Fig. 6.1
7th edition TNM classifications. T is classified as Tis: high-grade dysplasia; T1 cancer invades lamina propria, muscularis mucosae, or submucosa, T2 cancer invades muscularis propria, T3 cancer invades adventitia, T4a resectable cancer invades adjacent structures such as the pleura, pericardium, or diaphragm, and T4b unresectable cancer invades other adjacent structures, such as the aorta, vertebral body, or trachea. N is classified as N0 no regional lymph node metastasis, N1 regional lymph node metastases involving 1–2 nodes, N2 regional lymph node metastases involving 3–6 nodes, and N3 regional lymph node metastases involving 7 or more nodes. M is classified as M0 no distant metastasis and M1 distant metastasis
Table 6.1
2010 7th edition AJCC/UICC TNM classifications
Primary tumor (T) | |
TX | Primary tumor cannot be assessed |
T0 | No evidence of primary tumor |
Tis | High-grade dysplasiaa |
T1 | Tumor invades lamina propria, muscularis mucosae, or submucosa |
T1a | Tumor invades lamina propria or muscularis mucosae |
T1b | Tumor invades submucosa |
T2 | Tumor invades muscularis propria |
T3 | Tumor invades adventitia |
T4 | Tumor invades adjacent structures |
T4a | Resectable tumor invading pleura, pericardium, or diaphragm |
T4b | Unresectable tumor invading other adjacent structures, such as the aorta, vertebral body, trachea, etc. |
Regional lymph nodes (N)b | |
NX | Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed |
N0 | No regional lymph node metastasis |
N1 | Regional lymph node metastases involving 1–2 nodes |
N2 | Regional lymph node metastases involving 3–6 nodes |
N3 | Regional lymph node metastases involving 7 or more nodes |
Distant metastasis (M) | |
M0 | No distant metastasis |
M1 | Distant metastasis |
Histopathologic type | |
Squamous cell carcinoma | |
Adenocarcinoma | |
Histologic grade (G) | |
GX | Grade cannot be assessed—stage grouping as G1 |
G1 | Well differentiated |
G2 | Moderately differentiated |
G3 | Poorly differentiated |
G4 | Undifferentiated—stage grouping as G3 squamous |
Location c | |
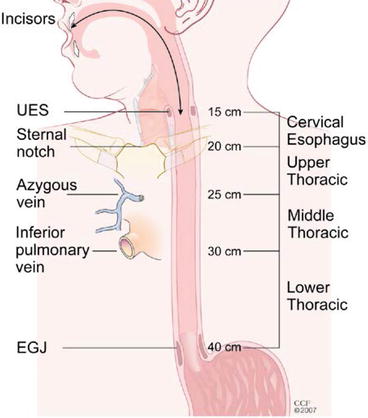
Upper or middle—cancers above lower border of inferior pulmonary vein | |
Lower—below inferior pulmonary vein | |
A regional lymph node has been redefined to include any paraesophageal lymph node extending from cervical nodes to celiac nodes (Table 6.1). Data analyses support convenient coarse groupings of the number of cancer-positive nodes (2–4). Regional lymph node (N) classification comprises N0 (no cancer-positive nodes), N1 (1 or 2), N2 (3–6), and N3 (7 or more). N classifications for cancers of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction are identical to stomach cancer N classifications.
The subclassifications M1a and M1b have been eliminated, as has MX (Table 6.1). Distant metastases are simply designated M0, no distant metastasis, and M1, distant metastasis.
7th Edition: Nonanatomic Cancer Characteristics
Nonanatomic classifications identified as important for stage grouping (Table 6.1) are histopathologic cell type, histologic grade, and tumor location (Fig. 6.2). The difference in survival between adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is best managed by separate stage groupings for stages I and II. Increasing histologic grade is associated with incrementally decreasing survival for early-stage cancers. For adenocarcinoma, distinguishing G1 and G2 (well and moderately differentiated) from G3 (poorly differentiated) is important for stage I and stage IIA cancers. For squamous cell carcinoma, distinguishing G1 from G2 and G3 is important for stage I and II cancers. Tumor location (upper and middle thoracic versus lower thoracic) is important for grouping T2–3N0M0 squamous cell cancers.