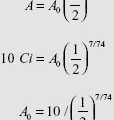10
SPECIALIZED TREATMENT
10.1 STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY
10.2 TOTAL BODY AND TOTAL SKIN IRRADIATION
10.1 STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY
What is the mechanical tolerance for the radiosurgery devices?
Question 2
What are the main characteristics of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
Question 3
What are the main features of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) plans?
Question 4
What types of radiation beams are used for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
Less than or equal to 1 mm.
Klein, EE, et al. Task Group 142 report: quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med Phys. 2009;36(9):4197–4212.
Answer 2
Stereotactic radiosurgery requires three-dimensional (3D) imaging, stereotactic targeting, steep dose gradients, and high accuracy of beam delivery.
Answer 3
High prescription doses per fraction and high degree of dose conformality.
Answer 4
Gamma-rays, megavoltage X-rays, and heavy-charged particles.
Which factors contribute to a sharp dose penumbra in linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)/stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) using circular cones and arcs?
Question 7
What is a typical quality assurance test used for linac-based radiosurgery?
Question 8
How does the Gamma Knife work?
The volume covered by the prescription isodose line divided by the volume of the target. The closer to one, the better the conformity is. This ratio should be ≤2. This index does not imply target coverage, which must be confirmed separately.
Answer 6
Multiple noncoplanar arcs, 4 to 6 MV beam energy, small collimator-to-tumor distance.
Answer 7
A Winston–Lutz test. A rod with a small ball bearing (bb) is attached to the treatment couch. The bb is placed at isocenter and images are taken with the linac beam at multiple gantry, collimator, and couch angles. The images are checked to ensure the bb remains in the center of the image, which ensures the isocenter is fixed with respect to motion of the gantry, collimator, and couch.
Lutz W, Winston KR, Maleki N. A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988;14(2):373–381.
Answer 8
The Gamma Knife contains 192 (Perfexion model) or 201 (B, C, and 4C models) cobalt-60 sources. The Perfexion is arranged in a cone shape with eight individual sectors and the B, C, and 4C models are arranged in hemispherical array and housed in a heavily shielded unit. Radiation is precisely collimated to deliver the high dose of radiation to the designated target(s) while sparing the surrounding tissues. Complex-shaped lesions can be treated by combining varying-sized collimators with selected sector/beam blocking and dose weighting using very sophisticated computer planning software.
Question 9
Which factors contribute to a sharp dose penumbra in Gamma Knife radiosurgery?
Question 10
What is the definition of the inhomogeneity index in radiosurgery?
Question 11
Which isotope is used in Gamma Knife radiosurgery and what is its average energy and half-life?
Question 12
What is a typical time between changing the cobalt-60 (Co-60) sources for Gamma Knife radiosurgery?
The very large number of noncoplanar isocentric beams (192 for Perfexion model, 201 for earlier models) and small collimator-to-target distance. The geometric penumbra is inversely proportional to source to collimator distance thus moving the collimator closer to the surface of the patient decreases the geometric penumbra.
Answer 10
The ratio of the maximum dose to the prescription dose of the target. This ratio should be ≤2.
Answer 11
Cobalt-60 (Co-60), average energy of 1.25 MeV (one gamma of 1.17 and one of 1.33 MeV). The half-life of Co-60 is 5.26 years.
Answer 12
About one half-life of cobalt-60 (Co-60), so between 5 and 6 years for a source exchange. The initial dose rate is around 3 Gy/min.
Question 14
Who must sign the Gamma Knife plan before treatment delivery?
Question 15
What agency regulates a Gamma Knife machine?
Question 16
What diseases and doses are treated in Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
1. Daily QA of the system
2. Attachment of the stereotactic frame to the patient’s head
3. Stereotactic imaging using high resolution MRI, CT, or angiogram as required
4. Localization of the images in the Gamma Knife frame of reference
5. Delineation of the target volumes
6. Dose planning and evaluation of the dose plans with all members of the radiosurgery team
7. Treatment delivery
8. Removal of the frame
Answer 14
The neurosurgeon, radiation oncologist, and a medical physicist; all of whom must be trained for Gamma Knife procedures.
Answer 15
Since the Gamma Knife uses cobalt-60, which is made in a nuclear reactor (by-product material), its use is regulated by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) or the State Departments of Health for the Agreement States.
Answer 16
| Tumor/Disorder | Dose (Gy) |
|---|---|
| Meningioma | 13–14 |
| Pituitary adenoma | Nonsecretory: 14–16 Secretory: 18–25 |
| Vestibular Schwannoma | 12–13 |
| Arteriovenous Malformation | 14–27 |
| Trigeminal Neuralgia | 80–90 (to 100% isodose line) |
| Brain Metastases | |
| 2 cm or less | 20–24 |
| 2.1–3 cm | 18 |
| 3.1–4 cm | 15 |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Gamma Knife versus linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
Question 18
What special equipment and imaging is required for linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)?
Question 19
When might fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) be preferable to single session radiosurgery?
| Type | Main Advantages | Main Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma Knife | High accuracy and precision; Less moving parts—easier QA; Used for about 50 years—much experience; Reliability of the machine—little down time | Brain only; Usually single session only; Can be used for multifractionation with Extend but no image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) capabilities; Needs to change sources in 5–6 years; Radiation safety precautions |
| Linac-based SRS | Single or fractionated treatments; image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) capabilities; Treatment of extracranial sites | With a heavy gantry, it is more difficult to maintain SRS required tolerance; Time needed for QA; Different manufacturers—more difficult to generalize collected data |
Answer 18
1. High definition multileaf collimators (MLC) (leaf width of 2.5 mm) or circular cones with diameters from 4 to 30 mm
2. Image-guidance systems like planar X-ray based, cone-beam CT (CBCT), optical, or ultrasound-based
3. Electronic portal image detectors (EPID) or films
Answer 19
1. For brain tumors with maximum dimension more than 4 cm
2. For lesions that are located very near to critical organs like optic apparatus, the full clinical dose to the target cannot be achieved without exceeding max safe dose of organ-at-risk (OAR).
3. For retreatments
Question 2
Why is total body irradiation (TBI) used and what is the typical dose range used?
Question 3
What is the most common prescription in total body irradiation (TBI)?
Question 4
Where is the dose prescription point usually located for anterior–posterior and posterior–anterior (AP/PA) fields with stationary photon beams for total body irradiation (TBI)?
TBI is a special radiotherapeutic technique, which delivers to a patient’s whole body a uniform dose to within ±10% of the prescribed dose.
Answer 2
It is used as a conditioning regimen for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. TBI can serve to eradicate any residual cancer and immunosuppress the host so that it cannot reject the allogeneic donor stem cells. 2 to 15 Gy is the typical dose range that is used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree