Drug |
Main Therapeutic Uses |
Main Doses and Schedule |
Major Toxicities |
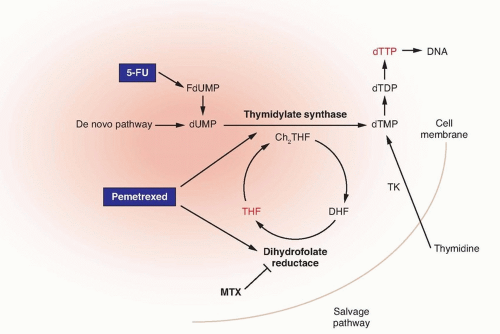
Methotrexate |
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Primary CNS lymphoma
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Breast cancer
Bladder cancer
Osteogenic sarcoma
Gestational trophoblastic cancer |
Low dose: 10-50 mg/m2 IV every 3-4 weeks
Low dose weekly: 25 mg/m2 IV weekly
Moderate dose: 100-500 m/m2 IV every 2-3 weeks
High dose: 1-12 gm/m2 IV over a 3- to 24-hour period every 1-3 weeks
Intrathecal (IT): 10-15 mg IT 2 times weekly until CSF is clear, then weekly dose for 2-6 weeks, followed by monthly dose |
Mucositis, diarrhea, myelosuppression, acute renal failure, transient elevations in serum transaminases and bilirubin, pneumonitis, neurologic toxicity |
Pemetrexed |
Mesothelioma
Non-small-cell lung cancer |
500 mg/m2 IV, every 3 weeks |
Myelosuppression, skin rash, mucositis, diarrhea, fatigue |
Pralatrexate |
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma |
30 mg/m2 IV, weekly for 6 weeks; cycles repeated every 7 weeks |
Myelosuppression, skin rash, mucositis, diarrhea, elevation of serum transaminases and bilirubin, mild nausea/vomiting |
5-Fluorouracil |
Breast cancer
Colorectal cancer
Anal cancer
Gastroesophageal cancer
Hepatocellular cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Head and neck cancer |
Bolus monthly schedule: 425-450 mg/m2 IV on days 1-5 every 28 days
Bolus weekly schedule: 500-600 mg/m2 IV every week for 6 weeks every 8 weeks
Infusion schedule: 2,400-3,000 mg/m2 IV over 46 hours every 2 weeks
120-hour infusion: 1,000 mg/m2/d IV on days 1-5 every 21-28 d
Protracted continuous infusion: 200-400 mg/m2/d IV |
Nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, mucositis, myelosuppression, neurotoxicity, coronary artery vasospasm, conjunctivitis |
Capecitabine |
Breast cancer
Colorectal cancer
Gastroesophageal cancer
Hepatocellular cancer
Pancreatic cancer |
Recommended dose for monotherapy is 1,250 mg/m2 PO bid for 2 weeks with 1 wk rest
May decrease dose of capecitabine to 850-1,000 mg/m2 bid on days 1-14 to reduce risk of toxicity without compromising efficacy
An alternative dosing schedule for monotherapy is 1,250-1,500 mg/m2 PO bid for 1 week on and 1 week off; this schedule appears to be well tolerated, with no compromise in clinical efficacy
Capecitabine should be used at lower doses (850-1,000 mg/m2 bid on days 1-14) when used in combination with other cytotoxic agents, such as oxaliplatin and lapatinib |
Diarrhea, hand-foot syndrome, myelosuppression, mucositis, nausea/vomiting, neurologic toxicity, coronary artery vasospasm |
Cytarabine |
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
Standard dose: 100 mg/m2/day IV on days 1-7 as a continuous IV infusion, in combination with an anthracycline as induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia
High-dose: 1.5-3.0 gm/m2 IV q 12 hours for 3 days as a high dose, intensification regimen for acute myelogenous leukemia
SC: 20 mg/m2 SC for 10 days per month for 6 months, associated with IFN-α for treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia
IT: 10-30 mg IT up to 3 times weekly in the treatment of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis secondary to leukemia or lymphoma. |
Nausea/vomiting, myelosuppression, cerebellar ataxia, lethargy, confusion, acute pancreatitis, drug infusion reaction, hand-foot syndrome
High-dose therapy: noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress and Streptococcus viridans pneumonia, conjunctivitis, and keratitis |
Gemcitabine |
Pancreatic cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer
Breast cancer
Bladder cancer
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Ovarian cancer
Soft tissue sarcoma |
Pancreatic cancer: 1,000 mg/m2 IV every week for 7 weeks with 1 week rest Treatment then continues weekly for 3 weeks followed by 1 week off
Bladder cancer: 1,000 mg/m2 IV on days 1, 8, and 15 every 28 days
Non-small-cell lung cancer: 1,000-1,200 mg/m2 IV on days 1 and 8 every 21 days |
Nausea/vomiting, myelosuppression, flulike syndrome, elevation of serum transaminases and bilirubin, pneumonitis, infusion reaction, mild proteinuria, and rarely, hemolytic-uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura |
6-Mercaptopurine |
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
Induction therapy: 2.5 mg/kg PO daily
Maintenance therapy: 1.5-2.5 mg/kg PO daily |
Myelosuppression, nausea/vomiting, mucositis and diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, immunosuppression |
6-Thioguanine |
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
Induction: 100 mg/m2 PO every 12 hours on days 1-5, usually in combination with cytarabine
Maintenance: 100 mg/m2 PO every 12 hours on days 1-5, every 4 weeks, usually in combination with other agents
Single agent: 1-3 mg/kg PO daily |
Myelosuppression, nausea/vomiting, mucositis and diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, immunosuppression |
Fludarabine |
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
25 mg/m2 IV on days 1-5 every 28 days For oral usage, the recommended dose is 40 mg/m2 PO on days 1-5 every 28 days |
Myelosuppression, immunosuppression with increased risk of opportunistic infections, mild nausea/vomiting, hypersensitivity reaction |
Cladribine |
Hairy cell leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
Usual dose is 0.09 mg/kg/d IV via continuous infusion for 7 days; one course is usually administered |
Myelosuppression, immunosuppression, mild nausea/vomiting, fever |
Clofarabine |
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
52 mg/m2 IV daily for 5 days every 2-6 weeks |
Myelosuppression nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, increased risk of opportunistic infections, renal toxicity |
CNS, central nervous system; IV, intravenously; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; PO, by mouth; bid, twice daily; SC, subcutaneously; IFN-α, interferon alpha. |