miRNA
Up/downregulated by CDF
Reference(s)
Let-7s
Upregulated
miR-21
Downregulated
miR-101
Upregulated
Bao et al. (2012d)
miR-143
Upregulated
Ali et al. (2012)
miR-200
Upregulated
miR-210
Downregulated
Bao et al. (2012c)
miR-874
Upregulated
Ahmad et al. (2015b)
4 Cancer Stem Cells
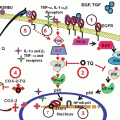
Cancer stem cells, due to their resistance to chemotherapy, are currently thought to be the cause of recurrence in all human cancers. In order to fight cancer, these cells need to be eradicated. In a study conducted in colon cancer model (Kanwar et al. 2011), treatment with CDF resulted in increased levels of apoptosis and decreased cellular growth. CDF, due to its ability to downregulate cancer stem cell properties and induce apoptosis, along with conventional chemotherapeutics could prove to be effective in reducing reemergence of tumor growth.
Under hypoxic conditions, maintenance of cancer stem cell functions occurs through hypoxia-inducing factor (HIF) signaling (Bao et al. 2012c). In mouse models, in response to hypoxia-induced aggressiveness, cancer stem cell signatures were decreased in pancreatic cancer after administration of CDF. Moreover, CDF downregulated the expression of CD44 and EpCAM cell surface markers, which are usually the hallmark of cancer stem cells (Kanwar et al. 2011). One way by which CDF targets cancer stem cells is that it inhibits the formation of pancreatospheres. Inhibiting the formation of pancreatospheres was consistent with gradual decrease in the expression of CD44 and EpCAM cancer stem cell markers, which led to the inhibition of tumor growth (Bao et al. 2011).
5 Sensitization of Drug-Resistant Cells by CDF
Drug resistance is a major clinical problem. CDF has been found to be effective against chemotherapy-resistant colorectal cancer cells which was in part due to the ability of CDF to restore the levels of tumor suppressor PTEN (Roy et al. 2013). PTEN is an anti-metastatic/tumor suppressing protein, responsible for self-renewal of stem cells. This restoration of tumor suppressor PTEN was accompanied by downregulation of miR-21 which is typically increased during drug resistance due to the inhibition in the expression of tumor suppressor genes.
CDF was also able to resensitize pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine (Ali et al. 2010). Gemcitabine resistance appears to be in part associated with downregulation of miR-200 and increased miR-21 levels in pancreatic cancer cells. Treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with CDF led to increased expression of miR-200 and decreased expression of miR-21 which resulted in the gemcitabine-resistant cells sensitive to gemcitabine, and thus induced cell growth inhibition and increased apoptotic cell death.
6 Epigenetics
EZH2 is an enzyme that is highly expressed in numerous human cancers. EZH2 uses epigenetic programming to regulate cancer stem cell function, proliferation of cancer cells, and cellular survival. Treating pancreatic cancer cells with CDF, we were able to decrease the expression of EZH2; CDF also seemed to increase the expression of tumor suppressor miRNAs, including let-7s, miR-101, and miR-200 which were previously discussed. By targeting the EZH2-miRNA regulatory circuit, CDF inhibited pancreatic tumor growth and decreased the aggressiveness of tumors (Bao et al. 2012d).
7 Conclusions and Perspectives
Curcumin has been widely investigated and has been proven to be a potent anti-inflammatory, as well as an antioxidant agent with antitumor activity in preclinical studies. However, it has been shown to possess low bioavailability, which has rendered it clinically unacceptable. The bioavailability concerns led us to synthesize CDF among many other analogues that we had synthesized. We were able to demonstrate that CDF accumulates at a greater concentration in blood and in many other organs, for example, the pancreas. It has now been well accepted that cancer is difficult to treat which is, in part, due to deregulated expression of multiple signaling pathways supporting rapid cell proliferation and evasion of apoptosis. Therefore, cancer is a disease of multi-gene defects, and thus a multipronged approach is expected to be a better approach for the eradication of cancer. To that end, it is important to note that CDF is a multi-targeted agent whose antitumor activity is mediated through deregulation of a variety of signal transduction cascades including miRNAs, NF-κB, AR/TMPR552/Wnt signaling, epigenetic reprograming, and attenuating the many cellular attributes of cancer stem cells. Through these mechanisms, treatment of cancer cells with CDF causes cancer cells to undergo apoptosis, decrease their replicative potential, and also reduce “stemness” characteristics of cancer stem cells, thus resulting in the inhibition of tumor growth. Moreover, CDF could serve as a powerful agent for overcoming drug resistance, a major problem in cancer treatment. In addition, the superior bioavailability of CDF together with potential of its systemic nontoxic attributes could become clinically attractive for further development of CDF as a new anticancer drug for the treatment of human malignancies with better therapeutic outcome. In conclusion, CDF and other nutraceuticals or their synthetic analogues may open new horizon in the discovery of newer anticancer drugs toward achieving the goal to eradicate cancers.
References
Ahmad A, Biersack B, Li Y, Kong D, Bao B, Schobert R et al (2013) Targeted regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/NF-kappaB signaling by indole compounds and their derivatives: mechanistic details and biological implications for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 13(7):1002–1013CrossRef
Ahmad A, Li Y, Bao B, Kong D, Sarkar FH (2014) Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-cancer stem cells nexus by nutraceuticals. Mol Nutr Food Res 58(1):79–86. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201300528 CrossRef
Ahmad A, Ginnebaugh KR, Li Y, Padhye SB, Sarkar FH (2015a) Molecular targets of naturopathy in cancer research: bridge to modern medicine. Nutrients 7(1):321–334. doi:10.3390/nu7010321 CrossRef
Ahmad A, Sayed A, Ginnebaugh KR, Sharma V, Suri A, Saraph A et al (2015b) Molecular docking and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 by novel difluorinatedbenzylidene curcumin analog. Am J Transl Res 7(2):298–308
Ali S, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Padhye S, Dominiak K, Schaffert JM et al (2010) Gemcitabine sensitivity can be induced in pancreatic cancer cells through modulation of miR-200 and miR-21 expression by curcumin or its analogue CDF. Cancer Res 70(9):3606–3617. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4598 CrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree