Richard G. Stefanacci, Jill L. Cantelmo
Quality Initiatives Aimed at Improving Medicare
Quality combined with cost is now a central component of a value-based system which is quite different from the priorities when Medicare was first introduced. When Medicare started, quality and costs were easily managed. In 1966, the year Medicare went into effect, expenses were limited by the scarce availability of, and demand for, services. The total number of Medicare beneficiaries was only around 10 million, with a life expectancy for a Medicare older adult at that time averaging about 4 years. Nearly a half-century later, the impact of the aging baby boomer generation, increasing life expectancy, rising health care costs, and an almost unlimited array of innovative and expensive services is challenging Medicare’s ability to provide health services in a financially sustainable manner to the 45 million subscribed beneficiaries, a number growing by 10,000 daily as baby boomers receive their Medicare cards.
As Medicare has expanded to become the single largest payer in the U.S. health care system, politically difficult restriction of benefits does not provide a valid approach for extending the viability of Medicare for future generations. Instead, a wealth of accumulating evidence has demonstrated the variations in care quality that exist across the nation, as well as numerous opportunities to increase the efficiencies of services provided. Although Medicare has a history of innovative program development, especially with regard to different payment approaches, it was not until 2010, when the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA; commonly referred to as the Affordable Care Act [ACA]) was signed into law—the largest piece of Medicare legislation since the Medicare Modernization Act (MMA) in 2003—that a centralized, nationwide effort was put forth, with various provisions to strengthen the integrity of the program through improvements in quality and efficiency.
Although the range of program initiatives specified as part of the ACA do not apply solely to Medicare, many of these have a direct impact on the health care providers that treat Medicare beneficiaries, Medicare beneficiaries themselves, and reimbursement of services that are covered by Medicare.
In broad terms, the main objectives of the ACA are to expand health care access, improve the quality and safety of care provided, and control costs through increased care efficiency.1 The various initiatives specified can be grouped into several main categories, according to their ultimate goals: quality and safety, including more extensive use of performance reporting on quality measures and disease prevention programs; health care delivery reform, including adjustments to hospital reimbursement for readmissions related to potentially preventable conditions and development of new models of reimbursement, such as bundled payments; and regulatory oversight and program integrity, including enhanced screening of providers and suppliers that wish to participate in Medicare and additional funding for antifraud activities.1
A rationale for the comprehensive mobilization of efforts to develop these programs and initiatives can be found in the wealth of evidence demonstrating important gaps in the current system2–5:
• Overuse of unnecessary care, increasing costs directly and incrementally when complications occur
• Enormous variations in the delivery of health care nationally, regionally, and locally
• Disparities in the quality of care provided, especially among certain races and ethnicities
• Limited use of screenings and programs to prevent complications of chronic diseases
This evidence indicates the need for new systemic improvements to the health care provided to Medicare beneficiaries. Although Medicare has been active in implementing programs for measuring and reporting quality of care, introducing innovative payment models, and ensuring that regulations are in place to prevent fraudulent activities, the comprehensive and enhanced approach to which these will be undertaken through the ACA will provide greater traction for the initiatives to have a meaningful impact on quality and efficiency and, ultimately, to preserve Medicare for the benefit of future generations. To this end, ACA created the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation, commonly referred to as the Innovation Center, for the purpose of testing “innovative payment and service delivery models to reduce program expenditures…while preserving or enhancing the quality of care” for those who receive Medicare, Medicaid, or Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) benefits.
Quality Measurement and Reporting
In the first 3 decades of Medicare, public data reporting rarely occurred. Even in the commercial world, data was limited to information available in HEDIS (Health Plan Employer Data and Information Set). Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) started collecting and using data through peer review organizations (PROs), now referred to as Quality Improvement Organizations (QIOs). QIOs systematically promoted improvements in quality measures tracked using voluntary, collaborative, and educational approaches.
Initially, reporting of quality measures was viewed as a way to promote self-improvement among providers through comparison with their peers. Over time the role has evolved, enabling patients to review performance data to select high-quality providers in a model of “consumer-directed health care.” Companies such as Healthgrades, a leading health care ratings organization, provide ratings and profiles of hospitals, nursing homes, and physicians to consumers, corporations, health plans, and hospitals. Consumer access to physician performance measures has helped move health care toward a more demand-type system, with patients selecting higher quality providers over lower quality providers, thus creating incentives for physicians to provide a higher quality of care.
Quality measurement and reporting in health care are recognized as crucial for identifying areas in need of improvement, monitoring progress, and providing consumers and purchasers with comparative information about health system performance. Spurred by rising costs and lagging quality improvement, large purchasers, health plans, and others began to implement approaches for rewarding high performance and creating incentives for quality improvement. An early example of these types of approaches was the pay-for-performance programs implemented by health plans with physicians. These programs provided important examples to assess the impact of quality reporting on the effectiveness and efficiency of a health care system and were the building blocks of subsequently developed programs, which have continued to evolve into the initiatives being implemented through the ACA.
Physicians
The vast majority of Medicare payments for physician services are made directly on the basis of a fee schedule, which has been in place since 1992. The Medicare fee schedule is intended to relate payments to the actual resources used in providing the health care services. In 2006, the Tax Relief and Health Care Act (TRHCA; P.L. 109-432) required the establishment of a physician quality reporting system, including an incentive payment for eligible professionals who satisfactorily reported data on quality measures for covered services furnished to Medicare beneficiaries during the second half of 2007. CMS named this program the Physician Quality Reporting Initiative (PQRI). In 2007, the Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children’s Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) Extension Act of 2007 (MMSEA) was enacted, authorizing CMS to make PQRI incentive payments for satisfactorily reporting quality measures data; eligible professionals would earn an incentive payment of 2% of the total allowed charges for Physician Fee Schedule (PFS)–covered professional services furnished during that same period. In 2008, the PQRI consisted of 119 quality measures, including two structural measures; one of these reported whether a professional had or used electronic health records (EHRs) and the other electronic prescribing. To test the effectiveness of this early pay-for-performance system, CMS implemented the Physician Group Practice demonstration, which provided rewards to large, multispecialty group practices for improving the quality of care and reducing the cost increases for their patients. Although results of this demonstration showed that a number of groups did not earn performance payments due to the inability to generate savings to the Medicare program, consistent improvements in quality on various measures were observed across participants.6 PQRI was developed as a pay-for-reporting program, designed to validate the utility of the clinical performance measures included, and serves as the foundation for future pay-for-performance programs.7
The PQRI was included as a key voluntary Medicare physician quality reporting initiative in the ACA, with penalties implemented in 2015 for all Medicare providers that failed to participate in the program. In 2011 the program underwent a name change, becoming the Physician Quality Reporting System (PQRS), with several other important changes to the program noted in response to requirements of the ACA, including the following8:
• Decrease in Medicare payment for practitioners not participating in 2015
• Update to the definition of a group practice from 200 to two or more practitioners
• Revision of measures available for reporting
• Establishment of an informal appeal process for practitioners
Participation in the PQRS allows Medicare physicians to assess the quality of care that they are providing to their patients, track their performance on various quality metrics, and enable comparison of performance compared with peers.9
Through 2014, eligible providers or group practices could receive an incentive payment of 0.5% of their total estimated Medicare Part B. PFS allowed charges for covered professional services furnished during that same reporting period for meeting the criteria for satisfactory submission of PQRS quality data, but unsatisfactory reporting would be subject to a 2% payment adjustment to their Medicare PFS amount for services provided in 2016.
Physicians and group practices must report their data through one of several methods to be eligible for incentive payments:
• Medicare Part B claims (physicians)
• Qualified PQRS registry (physicians and group practices)
• EHR using Certified EHR Technology (CEHRT; physicians and group practices)
• Web interface (group practices of 25+ only)
• CEHRT via a data submission vendor (physicians and group practices)
• Qualified clinical data registry (physicians)
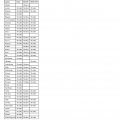
The program offers a selection of more than 200 separate quality measures that have been developed by provider associations, quality groups, and CMS and are typically applicable to patients based on combinations of Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, international classification of disease (ICDs) codes, and patient age at the time of their interaction with the provider (Table 128-1).7,9
TABLE 128-1
PQRS 2016 Measures
| Measure Title | Measure Description |
| Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control | Percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes who had hemoglobin A1c > 9.0% during the measurement period |
| Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C) Control (<100 mg/dL) | Percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes whose LDL-C was adequately controlled (<100 mg/dL) during the measurement period |
| Heart Failure (HF): Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of heart failure (HF) with a current or prior left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% who were prescribed ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy either within a 12-month period when seen in the outpatient setting OR at each hospital discharge |
| Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Antiplatelet Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) seen within a 12-month period who were prescribed aspirin or clopidogrel |
| Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Beta-Blocker Therapy—Prior Myocardial Infarction (MI) or Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVEF < 40%) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease seen within a 12-month period who also have prior MI OR a current or prior LVEF < 40% who were prescribed beta-blocker therapy |
| Heart Failure (HF): Beta-Blocker Therapy for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVSD) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of heart failure (HF) with a current or prior left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% who were prescribed beta-blocker therapy either within a 12-month period when seen in the outpatient setting OR at each hospital discharge |
| Anti-Depressant Medication Management | Percentage of patients 18 years of age and older who were diagnosed with major depression and treated with antidepressant medication, and who remained on antidepressant medication treatment. Two rates are reported |
| Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG): Optic Nerve Evaluation | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) who have an optic nerve head evaluation during one or more office visits within 12 months |
| Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Dilated Macular Examination | Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older with a diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) who had a dilated macular examination performed that included documentation of the presence or absence of macular thickening or hemorrhage AND the level of macular degeneration severity during one or more office visits within 12 months |
| Diabetic Retinopathy: Documentation of Presence or Absence of Macular Edema and Level of Severity of Retinopathy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy who had a dilated macular or fundus exam performed that included documentation of the level of severity of retinopathy and the presence or absence of macular edema during one or more office visits within 12 months |
| Diabetic Retinopathy: Communication With the Physician Managing Ongoing Diabetes Care | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy who had a dilated macular or fundus exam performed with documented communication to the physician who manages the ongoing care of the patient with diabetes mellitus regarding the findings of the macular or fundus exam at least once within 12 months |
| Perioperative Care: Selection of Prophylactic Antibiotic—First OR Second Generation Cephalosporin | Percentage of surgical patients aged 18 years and older undergoing procedures with the indications for a first OR second generation cephalosporin prophylactic antibiotic, who had an order for a first OR second generation cephalosporin for antimicrobial prophylaxis |
| Perioperative Care: Discontinuation of Prophylactic Parenteral Antibiotics (Non-Cardiac Procedures) | Percentage of non-cardiac surgical patients aged 18 years and older undergoing procedures with the indications for prophylactic parenteral antibiotics AND who received a prophylactic parenteral antibiotic, who have an order for discontinuation of prophylactic parenteral antibiotics within 24 hours of surgical end time |
| Perioperative Care: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis (When Indicated in ALL Patients) | Percentage of surgical patients aged 18 years and older undergoing procedures for which VTE prophylaxis is indicated in all patients, who had an order for low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH), low-dose unfractionated heparin (LDUH), adjusted-dose warfarin, fondaparinux or mechanical prophylaxis to be given within 24 hours prior to incision time or within 24 hours after surgery end time |
| Communication With the Physician or Other Clinician Managing Ongoing Care Post-Fracture for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older | Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older treated for a fracture with documentation of communication, between the physician treating the fracture and the physician or other clinician managing the patient’s ongoing care, that a fracture occurred and that the patient was or should be considered for osteoporosis treatment or testing. This measure is reported by the physician who treats the fracture and who therefore is held accountable for the communication |
| Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Discharged on Antithrombotic Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) with documented permanent, persistent, or paroxysmal atrial fibrillation who were prescribed an antithrombotic at discharge |
| Screening for Osteoporosis for Women Aged 65-85 Years of Age | Percentage of female patients aged 65-85 years of age who ever had a central dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) to check for osteoporosis |
| Osteoporosis: Pharmacologic Therapy for Men and Women Aged 50 Years and Older | Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older with a diagnosis of osteoporosis who were prescribed pharmacologic therapy within 12 months |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Use of Internal Mammary Artery (IMA) in Patients With Isolated CABG Surgery | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery who received an IMA graft |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Preoperative Beta-Blocker in Patients with Isolated CABG Surgery | Percentage of isolated coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgeries for patients aged 18 years and older who received a beta-blocker within 24 hours prior to surgical incision |
| Medication Reconciliation Post-Discharge | The percentage of discharges from any inpatient facility (e.g., hospital, skilled nursing facility, or rehabilitation facility) for patients 18 years and older of age seen within 30 days following discharge in the office by the physician, prescribing practitioner, registered nurse, or clinical pharmacist providing ongoing care for whom the discharge medication list was reconciled with the current medication list in the outpatient medical record. This measure is reported as three rates stratified by age group: |
| Care Plan | Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older who have an advance care plan or surrogate decision maker documented in the medical record or documentation in the medical record that an advance care plan was discussed but the patient did not wish or was not able to name a surrogate decision maker or provide an advance care plan. |
| Urinary Incontinence: Assessment of Presence or Absence of Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older | Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older who were assessed for the presence or absence of urinary incontinence within 12 months |
| Urinary Incontinence: Plan of Care for Urinary Incontinence in Women Aged 65 Years and Older | Percentage of female patients aged 65 years and older with a diagnosis of urinary incontinence with a documented plan of care for urinary incontinence at least once within 12 months |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Spirometry Evaluation | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of COPD who had spirometry results documented |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Inhaled Bronchodilator Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of COPD and who have an FEV1 less than 60% predicted and have symptoms who were prescribed an inhaled bronchodilator. |
| Asthma: Pharmacologic Therapy for Persistent Asthma—Ambulatory Care Setting | Percentage of patients aged 5 years and older with a diagnosis of persistent asthma who were prescribed long-term control medication |
| Emergency Medicine: 12-Lead Electrocardiogram (ECG) Performed for Non-Traumatic Chest Pain | Percentage of patients aged 40 years and older with an emergency department discharge diagnosis of non-traumatic chest pain who had a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) performed |
| Appropriate Treatment for Children With Upper Respiratory Infection (URI) | Percentage of children 3 months through 18 years of age who were diagnosed with upper respiratory infection (URI) and were not dispensed an antibiotic prescription on or three days after the episode |
| Appropriate Testing for Children With Pharyngitis | Percentage of children 3-18 years of age who were diagnosed with pharyngitis, ordered an antibiotic and received a group A streptococcus (strep) test for the episode |
| Hematology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Leukemia: Baseline Cytogenetic Testing Performed on Bone Marrow | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or an acute leukemia who had baseline cytogenetic testing performed on bone marrow |
| Hematology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS): Documentation of Iron Stores in Patients Receiving Erythropoietin Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) who are receiving erythropoietin therapy with documentation of iron stores within 60 days prior to initiating erythropoietin therapy |
| Hematology: Multiple Myeloma: Treatment With Bisphosphonates | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of multiple myeloma, not in remission, who were prescribed or received intravenous bisphosphonate therapy within the 12-month reporting period |
| Hematology: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Baseline Flow Cytometry | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older seen within a 12-month reporting period with a diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) made at any time during or prior to the reporting period who had baseline flow cytometry studies performed and documented in the chart |
| Breast Cancer: Hormonal Therapy for Stage IC-IIIC Estrogen Receptor/Progesterone Receptor (ER/PR) Positive Breast Cancer | Percentage of female patients aged 18 years and older with Stage IC through IIIC, ER or PR positive breast cancer who were prescribed tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor (AI) during the 12-month reporting period |
| Colon Cancer: Chemotherapy for AJCC Stage III Colon Cancer Patients | Percentage of patients aged 18 through 80 years with AJCC Stage III colon cancer who are referred for adjuvant chemotherapy, prescribed adjuvant chemotherapy, or have previously received adjuvant chemotherapy within the 12-month reporting period |
| Prevention of Central Venous Catheter (CVC)-Related Bloodstream Infections | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, who undergo central venous catheter (CVC) insertion for whom CVC was inserted with all elements of maximal sterile barrier technique, hand hygiene, skin preparation and, if ultrasound is used, sterile ultrasound techniques followed |
| Hepatitis C: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Testing Before Initiating Treatment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C who started antiviral treatment within the 12-month reporting period for whom quantitative hepatitis C virus (HCV) ribonucleic acid (RNA) testing was performed within 12 months prior to initiation of antiviral treatment |
| Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Genotype Testing Prior to Treatment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C who started antiviral treatment within the 12-month reporting period for whom hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype testing was performed within 12 months prior to initiation of antiviral treatment |
| Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Testing Between 4-12 Weeks After Initiation of Treatment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C who are receiving antiviral treatment for whom quantitative hepatitis C virus (HCV) ribonucleic acid (RNA) testing was performed between 4-12 weeks after the initiation of antiviral treatment |
| Acute Otitis Externa (AOE): Topical Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 2 years and older with a diagnosis of AOE who were prescribed topical preparations |
| Acute Otitis Externa (AOE): Systemic Antimicrobial Therapy—Avoidance of Inappropriate Use | Percentage of patients aged 2 years and older with a diagnosis of AOE who were not prescribed systemic antimicrobial therapy |
| Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting: pT Category (Primary Tumor) and pN Category (Regional Lymph Nodes) with Histologic Grade | Percentage of breast cancer resection pathology reports that include the pT category (primary tumor), the pN category (regional lymph nodes), and the histologic grade |
| Colorectal Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting: pT Category (Primary Tumor) and pN Category (Regional Lymph Nodes) with Histologic Grade | Percentage of colon and rectum cancer resection pathology reports that include the pT category (primary tumor), the pN category (regional lymph nodes) and the histologic grade |
| Prostate Cancer: Avoidance of Overuse of Bone Scan for Staging Low Risk Prostate Cancer Patients | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of prostate cancer at low risk of recurrence receiving interstitial prostate brachytherapy, OR external beam radiotherapy to the prostate, OR radical prostatectomy, OR cryotherapy who did not have a bone scan performed at any time since diagnosis of prostate cancer |
| Prostate Cancer: Adjuvant Hormonal Therapy for High Risk or Very High Risk Prostate Cancer | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of prostate cancer at high or very high risk of recurrence receiving external beam radiotherapy to the prostate who were prescribed adjuvant hormonal therapy (GnRH [gonadotropin-releasing hormone] agonist or antagonist) |
| Adult Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Suicide Risk Assessment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of major depressive disorder (MDD) with a suicide risk assessment completed during the visit in which a new diagnosis or recurrent episode was identified |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug (DMARD) Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older who were diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis and were prescribed, dispensed, or administered at least one ambulatory prescription for a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD). |
| Osteoarthritis (OA): Function and Pain Assessment | Percentage of patient visits for patients aged 21 years and older with a diagnosis of osteoarthritis (OA) with assessment for function and pain |
| Preventive Care and Screening: Influenza Immunization | Percentage of patients aged 6 months and older seen for a visit between October 1 and March 31 who received an influenza immunization OR who reported previous receipt of an influenza immunization. |
| Pneumonia Vaccination Status for Older Adults | Percentage of patients 65 years of age and older who have ever received a pneumococcal vaccine. |
| Breast Cancer Screening | Percentage of women 50 through 74 years of age who had a mammogram to screen for breast cancer within 27 months |
| Colorectal Cancer Screening | Percentage of patients 50-75 years of age who had appropriate screening for colorectal cancer |
| Antibiotic Treatment for Adults With Acute Bronchitis: Avoidance of Inappropriate Use | Percentage of adults 18 through 64 years of age with a diagnosis of acute bronchitis who were not prescribed or dispensed an antibiotic prescription on or 3 days after the episode |
| Diabetes: Eye Exam | Percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes who had a retinal or dilated eye exam by an eye care professional during the measurement period or a negative retinal or dilated eye exam (no evidence of retinopathy) in the 12 months prior to the measurement period |
| Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy—Diabetes or Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVEF < 40%) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease seen within a 12-month period who also have diabetes OR a current or prior left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) < 40% who were prescribed ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy |
| Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy | The percentage of patients 18-75 years of age with diabetes who had a nephropathy screening test or evidence of nephropathy during the measurement period |
| Adult Kidney Disease: Laboratory Testing (Lipid Profile) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (stage 3, 4, or 5, not receiving renal replacement therapy [RRT]) who had a fasting lipid profile performed at least once within a 12-month period |
| Adult Kidney Disease: Blood Pressure Management | Percentage of patient visits for those patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (stage 3, 4, or 5, not receiving renal replacement therapy [RRT]) with a blood pressure < 140/90 mm Hg OR ≥ 140/90 mmHg with a documented plan of care |
| Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Peripheral Neuropathy—Neurological Evaluation | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus who had a neurological examination of their lower extremities within 12 months |
| Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Ulcer Prevention—Evaluation of Footwear | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus who were evaluated for proper footwear and sizing |
| Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a BMI documented during the current encounter or during the previous six months AND with a BMI outside of normal parameters, a follow-up plan is documented during the encounter or during the previous six months of the current encounter Normal parameters: Age 65 years and older BMI ≥ 23 and < 30 kg/m2; age 18-64 years BMI ≥ 18.5 and < 25 kg/m2 |
| Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record | Percentage of visits for patients aged 18 years and older for which the eligible professional attests to documenting a list of current medications using all immediate resources available on the date of the encounter. This list must include ALL known prescriptions, over-the-counters, herbals, and vitamin/mineral/dietary (nutritional) supplements AND must contain the medications’ name, dosage, frequency and route of administration. |
| Pain Assessment and Follow-up | Percentage of visits for patients aged 18 years and older with documentation of a pain assessment using a standardized tool(s) on each visit AND documentation of a follow-up plan when pain is present |
| Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for Clinical Depression and Follow-Up Plan | Percentage of patients aged 12 years and older screened for clinical depression on the date of the encounter using an age-appropriate standardized depression screening tool AND if positive, a follow-up plan is documented on the date of the positive screen |
| Melanoma: Continuity of Care—Recall System | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a current diagnosis of melanoma or a history of melanoma whose information was entered, at least once within a 12-month period, into a recall system that includes: |
| Melanoma: Coordination of Care | Percentage of patient visits, regardless of age, with a new occurrence of melanoma who have a treatment plan documented in the chart that was communicated to the physician(s) providing continuing care within 1 month of diagnosis |
| Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Counseling on Antioxidant Supplement | Percentage of patients aged 50 years and older with a diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or their caregiver(s) who were counseled within 12 months on the benefits and/or risks of the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) formulation for preventing progression of AMD |
| Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG): Reduction of Intraocular Pressure (IOP) by 15% OR Documentation of a Plan of Care | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) whose glaucoma treatment has not failed (the most recent IOP was reduced by at least 15% from the pre-intervention level) OR if the most recent IOP was not reduced by at least 15% from the pre-intervention level, a plan of care was documented within 12 months |
| Oncology: Medical and Radiation—Pain Intensity Quantified | Percentage of patient visits, regardless of patient age, with a diagnosis of cancer currently receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy in which pain intensity is quantified |
| Oncology: Medical and Radiation—Plan of Care for Pain | Percentage of visits for patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of cancer currently receiving chemotherapy or radiation therapy who report having pain with a documented plan of care to address pain |
| Radiology: Exposure Time Reported for Procedures Using Fluoroscopy | Final reports for procedures using fluoroscopy that document radiation exposure indices, or exposure time and number of fluorographic images (if radiation exposure indices are not available) |
| Radiology: Inappropriate Use of “Probably Benign” Assessment Category in Mammography Screening | Percentage of final reports for screening mammograms that are classified as “probably benign” |
| Nuclear Medicine: Correlation with Existing Imaging Studies for All Patients Undergoing Bone Scintigraphy | Percentage of final reports for all patients, regardless of age, undergoing bone scintigraphy that include physician documentation of correlation with existing relevant imaging studies (e.g., x-ray, MRI, CT, etc.) that were performed |
| Falls: Risk Assessment | Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older with a history of falls who had a risk assessment for falls completed within 12 months |
| Falls: Plan of Care | Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older with a history of falls who had a plan of care for falls documented within 12 months |
| Oncology: Radiation Dose Limits to Normal Tissues | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of breast, rectal, pancreatic or lung cancer receiving 3D conformal radiation therapy who had documentation in medical record that radiation dose limits to normal tissues were established prior to the initiation of a course of 3D conformal radiation for a minimum of two tissues. |
| HIV/AIDS: Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia (PCP) Prophylaxis | Percentage of patients aged 6 weeks and older with a diagnosis of HIV/AIDS who were prescribed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis |
| Diabetes: Foot Exam | Percentage of patients aged 18-75 years of age with diabetes who had a foot exam during the measurement period |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Prolonged Intubation | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery who require postoperative intubation > 24 hours |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Deep Sternal Wound Infection Rate | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery who, within 30 days postoperatively, develop deep sternal wound infection involving muscle, bone, and/or mediastinum requiring operative intervention |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Stroke | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery who have a postoperative stroke (i.e., any confirmed neurological deficit of abrupt onset caused by a disturbance in blood supply to the brain) that did not resolve within 24 hours |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Postoperative Renal Failure | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery (without pre-existing renal failure) who develop postoperative renal failure or require dialysis |
| Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Surgical Re-Exploration | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing isolated CABG surgery who require a return to the operating room (OR) during the current hospitalization for mediastinal bleeding with or without tamponade, graft occlusion, valve dysfunction, or other cardiac reason |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Tuberculosis Screening | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who have documentation of a tuberculosis (TB) screening performed and results interpreted within 6 months prior to receiving a first course of therapy using a biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Periodic Assessment of Disease Activity | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who have an assessment and classification of disease activity within 12 months |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Functional Status Assessment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for whom a functional status assessment was performed at least once within 12 months |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Assessment and Classification of Disease Prognosis | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who have an assessment and classification of disease prognosis at least once within 12 months |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Glucocorticoid Management | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who have been assessed for glucocorticoid use and, for those on prolonged doses of prednisone ≥ 10 mg daily (or equivalent) with improvement or no change in disease activity, documentation of glucocorticoid management plan within 12 months |
| Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan | Percentage of patients aged 65 years and older with a documented elder maltreatment screen using an Elder Maltreatment Screening Tool on the date of encounter AND a documented follow-up plan on the date of the positive screen |
| Functional Outcome Assessment | Percentage of visits for patients aged 18 years and older with documentation of a current functional outcome assessment using a standardized functional outcome assessment tool on the date of encounter AND documentation of a care plan based on identified functional outcome deficiencies on the date of the identified deficiencies |
| Hepatitis C: Hepatitis A Vaccination | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C who have received at least one injection of hepatitis A vaccine, or who have documented immunity to hepatitis A |
| Colonoscopy Interval for Patients with a History of Adenomatous Polyps—Avoidance of Inappropriate Use | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older receiving a surveillance colonoscopy, with a history of a prior adenomatous polyp(s) in previous colonoscopy findings, who had an interval of 3 or more years since their last colonoscopy |
| Stroke and Stroke Rehabilitation: Thrombolytic Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke who arrive at the hospital within 2 hours of time last known well and for whom IV t-PA was initiated within 3 hours of time last known well |
| Cataracts: 20/40 or Better Visual Acuity within 90 Days Following Cataract Surgery | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of uncomplicated cataract who had cataract surgery and no significant ocular conditions impacting the visual outcome of surgery and had best-corrected visual acuity of 20/40 or better (distance or near) achieved within 90 days following the cataract surgery |
| Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of uncomplicated cataract who had cataract surgery and had any of a specified list of surgical procedures in the 30 days following cataract surgery which would indicate the occurrence of any of the following major complications: retained nuclear fragments, endophthalmitis, dislocated or wrong power IOL, retinal detachment, or wound dehiscence |
| Radiology: Stenosis Measurement in Carotid Imaging Reports | Percentage of final reports for carotid imaging studies (neck magnetic resonance angiography [MRA], neck computed tomography angiography [CTA], neck duplex ultrasound, carotid angiogram) performed that include direct or indirect reference to measurements of distal internal carotid diameter as the denominator for stenosis measurement |
| Ischemic Vascular Disease (IVD): Use of Aspirin or Another Antithrombotic | Percentage of patients 18 years of age and older who were discharged alive for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) or percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) in the 12 months prior to the measurement period, or who had an active diagnosis of ischemic vascular disease (IVD) during the measurement period and who had documentation of use of aspirin or another antithrombotic during the measurement period |
| HIV/AIDS: Sexually Transmitted Disease Screening for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis | Percentage of patients aged 13 years and older with a diagnosis of HIV/AIDS for whom chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis screenings were performed at least once since the diagnosis of HIV infection |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Knee Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the knee in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Hip Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the hip in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Lower Leg, Foot or Ankle Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the lower leg, foot or ankle in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Lumbar Spine Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the lumbar spine in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Shoulder Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the shoulder in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Elbow, Wrist or Hand Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the elbow, wrist or hand in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Neck, Cranium, Mandible, Thoracic Spine, Ribs, or Other General Orthopedic Impairments | Percentage of patients aged 18 or older that receive treatment for a functional deficit secondary to a diagnosis that affects the neck, cranium, mandible, thoracic spine, ribs, or other general orthopedic impairment in which the change in their risk-adjusted functional status is measured |
| Melanoma: Overutilization of Imaging Studies in Melanoma | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a current diagnosis of stage 0 through IIC melanoma or a history of melanoma of any stage, without signs or symptoms suggesting systemic spread, seen for an office visit during the one-year measurement period, for whom no diagnostic imaging studies were ordered |
| Radiology: Reminder System for Screening Mammograms | Percentage of patients undergoing a screening mammogram whose information is entered into a reminder system with a target due date for the next mammogram |
| Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older who were screened for tobacco use one or more times within 24 months AND who received cessation counseling intervention if identified as a tobacco user. |
| Controlling High Blood Pressure | Percentage of patients 18-85 years of age who had a diagnosis of hypertension and whose blood pressure was adequately controlled (<140/90 mm Hg) during the measurement period |
| Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly | Percentage of patients 66 years of age and older who were ordered high-risk medications. Two rates are reported. |
| Weight Assessment and Counseling for Nutrition and Physical Activity for Children and Adolescents | Percentage of patients 3-17 years of age who had an outpatient visit with a primary care physician (PCP) or obstetrician/gynecologist (OB/GYN) and who had evidence of the following during the measurement period. Three rates are reported. |
| Childhood Immunization Status | Percentage of children 2 years of age who had four diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis (DTaP); three polio (IPV), one measles, mumps and rubella (MMR); three H influenza type B (HiB); three hepatitis B (Hep B); one chickenpox (VZV); four pneumococcal conjugate (PCV); one hepatitis A (Hep A); two or three rotavirus (RV); and two influenza (flu) vaccines by their second birthday |
| Ischemic Vascular Disease (IVD): Complete Lipid Profile and LDL-C Control (< 100 mg/dL) | Percentage of patients 18 years of age and older who were discharged alive for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) or percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) in the 12 months prior to the measurement period, or who had an active diagnosis of ischemic vascular disease (IVD) during the measurement period, and who had each of the following during the measurement period: a complete lipid profile and LDL-C was adequately controlled (< 100 mg/dL) |
| Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Symptom Management | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) seen within a 12-month period with results of an evaluation of level of activity and an assessment of whether anginal symptoms are present or absent with appropriate management of anginal symptoms within a 12-month period |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation Patient Referral from an Outpatient Setting | Percentage of patients evaluated in an outpatient setting who within the previous 12 months have experienced an acute myocardial infarction (MI), coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), cardiac valve surgery, or cardiac transplantation, or who have chronic stable angina (CSA) and have not already participated in an early outpatient cardiac rehabilitation/secondary prevention (CR) program for the qualifying event/diagnosis who were referred to a CR program |
| Barrett’s Esophagus | Percentage of esophageal biopsy reports that document the presence of Barrett’s mucosa that also include a statement about dysplasia |
| Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting | Percentage of radical prostatectomy pathology reports that include the pT category, the pN category, the Gleason score and a statement about margin status |
| Quantitative Immunohistochemical (IHC) Evaluation of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing (HER2) for Breast Cancer Patients | This is a measure based on whether quantitative evaluation of Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing (HER2) by immunohistochemistry (IHC) uses the system recommended in the current ASCO/CAP Guidelines for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer |
| Ultrasound Determination of Pregnancy Location for Pregnant Patients with Abdominal Pain | Percentage of pregnant female patients aged 14 to 50 who present to the emergency department (ED) with a chief complaint of abdominal pain or vaginal bleeding who receive a transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasound to determine pregnancy location |
| Rh Immunoglobulin (Rhogam) for Rh-Negative Pregnant Women at Risk of Fetal Blood Exposure | Percentage of Rh-negative pregnant women aged 14-50 years at risk of fetal blood exposure who receive Rh-Immunoglobulin (Rhogam) in the emergency department (ED) |
| Statin Therapy at Discharge After Lower Extremity Bypass (LEB) | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older undergoing infra-inguinal lower extremity bypass who are prescribed a statin medication at discharge |
| Rate of Open Repair of Small or Moderate Non-Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) without Major Complications (Discharged to Home by Postoperative Day #7) | Percent of patients undergoing open repair of small or moderate sized non-ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms who do not experience a major complication (discharge to home no later than postoperative day #7) |
| Rate of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) of Small or Moderate Non-Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Without Major Complications (Discharged to Home by Postoperative Day #2) | Percent of patients undergoing endovascular repair of small or moderate non-ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) that do not experience a major complication (discharged to home no later than postoperative day #2) |
| Rate of Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) for Asymptomatic Patients, Without Major Complications (Discharged to Home by Postoperative Day #2) | Percent of asymptomatic patients undergoing CEA who are discharged to home no later than postoperative day #2 |
| Referral for Otologic Evaluation for Patients With Acute or Chronic Dizziness | Percentage of patients aged birth and older referred to a physician (preferably a physician specially trained in disorders of the ear) for an otologic evaluation subsequent to an audiologic evaluation after presenting with acute or chronic dizziness |
| Image Confirmation of Successful Excision of Image–Localized Breast Lesion | Image confirmation of lesion(s) targeted for image guided excisional biopsy or image guided partial mastectomy in patients with nonpalpable, image-detected breast lesion(s). Lesions may include: microcalcifications, mammographic or sonographic mass or architectural distortion, focal suspicious abnormalities on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or other breast imaging amenable to localization such as positron emission tomography (PET) mammography, or a biopsy marker demarcating site of confirmed pathology as established by previous core biopsy |
| Preoperative Diagnosis of Breast Cancer | The percent of patients undergoing breast cancer operations who obtained the diagnosis of breast cancer preoperatively by a minimally invasive biopsy method |
| Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Invasive Breast Cancer | The percentage of clinically node negative (clinical stage T1N0M0 or T2N0M0) breast cancer patients who undergo a sentinel lymph node (SLN) procedure |
| Biopsy Follow-up | Percentage of new patients whose biopsy results have been reviewed and communicated to the primary care/referring physician and patient by the performing physician |
| Epilepsy: Counseling for Women of Childbearing Potential With Epilepsy | All female patients of childbearing potential (12-44 years old) diagnosed with epilepsy who were counseled or referred for counseling for how epilepsy and its treatment may affect contraception OR pregnancy at least once a year |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive Care: Corticosteroid Sparing Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease who have been managed by corticosteroids greater than or equal to 10 mg/day of prednisone equivalents for 60 or greater consecutive days or a single prescription equating to 600 mg prednisone or greater for all fills that have been prescribed corticosteroid sparing therapy within the last 12 months |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive Care: Corticosteroid Related Iatrogenic Injury—Bone Loss Assessment | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with an inflammatory bowel disease encounter who were prescribed prednisone equivalents greater than or equal to 10 mg/day for 60 or greater consecutive days or a single prescription equating to 600 mg prednisone or greater for all fills and were documented for risk of bone loss once during the reporting year or the previous calendar year |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Testing for Latent Tuberculosis (TB) Before Initiating Anti-TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) for whom a tuberculosis (TB) screening was performed and results interpreted within 6 months prior to receiving a first course of anti-TNF (tumor necrosis factor) therapy |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Assessment of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Status Before Initiating Anti-TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) Therapy | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who had Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) status assessed and results interpreted within 1 year prior to receiving a first course of anti-TNF (tumor necrosis factor) therapy |
| Sleep Apnea: Assessment of Sleep Symptoms | Percentage of visits for patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea that includes documentation of an assessment of sleep symptoms, including presence or absence of snoring and daytime sleepiness |
| Sleep Apnea: Severity Assessment at Initial Diagnosis | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea who had an apnea hypopnea index (AHI) or a respiratory disturbance index (RDI) measured at the time of initial diagnosis |
| Sleep Apnea: Positive Airway Pressure Therapy Prescribed | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea who were prescribed positive airway pressure therapy |
| Sleep Apnea: Assessment of Adherence to Positive Airway Pressure Therapy | Percentage of visits for patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea who were prescribed positive airway pressure therapy who had documentation that adherence to positive airway pressure therapy was objectively measured |
| Dementia: Staging of Dementia | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia whose severity of dementia was classified as mild, moderate or severe at least once within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Cognitive Assessment | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia for whom an assessment of cognition is performed and the results reviewed at least once within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Functional Status Assessment | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia for whom an assessment of functional status is performed and the results reviewed at least once within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Neuropsychiatric Symptom Assessment | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia and for whom an assessment of neuropsychiatric symptoms is performed and results reviewed at least once in a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Management of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia who have one or more neuropsychiatric symptoms who received or were recommended to receive an intervention for neuropsychiatric symptoms within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Counseling Regarding Safety Concerns | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia or their caregiver(s) who were counseled or referred for counseling regarding safety concerns within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Counseling Regarding Risks of Driving | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia or their caregiver(s) who were counseled regarding the risks of driving and the alternatives to driving at least once within a 12-month period |
| Dementia: Caregiver Education and Support | Percentage of patients, regardless of age, with a diagnosis of dementia whose caregiver(s) were provided with education on dementia disease management and health behavior changes AND referred to additional sources for support within a 12-month period |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Annual Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis Review | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who had an annual assessment including a review of current medications (e.g., medications that can produce Parkinson-like signs or symptoms) and a review for the presence of atypical features (e.g., falls at presentation and early in the disease course, poor response to levodopa, symmetry at onset, rapid progression [to Hoehn and Yahr stage 3 in 3 years], lack of tremor or dysautonomia) at least annually |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Psychiatric Disorders or Disturbances Assessment | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were assessed for psychiatric disorders or disturbances (e.g., psychosis, depression, anxiety disorder, apathy, or impulse control disorder) at least annually |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Cognitive Impairment or Dysfunction Assessment | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were assessed for cognitive impairment or dysfunction at least annually |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Querying about Sleep Disturbances | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (or caregivers, as appropriate) who were queried about sleep disturbances at least annually |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Rehabilitative Therapy Options | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (or caregiver(s), as appropriate) who had rehabilitative therapy options (e.g., physical, occupational, or speech therapy) discussed at least annually |
| Parkinson’s Disease: Parkinson’s Disease Medical and Surgical Treatment Options Reviewed | All patients with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease (or caregiver(s), as appropriate) who had the Parkinson’s disease treatment options (e.g., non-pharmacological treatment, pharmacological treatment, or surgical treatment) reviewed at least once annually |
| Cataracts: Improvement in Patient’s Visual Function within 90 Days Following Cataract Surgery | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older in sample who had cataract surgery and had improvement in visual function achieved within 90 days following the cataract surgery, based on completing a pre-operative and post-operative visual function survey |
| Cataracts: Patient Satisfaction within 90 Days Following Cataract Surgery | Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older in sample who had cataract surgery and were satisfied with their care within 90 days following the cataract surgery, based on completion of the Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems Surgical Care Survey |
| Initiation and Engagement of Alcohol and Other Drug Dependence Treatment | Percentage of patients 13 years of age and older with a new episode of alcohol and other drug (AOD) dependence who received the following. Two rates are reported. Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|