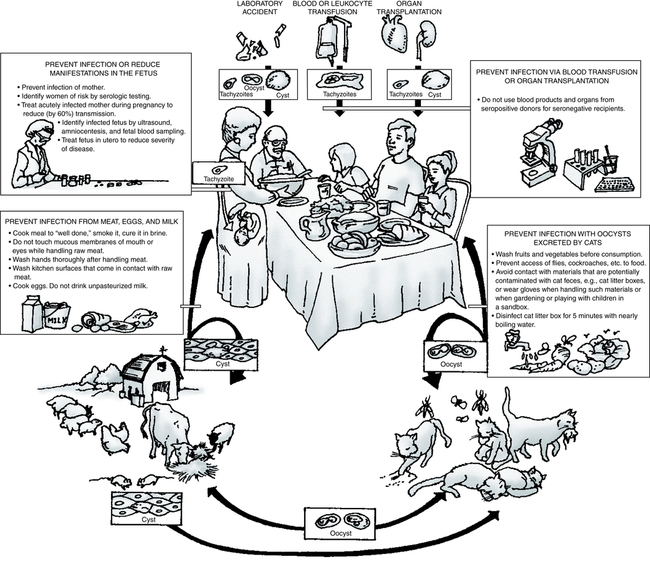
At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader should be able to: • Describe the etiology and epidemiology of toxoplasmosis. • Explain the signs and symptoms of acquired and congenital toxoplasmosis infection. • Discuss the immunologic manifestations and diagnostic evaluation of toxoplasmosis, including the quantitative determination of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii. • Analyze a case study related to toxoplasmosis. • Correctly answer case study related multiple choice questions. • Be prepared to participate in a discussion of critical thinking questions. • Describe the principle, interpretation, and limitations of the TORCH procedure. The definitive host is the house cat and other members of the Felidae family (Fig. 20-1). Domestic cats are a source of the disease because oocysts are often present in their feces. Accidental ingestion of oocysts by human beings and animals, including the cat, produces a proliferative infection in the body tissues. Fecal contamination of food or water, soiled hands, inadequately cooked or infected meat, and raw milk can be major sources of human infection. The risk for infection is higher in many developing and tropical countries, especially when people eat undercooked meat, drink untreated water, or are extensively exposed to soil. It is recommended that all pregnant women be tested for toxoplasmosis immunity. If a patient is susceptible, screening should be repeated during pregnancy and at delivery. Prevention of infection in pregnant women should be practiced to avert congenital toxoplasmosis (Box 20-1). To further prevent infection of the fetus, women at risk should be identified by serologic testing and pregnant women with primary infection should receive drug therapy. Toxoplasma can be harmful to individuals with suppressed immune systems. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS patients may result in death, even when treated (Fig. 20-2). Persons at risk can be identified by screening patients positive for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) for antibody to T. gondii.
Toxoplasmosis
Epidemiology
Transplacental Transmission
Signs and Symptoms
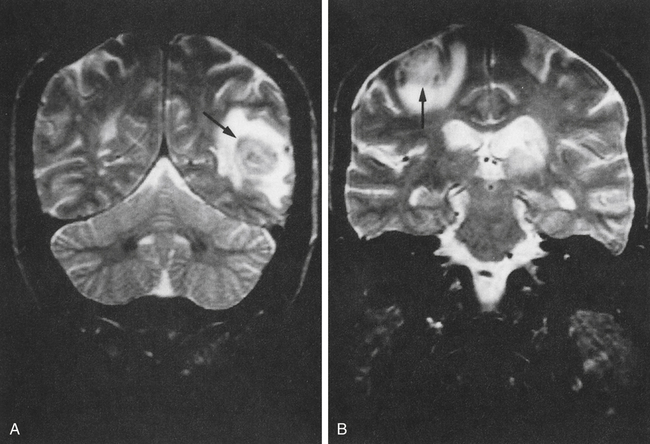
Shown are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scans of patients with AIDS. Arrows indicate areas infected with toxoplasmosis.
Oncohema Key
Fastest Oncology & Hematology Insight Engine