Chapter 66 Disorders of Coagulation in the Neonate
Table 66-1 Neonatal Versus Adult Hemostasis
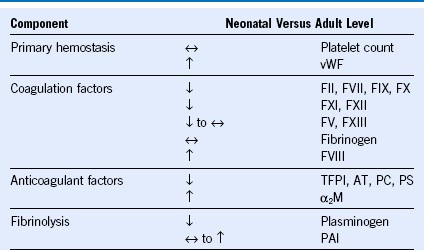
α2M, α2-Macroglobulin; AT, antithrombin; F, factor; PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PC, protein C; PS, protein S; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
Modified from Guzzetta NA, Miller BE: Principles of hemostasis in children: Models and maturation. Paediatr Anaesth 21:3, 2011.
Table 66-2 Reference Values (Ranges) for Common Coagulation Tests and Blood Coagulation Protein Levels by Age, Comparing Two Comprehensive Prospective Studies With Different Methodologies
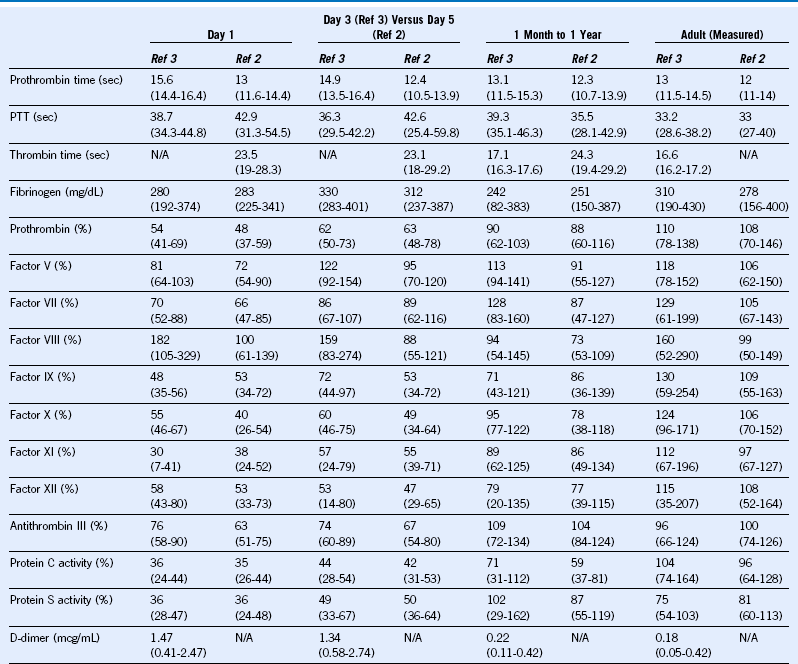
N/A, Not available; PTT, partial thromboplastin time.
Modified from Monagle P, Barnes C, Ignjatovic V, et al: Developmental haemostasis: Impact for clinical haemostasis laboratories. Thromb Haemost 95:362, 2006; and Andrew M, Paes B, Milner R, et al: Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant. Blood 70:165, 1987 (range inferred from published statistical documentation).
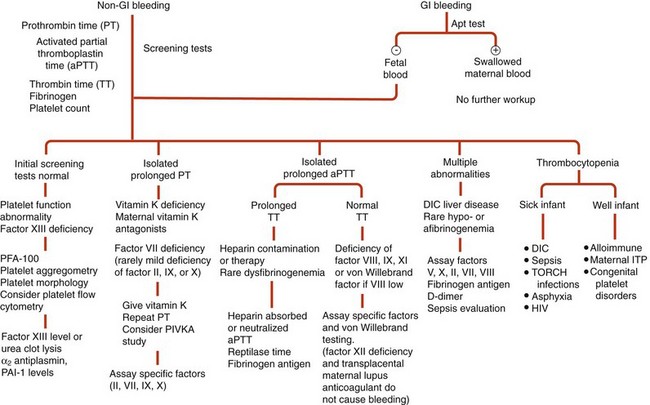
Figure 66-1 DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO THE BLEEDING NEONATE.
(Modified from Blanchette VS, Rand ML: Platelet disorders in newborn infants: diagnosis and management. Semin Perinatol 21:53, 1997.)
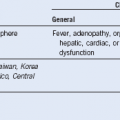
Table 66-3 Classification of Fetal and Neonatal Thrombocytopenia
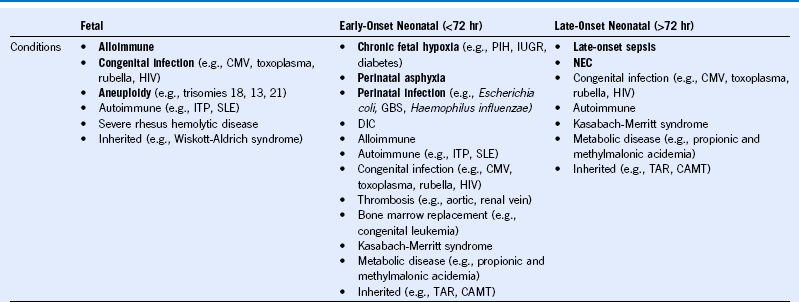
CAMT, Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia; CMV, cytomegalovirus; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; GBS, group B Streptococcus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ITP, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; PIH, pregnancy-induced hypertension; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus, TAR, thrombocytopenia with absent radii. The most frequently occurring conditions are in bold.
Modified from Roberts I, Stanworth S, Murray NA: Thrombocytopenia in the neonate. Blood Rev 22:173, 2008.
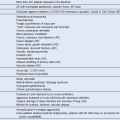
Table 66-4 Syndromic, Genetic, and Acquired Causes of Neonatal Thrombocytopenia
| INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM |
Methylmalonic acidemia (with acute acidosis) and cobalamin metabolic defects Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


|