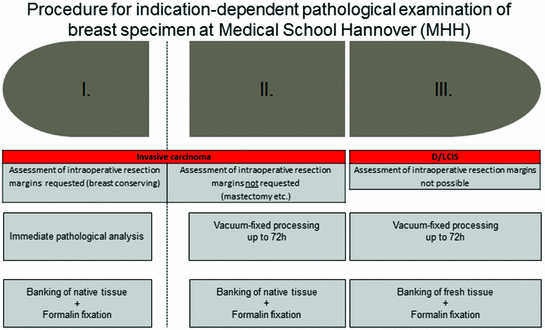
Indications and contraindications for a frozen section in mammapathology
Applicable
Non-applicable
Clarification of dignity in preoperative uncertain situations (e.g., multicentricity)
+
Clarification of representativeness (dense breast parenchyma, dislocation of wire mark)
+
Histological examination of the retromammillary region
+
Resection margins to invasive carcinoma
+
Sentinel lymph node (invasive carcinoma)
+
Clarification of dignity in core biopsies
+
Clarification of dignity in B3-lesions (core biopsy)
+
Resection margins to DCIS
+
Sentinel lymph node (DCIS) and invasive carcinoma in DCIS
+
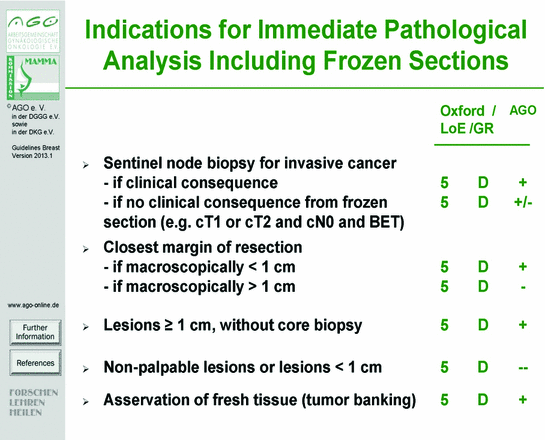
Fig. 1
Indications for immediate pathological analysis including frozen sections. Evidence-based recommendation of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynäko-logische Onkologie (AGO), differentiating between Oxford criteria “Level of Evidence” (LoE/GR) and AGO criteria “Grade of Recommendation” (++, +, +/-, −, and −−)
1 Investigation of Sentinel Lymph Node
Intraoperative investigation of sentinel lymph node has the advantage to circumvent a secondary surgery. In cases with histological sentinel lymph node metastases, a simultaneous axillary dissection can be performed by the surgeon.
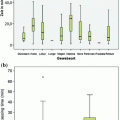
According to the literature, different analyses assigned frozen sections of sentinel lymph nodes a false negative rate of results [1–5]. Based on reduced specificity and sensitivity as well as limited possibility to supplementary immunohistochemical analysis, the S3-guidelines do not recommend a layered cut of sentinel lymph nodes in frozen sections [6, 7]. In contrast, a combined procedure of alternating frozen section and paraffin reprocessing guarantees a high specificity of nodal status assignment. Referring to this, a sentinel lymph node is laminated in slices of 0.2 cm vertical to its longitudinal axis and alternating slices are either paraffin embedded or frozen sectioned. From each slice at least 8 layered cut were produced (Fig. 2). In a series of 229 sentinel lymph nodes, a concordance in the technique of alternating slices of 97.9 % could be realized, in contrast to the so called OSNA-technique with a concordance of 90 % between lysate and frozen section as well as lysate- and paraffin-embedded tissue.
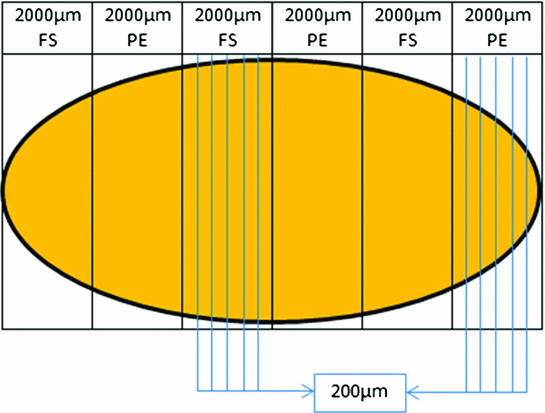

Fig. 2
Standardized investigation of sentinel lymph node. Vertical to the longitudinal axis of a lymph node alternating slices of frozen sectioned (FS) or paraffin-embedded (PE) tissue are sectioned, each of them measuring 2,000 µm. Of each slice 8–10 layer cuts are produced, each of them measuring 200 µm
2 Investigation of Breast Specimen
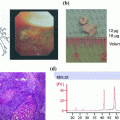
For prognostic molecular biologic analysis like ELISA-produced proof of uPA and PAI-I as well as for innovative diagnostic testing, asservation of unfixed native tumor tissue is recommended [8]. According to interdisciplinary guidelines, asservation of native tissue is restricted to institutions of pathology to warrant a standardized investigation of the tumor (Fig. 3).
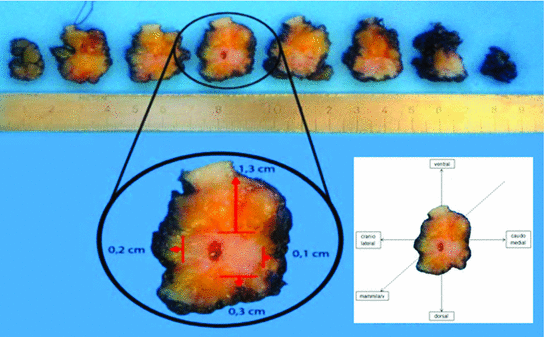

Fig. 3
Standardized investigation of breast specimen. A breast specimen with an invasive carcinoma is vacuum-fixed in the operation room and sent within 5–10 min to pathology. Surgeons receive immediate information by telephone about width of resection margins and tumor diameter. In case of narrow margins, surgeons can either demand histological verification by frozen section or they opt for further tissue removal from the resection cavity. Native breast specimens are inked and sectioned vertical to their longitudinal axis in slices from mammillary-far to mammillary-near and orientated ventral (12.00), caudomedial (3.00), dorsal (6.00) and craniolateral (9.00). Thickness of each slice is 0.3–0.5 cm. In the depicted example, the specimen is sectioned into eight slices. The tumor can be seen in the slices 3–6 with a maximal diameter of 1.6 cm and a minimal distance to the resection margins of 1.3 cm (ventral (12.00)), 0.1 cm (caudo medial (3.00)), 0.3 cm (dorsal (6.00)), 0.2 cm (cranio lateral (9.00)), and 0.8 cm (mammillary-far and -near)
3 Investigation of Native Breast Specimen—Immediate Pathological Analysis
According to the aforementioned Oxford criteria and guidelines of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft gynäkologische Onkologie (AGO)—an indication for immediate pathological analysis (including frozen sections) is given in cases with a lesion taller than 1 cm without a core biopsy, to clarify dignity in preoperative uncertain situations, the assessment of representativeness, the histological investigation of the retromammillary region, and the investigation of the surgical resection margins (Fig. 1 and Table 1).
Particularly, the investigation of resection margins by immediate pathological analysis helps to circumvent secondary surgery—which is declared with 15–50 % [9, 10]. Also therapeutic options like immediate reconstruction or intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) depend on reliable information of surgical resection margins [11, 12] and especially IORT needs—according to the Targit study [9, 13]—a residual tumor-free resection in a one-time intervention.
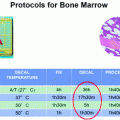
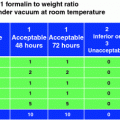
4 Investigation of Native Breast Specimen—Vacuum-Fixed Instead of Formalin-Fixed Tissue
According to the aforementioned Oxford criteria and guidelines of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft gynäkologische Onkologie (AGO)—no indication for immediate pathological analysis is given in cases with a non-palpable or less than 1 cm measured lesion, a clarification of dignity in corebiopsies and B3 lesions as well as an investigation of resection margins in DCIS (Fig. 1 and Table 1). Moreover, a recently published study showed a guideline controversy surgeon-dependent variety of practice patterns for handling surgical margins in breast conservation treatment [21]. In all these cases, formalin-fixed specimen have replaced native tissue specimen investigation and thus fresh tissue asservation was hampered in the last years.
In order to warrant fresh tissue asservation for biomarker analysis and tumor banking of all mammary resection specimens, the Medical School Hannover (MHH) uses in addition to immediate pathological investigation the possibility of vacuum-fixed processing of every native breast specimen for an indication-dependent pathological investigation algorithm (Fig. 4).