Drug |
Main Therapeutic Uses |
Clinical Pharmacology |
Major Toxicities |
Notes |
ALKYL SULFONATES |
Busulfan |
Bone marrow transplantation, especially in chronic myelogenous leukemia |
Bioavailability, 80%; protein bound, 33%; t1/2, 2.5 h |
Pulmonary fibrosis, hyperpigmentation thrombocytopenia, lowered blood platelet count and activity |
Oral or parenteral; high dose causes hepatic venoocclusive disease |
ETHYLENEIMINES/METHYLMELAMINES |
Altretamine |
|
Protein bound, 94%; t1/2, 5-10 h |
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and neurotoxicity |
Not widely used |
Thio TEPA |
Breast, ovarian, and bladder cancer; also bone marrow transplant |
t1/2, 2.5 h; urinary excretion at 24 h, 25%; substrate for CYP2B6 and CYP2C11 |
Myelosuppression |
Nadirs of leukopenia, occur 2 wk; thrombocytopenia, 3 wk (correlates with AUC of parent drug) |
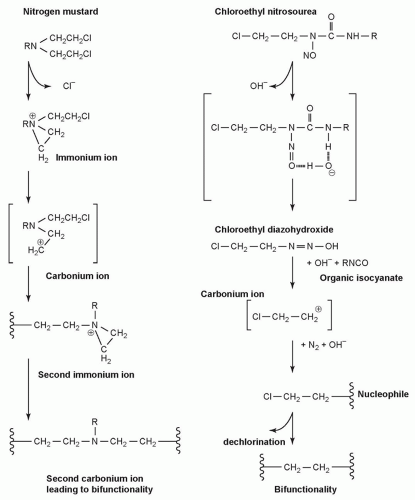
NITROGEN MUSTARDS |
Mechlorethamine |
Hodgkin lymphoma |
|
Nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression |
Precursor for other clinical mustards |
Melphalan (L-phenylalanine mustard) |
Multiple myeloma and ovarian cancer, and occasionally malignant melanoma |
Bioavailability 25%-90%; t1/2, 1.5 h; urinary excretion at 24 h, 13%; clearance, 9 mL/min/kg |
Nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression |
Causes less mucosal damage than others in class |
Chlorambucil |
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
t1/2, 1.5 h; urinary excretion at 24 h, 50% |
Myelosuppression, gastrointestinal distress, CNS, skin reactions, hepatotoxicity |
Oral |
Cyclophosphamide |
Variety of lymphomas, leukemias, and solid tumors |
Bioavailability, >75%; protein bound, >60%; t1/2, 3-12 h; urinary excretion at 24 h, <15% |
Nausea and vomiting, bone marrow suppression, diarrhea, darkening of the skin/nails, alopecia (hair loss), lethargy, hemorrhagic cystitis |
IV; primary excretion route is urine |
Ifosfamide |
Testicular, breast cancer; lymphoma (non-Hodgkin); soft tissue sarcoma; osteogenic sarcoma; lung, cervical, ovarian, bone cancer |
t1/2, 15 h; urinary excretion at 24 h, 15% |
As for cyclophosphamide |
Ifosfamide is often used in conjunction with mesna to avoid cystinuria |
NITROSOUREAS |
Carmustine |
Glioma, glioblastoma multiforme, medulloblastoma and astrocytoma, multiple myeloma and lymphoma (Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin) |
Bioavailability, 25%; protein bound, 80%; t1/2, 30 min |
Bone marrow and pulmonary toxicities are a function of lifetime cumulative dose |
Clinically, nitrosoureas do not share cross-resistance with nitrogen mustards in lymphoma treatment |
Streptozotocin |
Cancers of the islets of Langerhans |
t1/2, 35 min; excreted in the urine (15%), feces (<1%), and in the expired air |
Nausea and vomiting; nephrotoxicity can range from transient protein urea and azotemia to permanent tubular damage; can also cause aberrations of glucose metabolism |
A natural product from Streptomyces achromogenes |
TRIAZENES |
Dacarbazine |
Malignant melanoma and Hodgkin lymphoma |
t1/2, 5 h; protein bound, 5% hepatic metabolism |
Nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression |
IV or IM |
Temozolomide |
Glioblastoma; astrocytoma; metastatic melanoma |
Protein bound, 15%; t1/2, 1.8 h; clearance, 5.5 l/h/m2 |
Nausea, vomiting, myelosuppression |
Oral; derivative of imidazotetrazine, prodrug of dacarbazine; rapidly absorbed |
t1/2, half-life; TEPA, triethylenethiophosphoramide; AUC, area under curve; CNS, central nervous system; IV, intravenous; IM, intramuscular. |