Table 46.1 World Health Organization definition of obesity
| Classification | BMI (kg/m2) | Risk of comorbidities |
| Underweight | <18.5 | Low (other clinical problems) |
| Normal | 18.5-24.9 | Average |
| Overweight | 25–29.9 | Mildly increased |
| Obese Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 | >30 30–34.9 35–39.9 >40 | Moderate Severe Very severe |
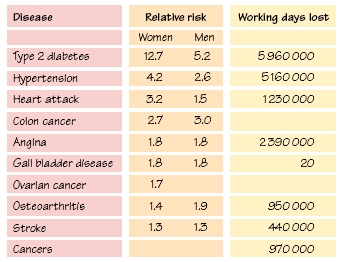
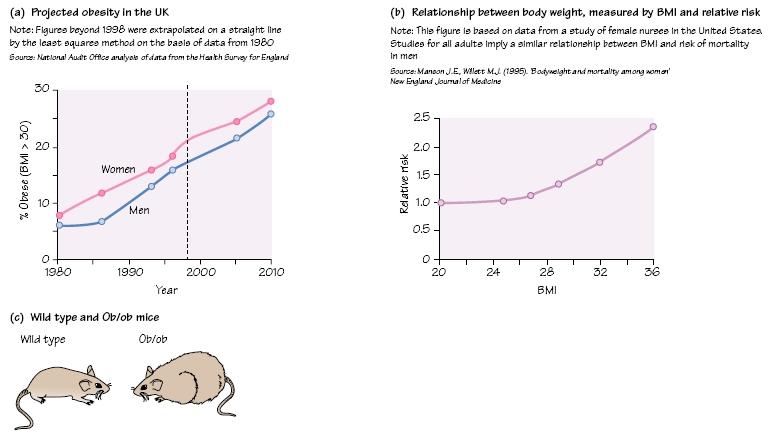
Obesity is a global problem in public health and rates of obesity are increasing throughout the world (Fig. 46a). The World Health Organization has defined obesity as ‘abnormal or excessive fat accumulation in adipose tissue to the extent that health is impaired ‘. Obesity is associated with an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, cardiovascular disease, sleep apnoea syndrome and respiratory failure, subfertility, arthritis and gallbladder disease. Targets are set using the measurement of Body Mass Index (BMI; weight [kg]/height2 [m2]) (Table 46.1).
The relationship between BMI and comorbidities (Fig. 46b) may vary between ethnic groups and certain studies use different cut-off points for that reason. Special charts have been developed to examine obesity rates in children. As central adiposity is associated with a higher risk of metabolic disorders, the waist–hip ratio or straightforward waist measurement has been widely used to identify high-risk groups.
It has been estimated that about 315 million people worldwide fall into the WHO category of obesity. In wealthy societies, all studies report a rate of about 20%, with more women falling into the obesity category but a higher percentage of men found to be overweight (BMI 25–29.9). In the US, around 60% of the population has a BMI >25kg/m2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree