Chapter 6 Acquired Disorders of Red Cell, White Cell, and Platelet Production
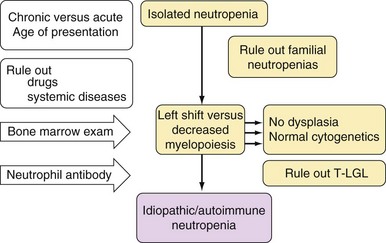
Table 6-2 Classification of Neutropenia
| Congenital | |
| Primary | Autoimmune neutropenia |
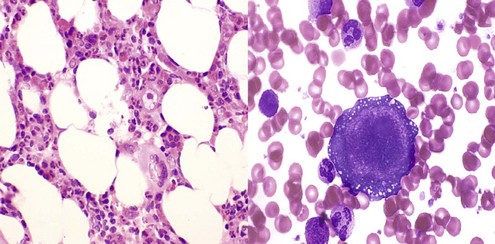
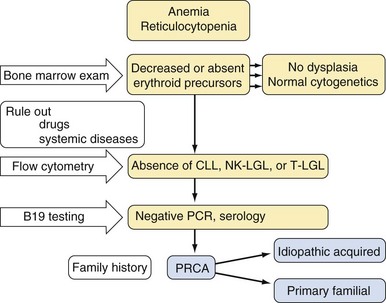
| Pure white cell aplasia | |
| Idiopathic | |
| Thymoma | |
| Hematologic malignancies (e.g., T-LGL leukemia) | |
| Infections/postinfectious | |
| Viral | |
| Measles,53 mumps, roseola,54,55 rubella,56 RSV, influenza57 | |
| Hepatitis A,58 B,58,59 and C60 | |
| CMV,61–63 EBV,64–66 HIV67,68 | |
| Parvovirus69–71 | |
| Bacterial | |
| Tuberculosis72,73 | |
| Brucellosis74–76 | |
| Tularemia77 | |
| Typhoid fever78 | |
| Rickettsial | |
| Rocky Mountain spotted fever79 | |
| Ehrlichiosis80,81 | |
| Fungal | |
| Histoplasmosis82,83 | |
| Parasitic | |
| Malaria,84 leishmaniasis85,86 | |
| Autoimmune conditions (e.g., SLE87,88, RA89) | |
| Drugs and chemicals | |
| Neutropenia associated with immunodeficiency90,91 | |
| Severe nutritional deficiencies92,93 | |
| Neutropenia due to increased margination | |
| Iatrogenic (e.g., hemodialysis94,95) |
CMV, Cytomegalovirus; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; RA, refractory anemia; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; T-LGL, T-cell large granular lymphocyte.
Table 6-3 Drugs Associated With Agranulocytosis

ACE, Angiotensin-converting enzyme; IAAAS, International Agranulocytosis and Aplastic Anemia Study.
Table 6-4 Immunophenotype and Laboratory Features of T-Cell Large Granular Lymphocyte Leukemia
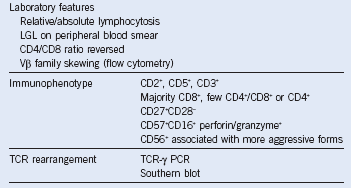
LGL, Large granular lymphocyte; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; TCR, T-cell receptor.