Most NF-κB inhibitors target the IKK complex, IκB proteins, or NF-κB transcription factors. The most promising classes of inhibitors include antioxidants, antiinflammatory compounds, natural compounds, statins, proteasome inhibitors, IKKβ inhibitors, biologics, gene therapy, and RNA interference. Targeting NF-κB is limited by intrinsic pathway complexity, cross-talk with other pathways, a lack of biomarkers, poor drug specificity, drug resistance, and difficulty with drug delivery. Future NF-κB targeting will be improved through better understanding of the pathway, more specific inhibitors, and multimodality therapies.
Key points
- •
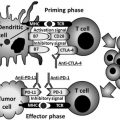
NF-κB comprises a family of transcription factors that stimulate tumor promotion and progression, chemoresistance, and radioresistance.
- •
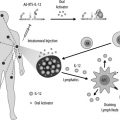
Hundreds of NF-κB inhibitors have been documented that target 3 main pathway sites of signaling integration: the IKK complex, IκBs and NF-κB transcription factors.
- •
Most NF-κB inhibitors such as synthetic IKKβ inhibitors, interfering RNAs, and gene therapy are not yet in clinical trial.
- •
Targeting NF-κB is limited by intrinsic pathway complexity, cross-talk with other pathways, lack of biomarkers, poor drug specificity, drug resistance, and drug delivery limitations.
- •
Future NF-κB targeting will be improved by better understanding of the pathway, more specific inhibitors, and multimodality therapies, which will reduce resistance and increase efficacy.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree