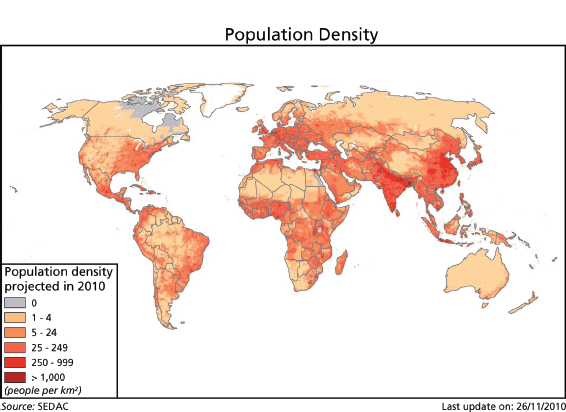
Definition: The maps opposite show the estimated number of people living within national boundaries in 2007 (top) and the number of people per square kilometer of land, the population density (bottom). National populations are generally estimated through intermittent national censuses, which attempt to enumerate all people alive and living in the country on a specified day. The United Nations recommends a census every 10 years. Between censuses, estimates of population are derived by extrapolation, using birth, death, and migration statistics and other survey data. The reliability of population estimates varies considerably, with, at one extreme, Iceland maintaining a full population register, while Somalia last conducted a national census in 1987. Population density at national level hides a great degree of internal heterogeneity, with populations more or less concentrated in cities.
Trends:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



