Chapter 56 Diseases of Platelet Number
Immune Thrombocytopenia, Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia, and Posttransfusion Purpura
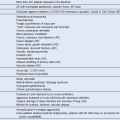
Table 56-1 Antibody-Mediated Thrombocytopenic Disorders Caused by Autoantibodies (Immune Thrombocytopenia), Alloantibodies (Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia) or Potentially Both (Posttransfusion Purpura)
GP, Glycoprotein; HPA, human platelet antigen; RBC, red blood cell.
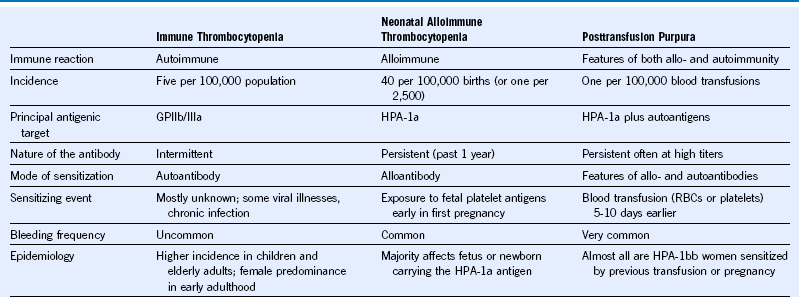
Table 56-2 Standardized Terminology and Definitions for Immune Thrombocytopenia Proposed by the International Working Group (Vicenza Consensus Conference) in 2009
| Terminology | Definition |
|---|---|
| ITP | Immune thrombocytopenia (rather than idiopathic or immune thrombocytopenic purpura) |
| Platelet threshold for ITP diagnosis | <100 × 109/L |
| Primary ITP | ITP with no associated cause (diagnosis of exclusion) |
| Secondary ITP | ITP in the setting of an underlying cause such as drugs, HIV, or SLE |
| Newly diagnosed ITP | Designation for patients at diagnosis (rather than “acute” ITP). |
| Persistent ITP | Sustained or recurrent thrombocytopenia lasting 3-12 months |
| Chronic ITP | Thrombocytopenia lasting >12 months |
| Complete response | Achievement of a platelet count of ≥100 × 109/L in the absence of bleeding |
| Response | Achievement of a platelet count of ≥30 × 109/L and at least a twofold increase from baseline in the absence of bleeding |
| Refractory ITP | Failure to achieve a response or relapse after splenectomy* and requirement for treatment(s) to minimize the risk of clinically significant bleeding. |
ITP, Immune thrombocytopenia; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
*Splenectomy failure may not be applicable in children.