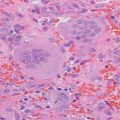
Fig. 11.1
Parathyroid subtraction imaging showing uptake in the pretracheal region
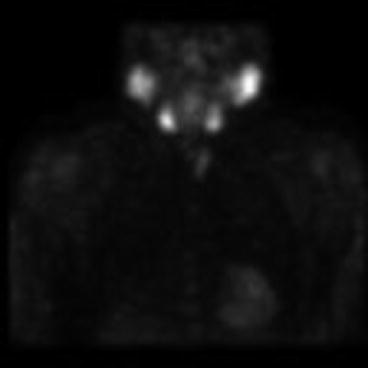
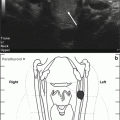
Fig. 11.2
SPECT sestamibi parathyroid imaging showing multiple pretracheal nodules
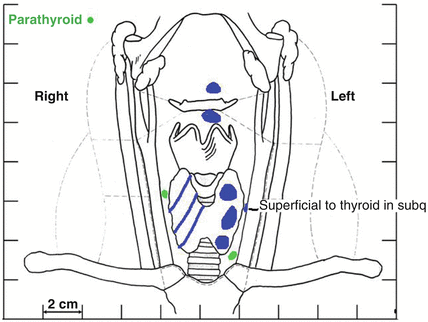
Fig. 11.3
Neck ultrasound demonstrating multiple subcutaneous nodules ranging in size from 0.5 to 1.2 cm, multiple nodules in the left thyroid (largest 1.8 cm), 9-mm nodule in the right thyroid bed, and a 1.3-cm nodule inferior to the left thyroid
She underwent cervical exploration with intraoperative PTH monitoring and intraoperative laryngeal nerve monitoring. Completion thyroidectomy confirmed multiple adenomatous nodules. The left inferior parathyroid gland was enlarged and excised, confirmed to be hypercellular and weighing 200 mg. The left superior parathyroid gland was grossly normal in size, and a biopsy confirmed parathyroid tissue. Adjacent to his was a small implant of hypercellular parathyroid tissue. There were six subcutaneous and intramuscular implants of hypercellular parathyroid tissue, several with atypia, excised. They ranged in size from 40 to 920 mg. A total of 1,540 mg of hypercellular parathyroid tissue was excised. Methylation-inhibited binding protein-1 (MIB-1) stain showed a moderate proliferative rate consistent with parathyromatosis. Intraoperative PTH levels normalized to 26 pg/ml.
Outcome
She remained normocalcemic for 8 months after her cervical re-exploration. At that time she had a mildly elevated calcium of 10.3 mg/dl. She was asymptomatic and followed conservatively for two more years. She developed progressive hypercalcemia and became symptomatic. At that time she underwent re-exploration at an outside institution with removal of three subcutaneous implants.
Clinical Pearls/Pitfalls
Care should be taken to minimize disruption of hypercellular parathyroid glands at the initial operation. If there is disruption of the parathyroid gland, then it is critical to remove any identifiable fragments of parathyroid tissue.
Parathyromatosis should be considered in the differential for patients with persistent or recurrent PHPT, particularly if they had a history of a large hypercellular parathyroid gland.
Multimodality imaging can be helpful for creating an intraoperative road map to identify the multiple sites of parathyromatosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree