Chapter 49 Complications After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
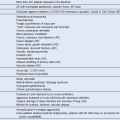
Table 49-1 Major Complications of Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Mo, Month; UCB, umbilical cord blood.
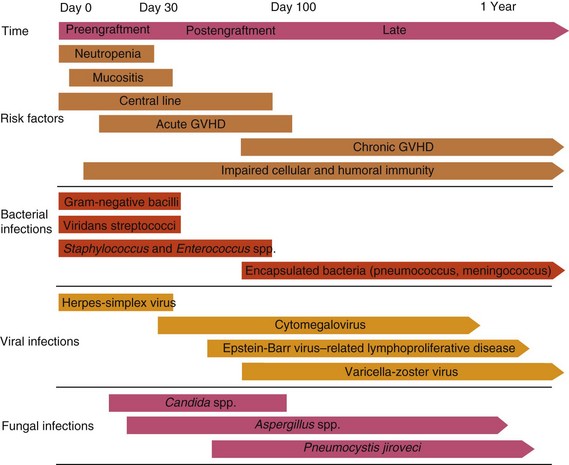
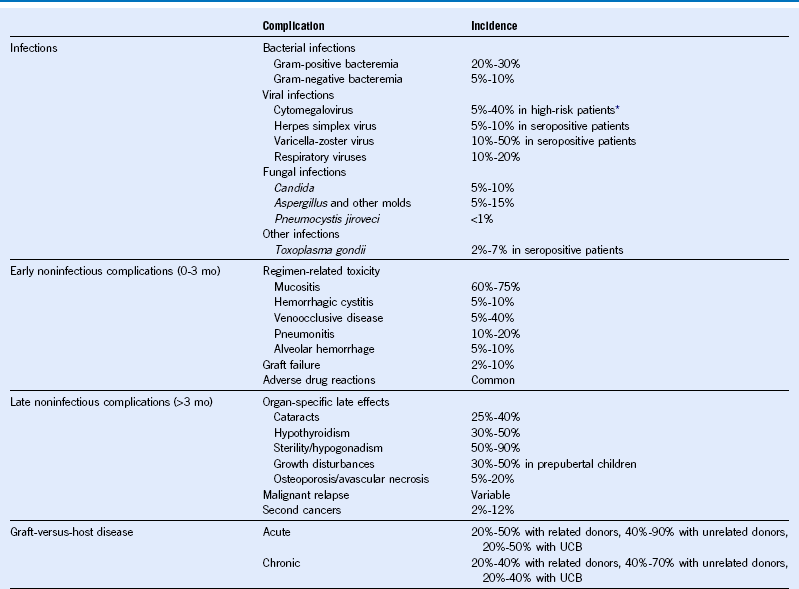
Table 49-2 Common Infections in Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients
CMV, Cytomegalovirus; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; GI, gastrointestinal; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; PTLD, posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder; TMP-SMX, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; wk, week.
* Includes Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis.
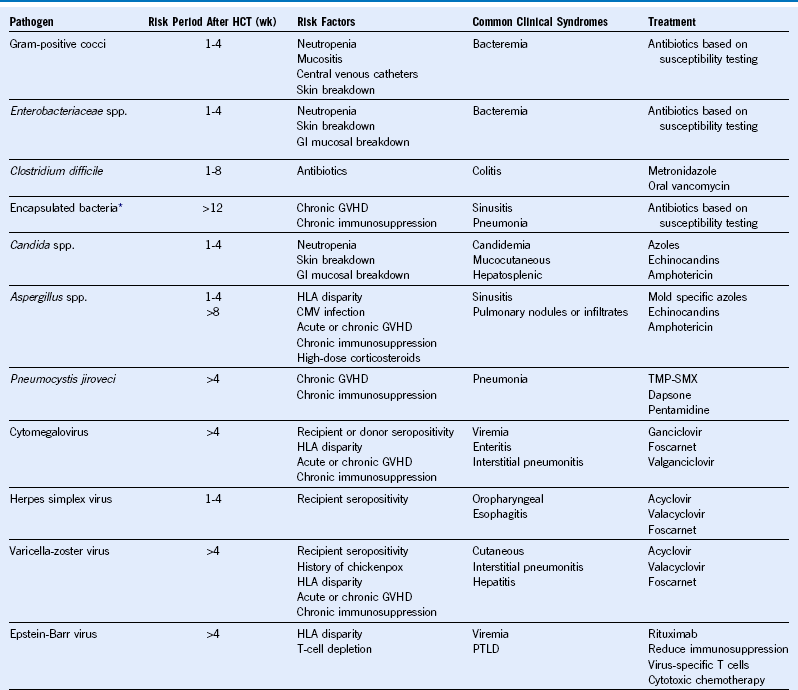
Table 49-3 Recommended Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Against Common Infections
| Pathogen | Preventing Early Disease (0-100 Days After HCT) | Preventing Late Disease (>100 Days After HCT) |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial infections | No specific recommendations* | Antibiotics (based on local resistance patterns) to prevent infections due to encapsulated bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis) in patients on chronic immunosuppression |
| Cytomegalovirus | Prophylaxis or preemptive treatment with ganciclovir or valganciclovir in high-risk patients† | Preemptive treatment with ganciclovir or valganciclovir in high-risk patients† |
| Herpes simplex virus | Acyclovir in seropositive patients | Acyclovir in patients with recurrent HSV infections |
| Yeast infections | Fluconazole | Fluconazole in patients on chronic immunosuppression |
| Mold infections | No specific recommendations‡ | No specific recommendations* |
| Pneumocystis jiroveci | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (preferred) or dapsone or pentamidine | Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (preferred) or dapsone or pentamidine in patients on chronic immunosuppression |
HCT, Hematopoietic cell transplantation; HSV, herpes simplex virus.
*Limited data exist favoring fluoroquinolones such as levofloxacin. No impact on infection-related mortality.
†Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-seropositive HCT recipients or CMV-seronegative recipients with a CMV-seropositive donor.
‡Limited data available. Prospective testing of voriconazole and posaconazole suggests possible benefit as prophylaxis. No impact on mold-related mortality.
Table 49-4 Recommended Vaccinations for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients
| Vaccine* | Time After HCT to Initiate Vaccine | No. of Doses† |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumococcal conjugate | 3-6 mo | 2-3‡ |
| DTaP§ | 6-12 mo | 3 |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate | 6-12 mo | 3 |
| Inactivated poliovirus | 6-12 mo | 3 |
| Recombinant hepatitis B | 6-12 mo | 3 |
| Inactivated influenza | 4-6 mo | 1-2 yearly‖ |
| Measles, mumps, and rubella virus (live) | 24 mo | 1-2¶ |
| Varicella-zoster | 24 mo | 1¶ |
DTaP, Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation.
*Vaccinations are deferred in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) until discontinuation of immunosuppression.
†A minimum of 1-month interval between doses is suggested.
‡Following the primary series of three pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) doses, a dose of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) to broaden the immune response might be given. For patients with chronic GVHD who are likely to respond poorly to PPSV23, a fourth dose of the PCV should be considered instead of PPSV23.
§DTaP is preferred; however, tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap) can be used if DTaP is not available.
‖For children younger than 9 years of age, two doses are recommended yearly between transplant and 9 years of age.
¶Not recommended less than 24 months post-HCT, in patients with active GVHD, and in patients on immune suppression. In children, two doses of measles, mumps, and rubella virus vaccine live are favored. Lower viral-dose vaccines (varicella vaccine live [Varivax], not zoster vaccine live [Zostavax]) may be preferred as potentially safer.
Approach to Prevention and Treatment of Cytomegalovirus Infection
Prevention
1. Seronegative recipient with seronegative donor (allogeneic and autologous): Transfuse only cytomegalovirus (CMV)-safe blood products. Leukocyte depletion by filtration and blood from CMV-seronegative donors are clinically equivalent alternatives.
2. Seronegative recipient with seropositive donor (allogeneic): Deliver only CMV-safe blood products (seronegative or leukocyte depleted), but administer chemoprophylaxis as well to prevent reactivation of donor-derived endogenous virus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree