Radiological finding
Fungus
Granulomas or solid enhancing lesions
Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Candida, Paracoccidioides
Abscesses
Aspergillus, Blastomyces (epidural), Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Candida, dematiaceous fungi, Pseudallescheria boydii (Scedosporium apiospermum)
Parenchymal/leptomeningeal nodules; pseudocysts
Cryptococcus
Hemorrhagic/infarcted lesions
Aspergillus
Meningeal enhancement
Blastomyces, Coccidioides (chronic granulomatous), Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Paracoccidioides, Aspergillus
Hydrocephalus
Cryptococcus, Coccidioides, Paracoccidioides
CNS Mass Lesions
Intracerebral masses are one of the more common findings in fungal brain infections. Predominantly, granulomas or solid-enhancing lesions are reported. In Aspergillus infections, these have sometimes been referred to as “aspergillomas.” Likewise, in patients with cryptococcal infections, the term “cryptococcoma” has been used. Cryptococcomas can be single or multiple punctate (i.e., miliary) hyperintense round lesions on T2-weighted images (T2WI) usually less than 3 mm in size [4, 5]. Intraparenchymal cryptococcomas show low signal intensity on T1-weighted images (T1WI) and high intensity on T2WI [1, 6, 7]. Granulomas are preferentially seen on the ependyma of the choroid plexus [1]. Immunocompetetent patients are more likely to present with cryptococcomas [1] and are more likely to demonstrate enhancement in an immunocompetent host, secondary to the ability to mount an immune response [1, 8]. Persistence of cryptococcomas over a prolonged period of time has been documented and found to be inconsistent with active disease [9]. Pseudocysts are also seen in cryptococcal infection, and are CSF-equivalent (low signal intensity on T1WI and high signal intensity on T2WI) that are predominately seen in the basal ganglia, thalami, midbrain, cerebellum, and periventricular matter (Fig. 6.1). Lesions in the basal ganglia and thalami strongly suggest cryptococcal infection [1, 8]. Single- or multiple-enhancing brain lesions have also been reported in Histoplasma, Candida, and Paracoccidioides infections.
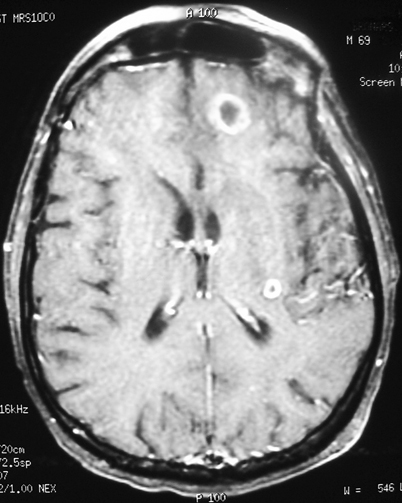

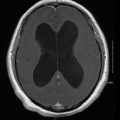
Fig. 6.1
Contrast-enhanced TI transaxial MRI image of the brain demonstrating low-signal-intensity lesions in the bilateral basal ganglia (left greater than right) associated with no significant enhancement, consistent with gelatinous pseudocysts of cryptococcosis. Also note mild meningeal enhancement. MRI magnetic resonance imaging
Abscesses are frequently found in fungal brain infections [10]. These lesions can be multiple, hypodense, and may exert little mass effect. They may or may not enhance [11] (Fig. 6.2). Although abscesses occur most commonly in the cerebral hemispheres, they have also been visualized in the cerebellum and brainstem [12]. Organisms reported to cause abscess formation include Aspergillus, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, and Candida. Candidal organisms tend to cause focal necrosis producing microabscesses [13, 14]. Less commonly, the dematiaceous moulds and Pseudallescheria boydii have been reported to cause one or multiple brain abscesses [15]. CNS abscesses outside the brain parenchyma are not common, although Blastomyces has been reported to cause epidural abscesses [16].
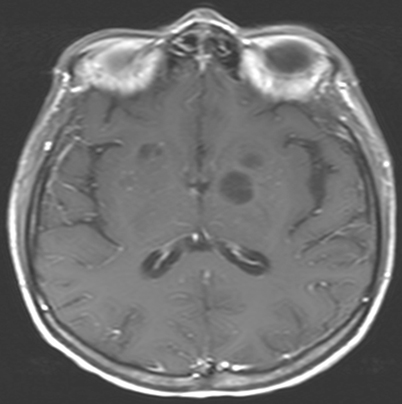

Fig. 6.2
Contrast-enhanced MRI showing multiple ring-enhancing brain abscesses in immunocompromised patient with disseminated aspergillosis. Note the lack of surrounding edema. MRI Magnetic resonance imaging. (Courtesy of Dr. D. R. Hospenthal)
Other intracerebral masses associated with fungal pathogens include edematous, hemorrhagic, or infarcted lesions such as those seen in Aspergillus infections [11]. The hemorrhagic lesion, usually a consequence of an area of infarction, is an early radiologic sign owing to the angioinvasive nature of certain fungi [10, 17]. A peripheral ring of isointensity or low signal intensity on T2WI relates to a dense population of fungal hyphae containing paramagnetic elements and small areas of hemorrhage [1, 18]. On cross-sectional imaging, these lesions show little or no enhancement or mass effect [11]. Similarly to pyogenic abscesses, fungal abscesses demonstrate decreased diffusion [1, 19].
Meningeal Enhancement
Diffuse enhancement of the meninges on MRI is another common radiological finding of fungal infection of the CNS, thought to be due to active inflammation (meningitis). Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Paracoccidioides, Cryptococcus, as well as Aspergillus have all been observed to produce meningeal enhancement. Coccidioides meningitis early in its course can cause focal or nodular enhancement in the basal cisterns which represent focal organization of the fungus surrounded by inflammation [20]. Meningeal involvement may be seen secondary to direct extension from fungal infections involving the paranasal sinuses, such as blastomycosis and mucormycosis [1, 21]. Leptomeningeal enhancement in coccidiomycosis has been known to extend into the spinal canal as well [1].
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is usually a communicating hydrocephalus and is a consequence of meningeal involvement (acutely due to meningeal exudate and later because of meningeal adhesions); it is an additional finding associated with infections by Cryptococcus, Coccidioides and Paracoccidioides [1, 8, 22] (Fig. 6.3). While CT is helpful in identifying dilated ventricles, MRI appears better in determining the patency of the aqueduct of Sylvius. Other nonspecific CNS radiological findings include early vascular enhancement and diffuse cerebral edema.
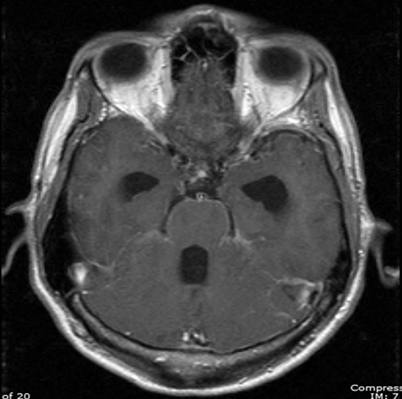

Fig. 6.3
MRI of brain revealing leptomeningeal enhancement and hydrocephalus in a patient with coccidioidomycosis. MRI Magnetic resonance imaging
Respiratory Tract Imaging
Sinus Imaging
CT is the imaging modality of choice in the evaluation of sinusitis [23]. It is certainly useful in evaluating the extent of fungal sinus disease [24]. The CT scan defines soft tissue invasion, necrosis, early bone erosion and cavernous sinus thrombosis [25]. When findings are suggestive of fungal sinusitis but the diagnosis is uncertain, MRI with or without gadolinium is the best radiological means to further evaluate the disease [23, 24, 26–28]. Central areas of hyperattenuation on CT correspond to hypointense signals on T1WI and signal void with T2WI MRI [29–31]. Early changes in major vessels and intracranial extension are also best seen on MRI, as is possible cavernous sinus thrombosis and embolic phenomena.
The paranasal sinuses are the most frequently affected, with the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses being the most commonly involved, followed by the sphenoid sinuses. Bilateral involvement is slightly more common than unilateral involvement [32]. Radiologic findings include opacification of multiple paranasal sinuses, with possible demonstration of sinus cavity expansion and erosion of the involved sinus wall. Bone destruction, erosion, and osteomyelitis have been reported in both the invasive and allergic form of Aspergillus sinusitis, as well as infections due to Mucorales (agents of mucormycosis) [26, 33, 34] (Fig. 6.4). A soft tissue mass or a sinus “aspergilloma” is reported as a major CT finding of the invasive granulomatous form of fungal sinusitis from Aspergillus. It can appear as sinus opacification associated with flocculent calcifications [35] (Fig. 6.5). The mass may either present as a homogenous density or have components of lower attenuation. Intraorbital and/or intracranial extension may occasionally occur [34, 36]. Air–fluid levels may be found though these are rare in either the invasive or noninvasive forms of fungal sinusitis [25]. Other findings include scattered intrasinus high-attenuation areas amid mucosal thickening on unenhanced CT scans.
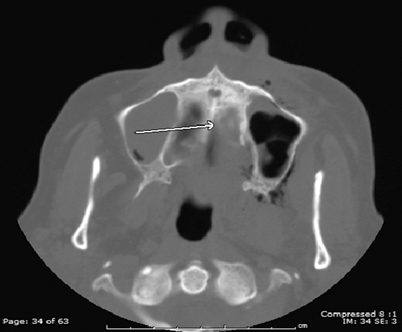
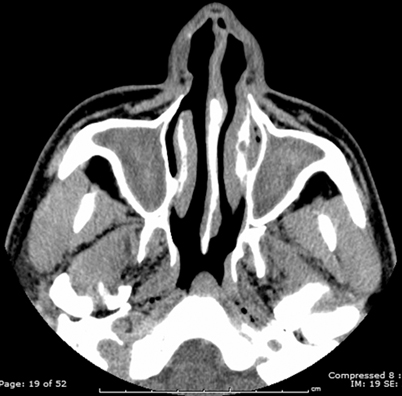

Fig. 6.4
Transaxial sinus CT of patient with mucormycosis demonstrating osteolysis of the hard palate (arrow) and left maxillary sinus mucosal thickening with surrounding soft tissue air. CT computed tomography

Fig. 6.5
Transaxial CT image through the sinuses demonstrating high-density opacification of the maxillary sinuses consistent with fungal sinusitis. CT computed tomography
Pulmonary Imaging
Definitive diagnosis of a pulmonary fungal infection by radiological imaging alone is not possible as other infectious organisms, and likewise, noninfectious pulmonary syndromes, can mimic radiological findings [37]. The most useful tools to assess lung infections include chest roentgenography and CT [38–40]. Chest radiography in the earlier stages of fungal disease may be normal, thus CT is the superior imaging modality as it has been shown to reveal abnormalities much earlier than chest X-rays. MRI, though reported to have been useful in the workup for Pneumocystis disease, has not been recognized as a significant diagnostic tool for the majority of pulmonary fungal infections [39]. Fungal infection of the lung presents generally with a wide variety of nonspecific radiographic patterns (Table 6.2).
Table 6.2
Abnormalities more commonly seen in pulmonary imaging of fungal infections
Radiological finding | Fungus |
|---|---|
Alveolar infiltrates | Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Candida, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Pneumocystis, Mucorales |
Interstitial infiltrates | Aspergillus, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Paracoccidioides, Penicillium, Pneumocystis |
Nodules | Aspergillus/Mucorales (halo sign), Candida, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Paracoccidioides, Pneumocystis |
Masses | Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Mucorales |
Cavitation | Aspergillus/Mucorales (air crescent sign), Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Paracoccidioides, Pneumocystis |
Abscesses | Candida, Pseudallescheria (Scedosporium), Mucorales |
Adenopathy | Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma |
Pleural effusion | Candida, Coccidioides, Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Pneumocystis |
Airspace and Interstitial Opacities
Nonspecific airspace opacities are the most frequent radiologic findings found with any pulmonary infectious process. Alveolar, “patchy,” “air-space,” or “mass-like” opacities have been identified in many fungal diseases, often progressing to areas of consolidation in the lung. Alveolar opacities have been noted in both endemic and opportunistic fungal infections. Airspace opacities have been noted as a frequent initial pattern in invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA). Opacities may be unifocal or multifocal and then progress to diffuse consolidation, though segmental areas of consolidation have been noted as one of the most common CT patterns in IPA [41, 42] (Fig. 6.6). Other disease processes resulting from Aspergillus infection such as bronchopneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, chronic necrotizing aspergillosis, and semi-invasive aspergillosis have also presented with alveolar opacities, often progressing to consolidation [38, 41, 43]. Patchy, ill-defined opacities progressing to more diffuse, bilateral airspace consolidation are common findings in blastomycosis (seen with a prevalence of 26–76 %) [21].
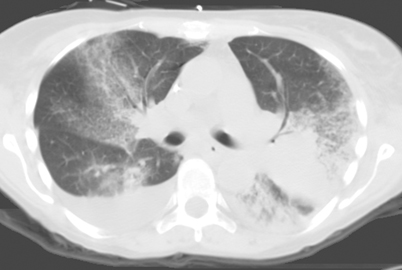

Fig. 6.6
Transaxial CT image through the chest of patient with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis demonstrating diffuse ground-glass opacity and bibasilar consolidation. CT computed tomography. (Courtesy of Dr. D. R. Hospenthal)
Interstitial, “reticular,” “reticulonodular,” and “linear” opacities have also been observed in many fungal infections. Diffuse bilateral interstitial opacities in a perihilar distribution [37, 44, 45] are the most common pattern seen in Pneumocystis infection (Fig. 6.7). Chest CT often reveals perihilar ground-glass opacity in a mosaic pattern with patchy distribution of affected lung interspersed with areas of normal lung, and noted thickening of the interlobular septa [38]. Interstitial opacities are also the most common pattern seen in cryptococcosis [46]. Ground-glass attenuation may be seen in AIDS patients with this infection. Aspergillus is able to affect the lung in a variety of ways, most of which can present in an interstitial pattern. These range from nodular opacities of invasive and semi-invasive disease, mimicking the radiologic findings of reactivation tuberculosis (TB), to coarse reticulation found in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis [38, 41]. A miliary or reticulonodular pattern is commonly seen in Blastomyces infection. Coccidioides pneumonia has been noted with diffuse reticulonodular lesions, especially in the setting of AIDS. Heavy exposure to Histoplasma can similarly present with diffuse reticulonodular opacities, such as those found in acute disseminated disease [47]. Other organisms commonly demonstrating interstitial opacities include Penicillium marneffei in the setting of HIV infection and paracoccidioidomycosis. In Paracoccidioides infection, the “reversed halo sign” of ground-glass opacity surrounded by denser airspace consolidation of crescent and ring shapes, has been reported in 10 % of patients [48, 49]. The lesions predominate in the mid to lower lungs, particularly in the periphery [49]. The reversed halo sign has also be described in zygomycosis and IPA, as well as histoplasmosis and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. In an immunosuppressed patient with reversed halo sign, invasive fungal infection should be considered until proven otherwise [50].
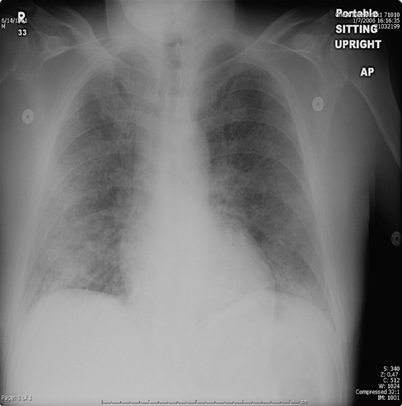

Fig. 6.7
Chest radiograph showing interstitial prominence and ground-glass opacity in a patient with Pneumocystis pneumonia
Distribution and location of opacities are also nonspecific. Opacities may be confined to a lobe or they may be diffuse as seen in disseminated disease. Hematogenous candidal spread can manifest as perivascular pulmonary opacities [51]. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis often presents with fleeting or migratory upper lobe opacities [41]. Phantom opacities which resolve in one segment then reappear in another lung field have also been seen in coccidioidomycosis [51].
The shape of infiltrates can sometimes aid in the diagnosis. Wedge-shaped opacities, reflecting invasion of blood vessels with subsequent lung infarction, are suggestive of invasive Aspergillus or Mucorales [52].
Uncommon pathogens which can cause infections presenting with nonspecific pulmonary opacities include Fusarium, Trichosporon, Malassezia furfur, and the phaeohyphomycetes [53].
Nodules
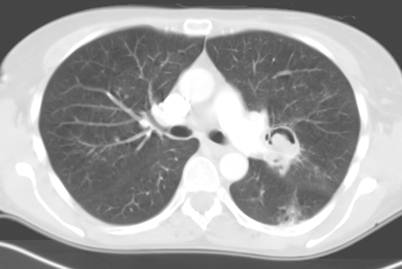
A well-defined nodule, either single or multiple, has been reported as a frequent initial radiographic pattern of IPA [54]. This nodular lesion may be surrounded by a rim of hemorrhage from thrombosis of fungi within pulmonary vessels [55]. Days to weeks after treatment of neutropenia, patients infected with Aspergillus may present with ground-glass attenuation around the nodules recognized as the “halo sign” [41, 56, 57] (Fig. 6.8). The “halo sign” is highly suggestive of angioinvasive aspergillosis, but is nonspecific. It is thought that the surrounding ground-glass opacity may be related to hemorrhage from the vascular involvement. Other infectious processes including the mucormycosis, Candida, herpes simplex virus, and cytomegalovirus infections, as well as noninfectious processes such as Wegener’s granulomatosis, Kaposi’s sarcoma, and hemorrhagic metastatic malignancies have also been presented with “halo signs” [58–60]. Nodular lesions may also be observed with branching linear opacities recognized as the “tree-in-bud” pattern seen in Aspergillus bronchiolitis [38]. “Tree-in-bud” pattern suggests a small airways process; a disease process which may be spread endobronchially. Similar lesions are found in endobronchial spread of mycobacterial, viral, and mycoplasma pneumonia. Nodules from Mucorales can be indistinguishable from IPA. The most common finding in pulmonary cryptococcosis are nodules, solitary or multiple, with or without cavitation, ranging from 5 to 20 mm in size with smooth or irregular margins, associated with other parenchymal findings such as masses and consolidation [61–63]. Miliary nodules are less commonly found in the AIDS patient with cryptococcosis [64]. Other organisms which can present with diffuse nonspecific nodular lesions include disseminated Candida and Histoplasma. Nodules can turn to “buck shot” calcifications in pulmonary histoplasmosis [52]. Approximately 5 % of those who develop Coccidioides pneumonia may develop solitary pulmonary nodules. Infections with Pneumocystis, Scedosporium, and Paracoccidioides have also demonstrated pulmonary nodules.
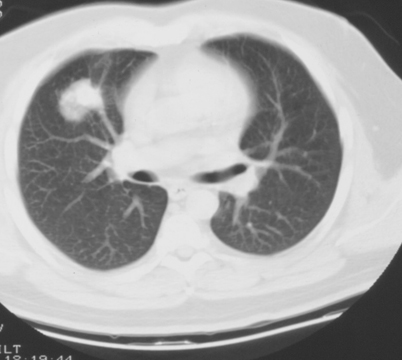

Fig. 6.8
Transaxial CT image of the chest with a right middle lobe nodule with surrounding ground-glass opacity (halo sign). This is consistent with invasive aspergillosis in an immunocompromised patient. CT computed tomography
Masses
Parenchymal masses may include aspergillomas, 3–5 cm mobile, round or oval masses, usually solitary, and seen in the upper lobe within a preexisting cavity (Fig. 6.9) or ectatic bronchus. These masses may be partially surrounded by a radiolucent crescent (Monod’s sign) of varying thickness [41, 65, 66]. This is the pattern most often seen in immunocompetent hosts [66]. Occasionally, coccidioidal infections may leave persistent chest X-ray lesions, most common being the coccidioidoma and the peripheral cavity [51]. The occasional “fungus ball” can form inside the cavity, rupture into the pleural space and produce an air–fluid level on an upright chest X-ray. Nonspecific mass lesions have been reported in infections with Cryptococcus, Pneumocystis, and the Mucorales. As fungal infections may present with nodules and masses which may have irregular or speculated borders, it is not uncommon to mistake them for malignancy. Fungal infections mimicking malignancy include coccidiomycosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, and cryptococcus. Some have advocated for use of fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)/positron emission tomography (PET) to differentiate between infection and malignancy; however, there is a high rate of false positives secondary to hypermetabolic nature of fungal infections. However, PET/CT does have a high negative predictive value [67].
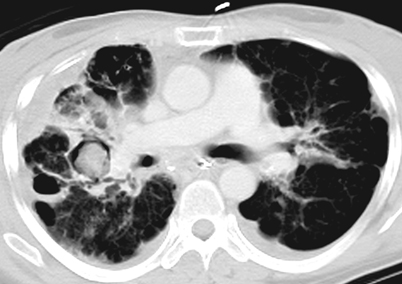

Fig. 6.9
Transaxial CT image of the chest showing bilateral upper lobe bronchiectasis, right pleural thickening, and right upper lobe ground-glass opacity and aspergilloma (soft tissue mass in preexisting cavity). CT computed tomography
Nonparenchymal masses may be seen in the hilar or mediastinal areas. Chronic pulmonary blastomycosis might present with a single large perihilar mass that often warrants a thoracotomy to rule out possible carcinoma. In fact, up to 31 % of patients present with paramediastinal or perihilar masses, which unlike histoplasmosis, rarely contain calcification [21]. Other findings of cryptococcosis in AIDS patients include mediastinal masses.
Cavitation
Virtually any nodular lesion has the potential to cavitate. Nodular lesions seen in Aspergillus and Mucorales infections may progress to cavitate to what is recognized as the “air crescent sign” [41, 57, 58, 68]. The air crescent sign represents cavitation of nodules caused by resorption of necrotic tissue by returning neutrophils [55] (Fig. 6.10). It is usually unilateral and frequently in the upper lobes [38]. Other nodules, single or multiple, can cavitate and then proceed to either diffuse pulmonary consolidation or abrupt development of large wedge-shaped pleural-based lesions mimicking bland infarction. Thin- or thick-walled cavities as well as cavitary infiltrates can appear in subacute invasive aspergillosis and chronic progressive coccidioidomycosis, both of which can mimic TB [52]. Approximately 5 % of those who develop Coccidioides pneumonia develop thin-walled solitary cavities, typically near the pleura (Fig. 6.11). A chronic form of Coccidioides pneumonia presents as a slowly progressive fibrocavitary process of biapical fibronodular lesions with retraction and cavitation. In pulmonary histoplasmosis, upper lobe cavities are common, except in those with HIV infection. Cavitary infiltrates have also been demonstrated in disseminated disease. Fibrotic apical infiltrates with cavitation have been reported in chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis which can be confused with TB infection or co-infection on chest X-ray [52]. Other fungal infections reported to cause cavitary disease include sporotrichosis and paracoccidioidomycosis; nodular areas are sometimes confluent, often in the lower lobes; cavitation occurs in one third of cases. Cavitation from blastomycosis is unusual and not as commonly seen as in mycobacterial or Histoplasma infections. Cryptococcal infection may present with cavitary masses or nodules, though this is uncommonly seen in the setting of AIDS infection. In cancer patients infected with Pneumocystis previously given prophylactic aerosolized pentamidine, upper lobe infiltrative disease suggestive of tuberculosis may be seen, but cavitary lesions are very uncommon.