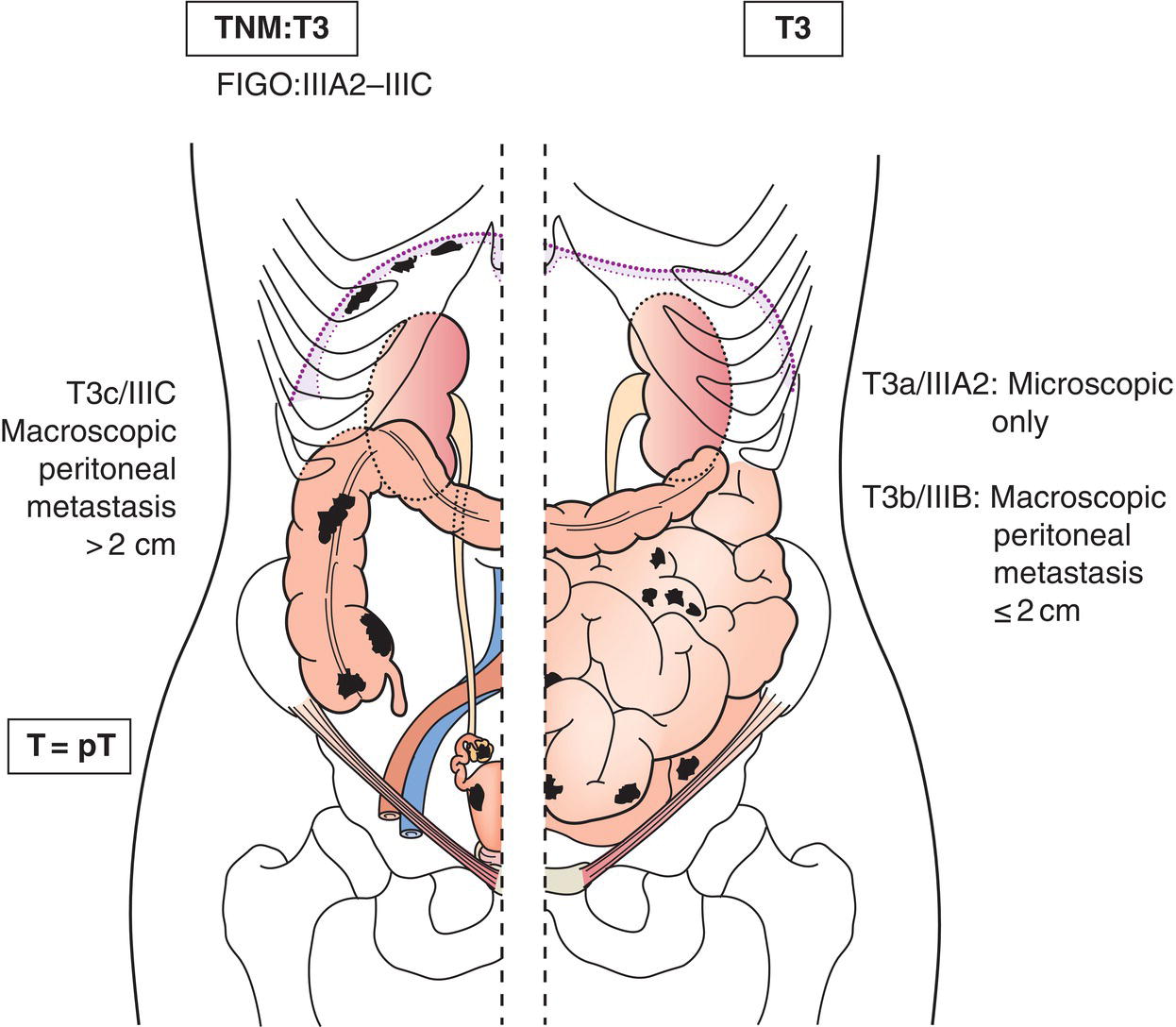
T3c and/or N1
IIIA2
Microscopic extrapelvic (above the pelvic brim) peritoneal involvement with or without retroperitoneal lymph node, including bowel involvement (Fig. 459)
T3b any N
IIIB
Macroscopic peritoneal metastasis beyond pelvic brim 2 cm, or less in greatest dimension, including bowel involvement outside the pelvis with or without retroperitoneal nodes (Fig. 459)
T3c any N
IIIC
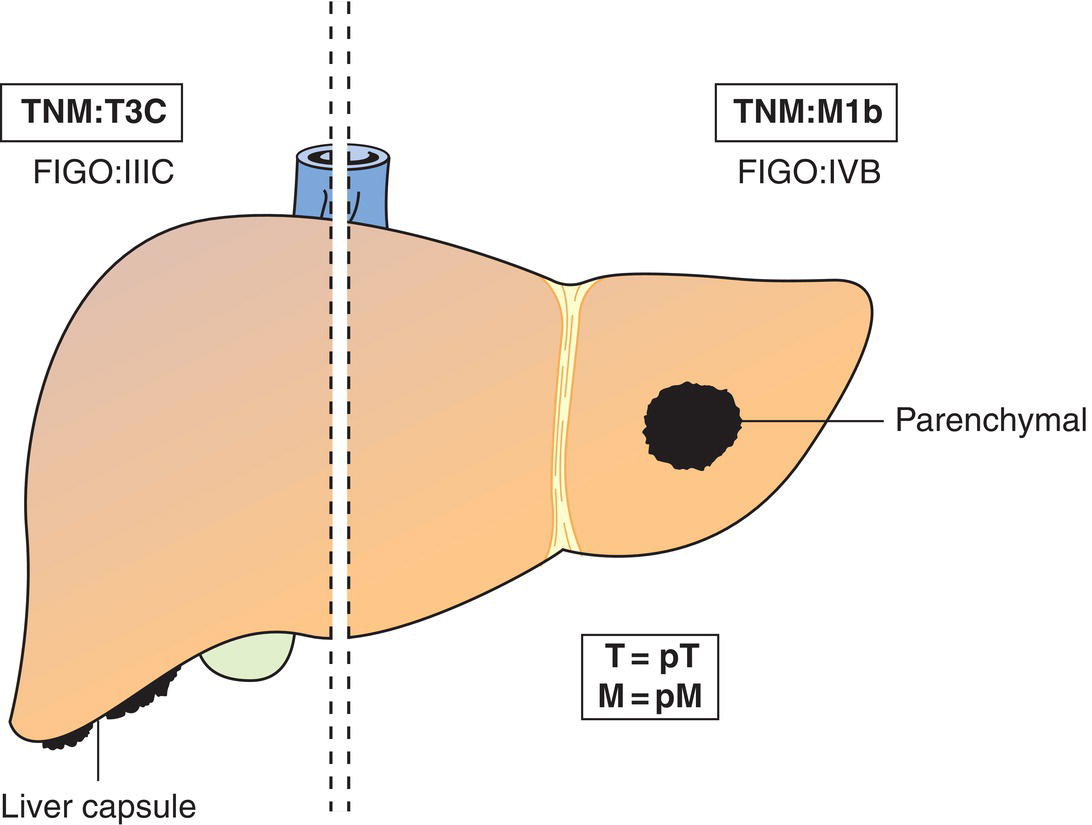
Peritoneal metastasis beyond pelvic brim more than 2 cm in greatest dimension and/or retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis (includes extension of tumour to capsule of liver and spleen without parenchymal involvement of either organ) (Fig. 459, 460)
M1
IV
Distant metastasis (excludes peritoneal metastasis)
M1a
IVA
Pleural effusion with positive cytology
M1bb
IVB
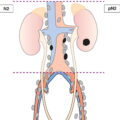
Parenchymal metastasis and metastasis to extra abdominal organs (including inguinal lymph nodes and lymph nodes outside the abdominal cavity) (Fig. 460)
aLiver capsule metastasis is T3/stage III.
N – Regional Lymph Nodes
NX
Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Regional lymph node metastasis (Fig. 458)
N1 IIIA1
Retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis only
N1a IIIA1i
Lymph node metastasis no more than 10 mm in greatest dimension
N1b IIIA1ii
Lymph node metastasis more than 10 mm in greatest dimension
M – Distant Metastasis
M0
No distant metastasis
M1
Distant metastasis
M1a
Pleural effusion with positive cytology
M1b
Parenchymal metastasis and metastasis to extra‐abdominal organs (including inguinal lymph nodes and lymph nodes outside the abdominal cavity) (Fig. 460)
pTNM Pathological Classification
pM1
Distant metastasis microscopically confirmed
pM1a
Pleural effusion with positive cytology
pM1b
Parenchymal metastasis and metastasis to extra‐abdominal organs (including inguinal lymph nodes and lymph nodes outside the abdominal cavity)
pM0 and pMX are not valid categories.
pN0
Histological examination of a pelvic lymphadenectomy specimen will ordinarily include 6 or more lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes are negative, but the number ordinarily examined is not met, classify as pN0.
Summary
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree