as HOX13B, which are more common in patients with early-onset and familial disease, but this variant is rare (occurring in 0.1% of the population) and it is not associated with the lethal form of the disease.13 In contrast, men who carry BRCA2 mutations are more likely to develop early-onset prostate cancer, which is more likely to be aggressive and lethal.14
that reduces the size of the prostate and relieves voiding symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Hence, it was logical to test the hypothesis that finasteride, or other 5αRIs, could prevent prostate cancer. The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) randomly assigned 18,882 men, age 55 years or older, who had a normal digital rectal examination (DRE) and PSA, to receive finasteride or placebo over a 7-year period.32 Finasteride reduced by 25% the risk of detecting prostate cancer on biopsy (either end-of-study biopsy or one ordered during study “for cause”). Toxicity was low, but there were more high-grade cancers (Gleason score ≥7) in the finasteride group.33 Many subsequent analyses strongly suggested that the small increase in high-grade cancers was probably a detection artifact resulting from the 20% shrinkage of the prostate by the drug,34 and there were no differences in long-term survival in either arm.35
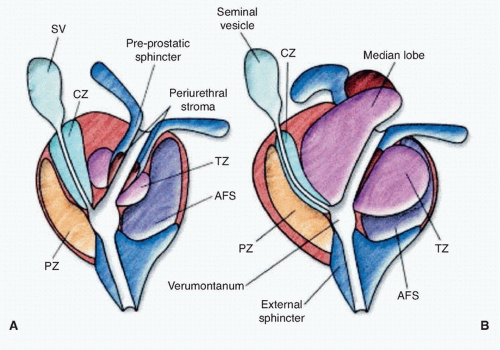
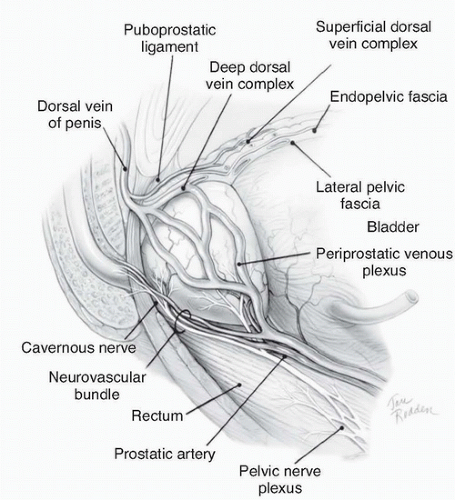 Figure 42.2 Lateral view of normal anatomy of the pelvis. (Redrawn from Ohori M, Scardino PT. Localized prostate cancer. Curr Probl Surg 2002;39: 833-957.) |
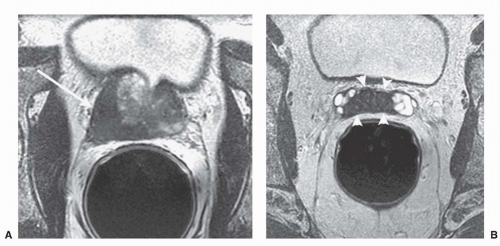
ducts, the transition zone surrounds the urethra, and the peripheral zone makes up the bulk of the normal gland. The posterior peripheral zone lies against the rectum and is the area that is palpable by DRE. These zonal boundaries are indistinct in the prostate of a normal postpubescent male, but as men age the transition zone enlarges from nonmalignant growth (BPH). The frequency of malignancy in the different zones is disproportionate to the glandular tissue present. Very few cancers originate in the central zone, and only 15% originate in the transition zone; most originate in the peripheral zone.
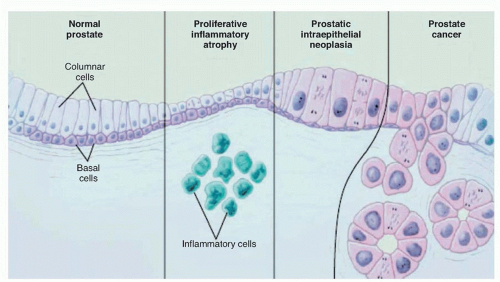
is actually transformed. Recognizable changes begin with proliferation of cells within glands, termed PIN, often found adjacent to areas of proliferative inflammatory atrophy.44 PIN is defined by the presence of cytologically atypical or dysplastic epithelial cells within architecturally benign-appearing acini, and is subdivided into low- and high-grade. Only high-grade PIN is considered a precursor for some invasive carcinomas.45,46 Because high-grade PIN develops preferentially in the peripheral zone where most cancers originate, it precedes the development of cancer by 10 years or more,47 and prostates with extensive high-grade PIN tend to have multifocal tumors. With subsequent loss of the basal cell layer surrounding prostatic glands and the development of anaplastic cellular morphology with nuclear pleomorphism and prominent nuclei, the tumor invades the basement membrane, spreads locally, and begins to metastasize. Not all lesions progress to invasive prostatic cancer during the lifetime of the host. Foci of small atypical acini that display some but not all features diagnostic of adenocarcinoma are referred to as atypical small acinar proliferation, a significant predictor of invasive cancer on subsequent prostate biopsy.48,49 Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, on the other hand, is not considered a malignant precursor lesion.
TABLE 42.1 Proportion of Prostate Cancer Deaths in Men Defined as at High Risk by Family History, Race, or Prostate-Specific Antigen in Middle Age | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
to detect changes in the cancer that indicate it has become more aggressive and therefore requires more definitive intervention(s).
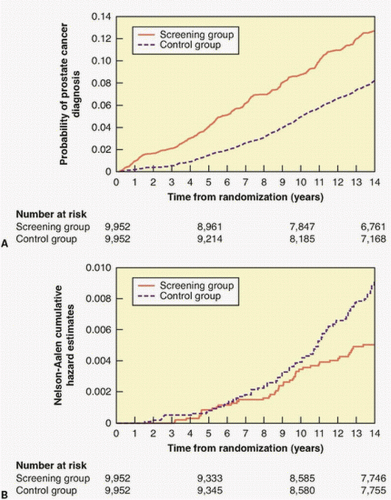
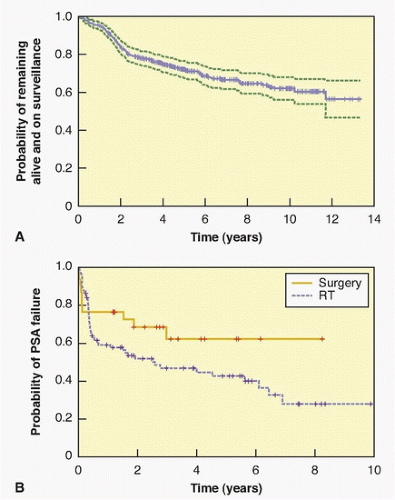
with opportunistic screening. At the most recent (13-year) followup, the cancer detection rate was slightly higher (RR = 1.12) in the screened arm, but there was no difference in the risk of dying of prostate cancer.
measured in ng/ml per cm3.103 As more PSA is released into the serum by cancer (3 ng/g) than by BPH (0.3 ng/g),104 PSAD can help to discriminate cancer from BPH. Because DRE correlates poorly with gland volume, an imaging study (transrectal ultrasound [TRUS] or magnetic resonance imaging [MRI]) is required to measure PSAD accurately, so PSAD is generally useful only in men who have had an ultrasound during a biopsy. PSAD has proved to be more valuable in prognosis than in detection, where it has been largely replaced by the free/total PSA ratio. The percent-free PSA in serum is higher in men with BPH than in men with cancer and can be used to discriminate cancer from BPH. Percent-free PSA values <10% are more indicative of cancer in men with values in the 4 to 10 ng/ml range.62,105
TABLE 42.2 Probability of a Positive Prostate Biopsy Based on the Results of the Digital Rectal Examination and Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Level | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
as routine. Today, more attention is being focused on targeted biopsies of suspicious lesions seen on MRI.124
For patients with PSA levels between 10 ng/ml and 50 ng/ml or >50 ng/ml, the probability of a positive bone scan is 10% and 50%, respectively.131 Bone scans are frequently used to assess the response to hormonal therapy and chemotherapy in men with metastatic disease.
TABLE 42.3 Comparison of the 1992, 1997, 2002, and 2010 American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer Tumor, Node, Metastasis Staging System | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(e.g., PSA 10 to 20 ng/ml) rather than continuous values, and assigning a patient to an increased risk group if any single variable is high (e.g., tumor stage cT2c, Gleason 8 to 10, or PSA >20 ng/ml), is inherently inaccurate. Predictions are much more accurate when nomograms are used to combine individual prognostic factors into a single prognostic score assigned to an individual patient. Consequent comparisons of the results of different treatments are also more accurate when patients are more precisely matched.
include prolonging life, relieving pain or other symptoms, and/or reducing toxicity relative to an established standard. It is also important to demonstrate that a new approach, whether it is a therapeutic procedure or a drug, is safe and well tolerated in an elderly population.
of patients were treated within 5 years, and 40% by 10 years (Fig. 42.8). Delayed intervention was associated with a relatively low rate of cancer control, raising concerns that treatment for men with a short PSADT (<2 years) was too late.
regions not sampled during an external iliac-only PLND.166 Some surgeons resect only the external iliac LN unless imaging suggests abnormal LN in other regions, whereas other surgeons routinely perform a more extensive dissection that includes the obturator, external iliac, and hypogastric areas.175 No sentinel LN has been identified in prostate cancer. The more extensive the PLND, the greater the number of LN removed, and the greater the number of positive nodes.166,168,171,172,173 Nevertheless, the total number of positive LN is one in 50% of patients, two in 30%, and three or more in only 20% of patients who have an extended LN dissection.166 A PLND that includes the external iliac, hypogastric, and obturator node packets is feasible in both open and minimally invasive RP, and carries no greater risk than a PLND limited to the external iliac nodes alone.
trial was conducted in the United States and randomly assigned 731 men with clinically localized prostate cancer to RP or observation. The mean age was 67, the median PSA level was 7.8 ng/ml, and approximately three-quarters of the men had a biopsy as a consequence of an elevated PSA; half had no palpable tumor (cT1c) and 70% had low-grade (Gleason ≤6) cancer on biopsy. With a median of 10 years of follow-up, 48% of the patients had died, but only 7% had died from prostate cancer. There were no differences in overall or cancer-specific mortality between the two arms of the trial. But there were clear indications that RP reduced the risk of dying of cancer in the subset of men who had aggressive cancers, including those whose PSA was >10.0 ng/ml and those with high-risk cancers.
TABLE 42.4 Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Surgical Approaches to Radical Prostatectomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 42.5 Freedom from Prostate-Specific Antigen Progression After Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
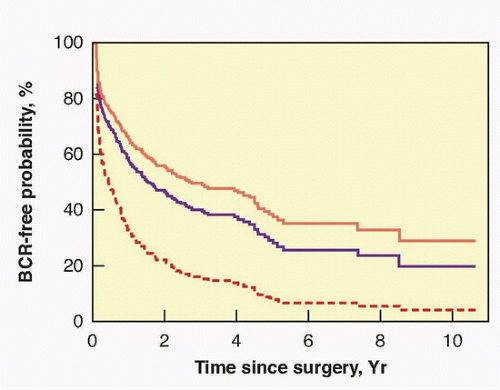
hormonal treatment. At 5 years 84% of patients, at 10 years 78%, and at 15 years 73% were free of progression (see Table 42.5).
TABLE 42.6 Actuarial 5-, 10-, and 15-Year (Prostate-Specific Antigen-Based) Nonprogression Rates (%) After Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer According to Preoperative and Pathologic Factors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
progression at 5 years and 88% to 96% remain free 10 years after RP.194 Focal penetration through the capsule into the periprostatic soft tissue alone, in the absence of SVI, results in a 73% 10-year nonprogression rate. Established (extensive) penetration through the prostatic capsule into the periprostatic soft tissue, in the absence of SVI, results in a 42% 10-year nonprogression rate. Even some patients with SVI (pT3cN0) can be cured with surgery, with 30% being free of disease recurrence at 10 years (see Table 42.6).
TABLE 42.7 Risk of Prostate Cancer-Specific Mortality at 10 and 15 Years After Radical Prostatectomya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree