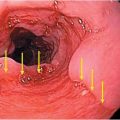
Figure 182.1 Cytomegalic inclusion disease. Arrows point to characteristic CMV-infected cells, which are large and contain intranuclear and ground-glass cytoplasmic inclusions. H&E staining.
Quantification of CMV DNA by PCR predicts or assesses CMV disease and prognosis. Having a measurable amount of CMV DNA in blood, CSF, BALF, vitreous fluid, or amniotic fluid is evidence of CMV replication. Latent CMV DNA levels in these fluids are below the lower limit of detection reported in clinical assays. In HSCT and SOT recipients, the level of CMV DNA in blood (DNAemia) guides use of anti-CMV therapy for pre-empting or treating CMV disease. While this test is useful in assessing response to anti-CMV therapy in transplant patients, the monitoring of CMV DNAemia has poor positive predictive value for progression or relapse of AIDS-associated retinitis. The COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan CMV test (Roche Molecular Diagnostics) is the first US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved assay that uses the World Health Organization (WHO) International Standard to quantify CMV DNA load in plasma. Importantly, CMV DNAemia might also be absent during tissue-invasive CMV disease. In AIDS-associated CMV retinitis, for example, CMV DNAemia is often absent. Risk of sequelae in congenitally infected newborns correlates with level of CMV DNAemia in the neonates. Detection of CMV DNA in amniotic fluid indicates congenital CMV infection.
Measurement of CMV pp65 antigen in blood leukocytes is an alternative approach for detecting and semi-quantifying level of active CMV infection, though it is less sensitive than nucleic acid amplification and is reduced by neutropenia. Assessment of CMV-specific T-cell response (i.e., interferon-γ [IFN-γ] release in response to CMV antigen) for predicting CMV reactivation and disease may have clinical utility in the transplant population.
Therapy
The FDA approved use of ganciclovir, valganciclovir, cidofovir, and foscarnet for specific CMV treatment indications. Table 182.1 summarizes the recommended dosing schedules for these agents and of their use in clinical practice. Fomivirsen, a therapeutic agent administered by intraocular injection, is an FDA-approved agent that is no longer manufactured, and oral ganciclovir is not available in the United States. Investigational anti-CMV drugs (e.g., cyclopropavir, brincidofovir, and letermovir) are in clinical development.
| Agent | Indications | Dosing regimen | Toxicities | Monitoring | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous | |||||
| Ganciclovir | Treatment of visceral or disseminated disease Prophylaxis or pre-emptive therapy in transplant recipients | Induction: 5 mg/kg q12h × 14–21 d Maintenance: 5 mg/kg qd (modify dose in renal failure) 5 mg/kg qd or BID (modify dose in renal failure) | Catheter-related complications, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure | Induction: CBC 2×/wk, Cr weekly Maintenance: CBC qwk, Cr q1–3wk | If ANC 500–750, consider SQ G-CSF If ANC ≤500 or platelets ≤25 K, hold ganciclovir Increased toxicity of zidovudine or imipenem; increased level of didanosine Causes infertility, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity in animals |
| Foscarnet | Treatment of visceral or disseminated disease | Induction: 90 mg/kg q12h (or 60 mg/kg q8h) × 14–21 d Maintenance: 90–120 mg/kg qd (modify dose in renal failure) Maximum dose is 120 mg/kg qd | Catheter-related complications, nephrotoxicity, paresthesias, cation chelation, genital ulcerations, nausea, marrow suppression | Induction: CBC, Cr, cations (K+, Mg2+, Ca2+), and phosphate 2–3× qwk Maintenance: Cr, cations, and phosphate qwk, CBC q2wk | If Cr >2.8, hold foscarnet until Cr ≤2.1 mg/dL Adjust dosage for reduced renal function Hydration reduces renal toxicity Caution if seizures |
| Cidofovir | Treatment of retinitis (limited experience with use for salvage therapy for CMV disease in other viscera) | Induction: 5 mg/kg/wk × 2; infuse over 1 h Maintenance: 5 mg/kg q2wk; infuse over 1 h (reduce dose to 3 mg/kg if Cr increase 0.3 mg/dL) | Nephrotoxicity with Fanconi syndrome, neutropenia, uveitis, ocular hypotony, probenecid rash Probenecid contraindicated in persons with severe sulfa allergy | Induction: Cr and UA every dose Maintenance: Same plus intraocular pressure qmo | 1–2 L saline hydration, with 1 L given before cidofovir infusion; probenecid, given 3 h before (2 g), at 3 h (1 g) and 8 h (1 g) after cidofovir infusion Caution if diabetes mellitus Do not use if Cr >1.5 mg/dL CrCl ≤55 mL/min, ≥100 mg/dL proteinuria, or receiving other nephrotoxic agents |
| Intraocular | |||||
| Ganciclovir implant | Treatment of retinitis | Surgical: Intraocular implantation via pars plana of (4.5 mg) implant; replacement q6–8mo Concomitant systemic therapy: see oral valganciclovir maintenance | Transient blurred vision, retinal detachment, hemorrhage, infection | Ophthalmologic follow-up | Requires addition of systemic therapy to reduce CMV disease risk in contralateral eye and other organs Implant releases 1 μg/h of ganciclovir Contraindicated if there is external eye infection and thrombocytopenia |
| Ganciclovir intravitreal injection | Treatment of retinitis | Induction: 200 μg to 2 mg in 0.1 mL twice per week for 2–3 wk Maintenance: once weekly | Less systemic side effects; procedural-related complications such as retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, endophthalmitis, and cataract | Ophthalmologic follow-up | Requires addition of systemic therapy to reduce CMV disease risk in contralateral eye and other organs Contraindicated in external eye infection and thrombocytopenia |
| Foscarnet intravitreal injection | Treatment of retinitis | 2.4 mg in 0.1 mL twice per week for 2–3 wk | Less systemic side effects; procedural-related complications such as retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, endophthalmitis, and cataract | Ophthalmologic follow-up | Requires addition of systemic therapy to reduce CMV disease risk in contralateral eye and other organs Contraindicated in external eye infection and thrombocytopenia |
| Oral | |||||
| Valganciclovir | Treatment of visceral or disseminated disease Prophylaxis or pre-emptive therapy in transplant | Induction: 900 mg BID × 14–21 d Maintenance: 900 mg qd (modify dose in renal failure 900 mg qd or BID, with food (modify dose in renal failure) | Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia | Induction: CBC 2×/wk, Cr weekly Maintenance: CBC qwk, Cr q1–3wk | If ANC 500–750, consider SQ G-CSF If ANC ≤500 or platelets ≤25 K, if Hg <8 mg/dL consider holding dose Increased toxicity of zidovudine or imipenem; increased level of didanosine Causes infertility, teratogenicity, and embryotoxicity in animals |
| Valacyclovir | Prophylaxis in solid organ transplant recipients | 2 g QID (modify dose in renal failure) | Hallucinations, confusion, Marrow toxicity | CBC and Cr q2wk | Less effective than ganciclovir; therefore, use limited to low-risk patients |
| CMV hyperimmunoglobulin | |||||