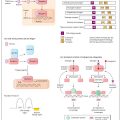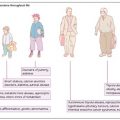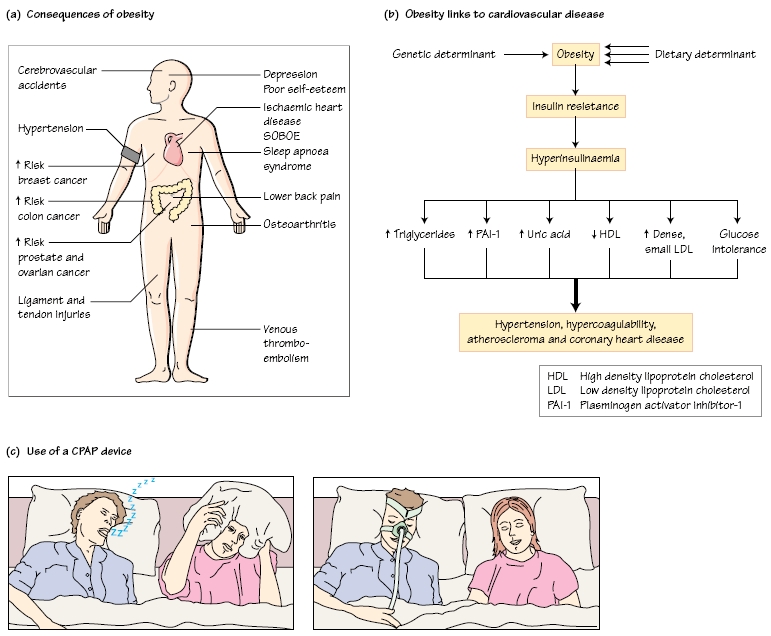
Obesity is associated with a number of complications and comorbidities. Cardiovascular disease is the major cause of death in obese patients and there is a direct link between the degree of obesity and the degree of hypertension. Other risk factors for coronary heart disease, such as smoking and hyperlipidaemia, should be addressed. There is also a higher risk of thromboembolism and stroke in the obese population. Other complications include osteoarthritis, back pain, ligament and tendon injury, gallstones and an increased risk of certain cancers, in particular those of the colon, rectum, breast, endometrium and prostate (Fig. 47a). Sleep apnoea syndrome is more common in the obese, particularly men.
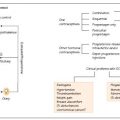
Cardiovascular complications of obesity
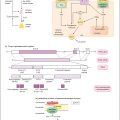
Obesity not only relates to but also predicts coronary atherosclerosis in both men and women, even with minimal increases in BMI (Fig. 47b
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree