Rarer causes
These include inadequate alkaline phosphatase activity (hypophosphatasia), inhibition of mineralization by excess fluoride ingestion and abnormal bone matrix, for example in osteogenesis imperfecta or fibrogenesis imperfecta.
Clinical presentations
Osteomalacia may be asymptomatic and present radiologically as osteopenia. Clinically, patients with osteomalacia may present with diffuse bone pain and tenderness, fractures with little or no trauma (typically in the ribs, vertebrae and long bones) and proximal muscle weakness, which may be associated with a waddling gait.
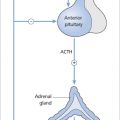
History and physical examination should look for symptoms and signs of the possible underlying cause.
Children with rickets may present with hypotonia, growth retardation and skeletal deformities.
The laying down of uncalcified osteoid at the metaphases leads to widening of the ends of the long bones. This may be seen as ‘rachitic rosary’ in the ribs (enlarged ends of the ribs resembling beads at the costochondral junction) and at the level of the ankle and the wrist. Other skeletal deformities include frontal bossing, pectus carinatum and bowing of the long bones.
Investigations
Radiographic findings
A spine X-ray
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree