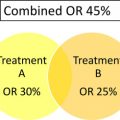
Well-differentiated gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors (GINETs) tend to be slow growing, but treatment of advanced disease remains a challenge. Somatostatin analogues (SSAs) are considered standard therapy for carcinoid syndrome. SSAs delay tumor progression in advanced well-differentiated gastroenteropancreatic NETs. Cytotoxic chemotherapy and interferon play a limited role in the treatment of nonpancreatic GINETs. There is no standard approach to treatment of patients with disease progression. Identification of systemic agents with antitumor activity in advanced disease remains an unmet medical need. Enrollment to clinical trials is encouraged; potential therapeutic targets include the vascular endothelial growth factor and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathways.
Key points
- •
Low- and intermediate-grade neuroendocrine tumors are an indolent group of malignancies that can cause symptoms from hormone hypersecretion and/or tumor mass.
- •
Somatostatin analogues are the mainstay of therapy for the control of symptoms associated with carcinoid syndrome.
- •
Systemic treatment of advanced disease remains a challenge; only somatostatin analogues have proven antitumor activity in advanced gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors.
- •
Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors represent an active area of research. Clinical trials with peptide receptor radionuclide therapy, inhibitors of the mammalian target of rapamycin and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways, immunotherapy, and other therapeutic approaches are ongoing.
- •
Improved understanding of the underlying molecular biology may lead to additional treatment advances.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree