O
octreotide acetate
(ok-tree’-oh-tide as’-eh-tayte)
 Brand Name(s): Sandostatin, Sandostatin LAR Depot
Brand Name(s): Sandostatin, Sandostatin LAR Depot
Chemical Class: Somatostatin analog
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
Special Considerations
ofloxacin
 Brand Name(s): Floxin, Floxin Otic, Ocuflox
Brand Name(s): Floxin, Floxin Otic, Ocuflox
Chemical Class: Fluoroquinolone derivative
Lower respiratory tract, skin, and skin-structure infections: PO 400 mg q12h for 10 days.
Prostatitis, sexually transmitted diseases (cervicitis, urethritis): PO 300 mg q12h.
Acute, uncomplicated gonorrhea: PO 400 mg 1 time.
Bacterial conjunctivitis: Ophthalmic 1-2 drops q2-4h for 2 days, then 4 times a day for 5 days.
Otitis externa: Otic 10 drops into the affected ear once a day for 7 days.
| Creatinine Clearance | Adjusted Dose | Dosage Interval |
|---|---|---|
| greater than 50 ml/min | None | q12h |
| 10-50 ml/min | None | q24h |
| less than 10 ml/min | ½ | q24h |
 Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any quinolones
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any quinolones
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
olanzapine
 Brand Name(s): Zyprexa, Zyprexa Intramuscular, Zyprexa Zydis
Brand Name(s): Zyprexa, Zyprexa Intramuscular, Zyprexa Zydis
Chemical Class: Thienbenzodiazepine derivative
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 Use with caution in older patients with: Diabetes, glucose intolerance, cardiovascular disease
Use with caution in older patients with: Diabetes, glucose intolerance, cardiovascular disease
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Behavior disturbances in the setting of dementia
Other Uses in Geriatric Patient: Behavior disturbances in the setting of dementia
 Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Direct comparisons between older and newer antipsychotic drugs in demented elderly persons are scarce. Newer agents have the theoretical advantage of a lower incidence of tardive dyskinesia but may cause weight gain, impaired glycemic control, and increased risk for cardiovascular events. These agents should be used with caution in demented elderly persons, with frequent monitoring for side effects and a low threshold for discontinuing use. Indeed, the Food and Drug Administration has recently released an advisory about these medications outlining the risk for increased mortality.
Geriatric Considerations – Summary: Direct comparisons between older and newer antipsychotic drugs in demented elderly persons are scarce. Newer agents have the theoretical advantage of a lower incidence of tardive dyskinesia but may cause weight gain, impaired glycemic control, and increased risk for cardiovascular events. These agents should be used with caution in demented elderly persons, with frequent monitoring for side effects and a low threshold for discontinuing use. Indeed, the Food and Drug Administration has recently released an advisory about these medications outlining the risk for increased mortality.
1 Sink KM, Holden KF, Yaffe K. Pharmacological treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. JAMA. 2005;293:596-608.
2 Alexopoulos GS, Streim J, Carpenter D, Docherty JP. Using antipsychotic agents in older patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65(Suppl 2):5-99.
3 Cohen D. Atypical antipsychotics and new onset diabetes mellitus. An overview of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2004;37:1-11.
4 Deaths with antipsychotics in elderly patients with behavioral disturbances. Available at: www.fda.gov/cder/drug/advisory/antipsychotics.htm
5 Katz IR. Optimizing atypical antipsychotic treatment strategies in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52:S272-S277.
olsalazine sodium
Chemical Class: Salicylate derivative
Maintenance of controlled ulcerative colitis: PO 1 g/day in 2 divided doses, preferably q12h.
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
 Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to salicylates
Contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to salicylates
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
omalizumab
Chemical Class: Monoclonal antibody
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Side Effects
Side Effects
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
 Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters
 Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
omega-3-acid ethyl esters
(oh-meg’-a-three-as’-id eth’-ul es’-terz)
Pharmacokinetics: EPA and DHA are absorbed well when given orally as ethyl esters.
Hypertriglyceridemia: PO 4g (4 capsules) once daily or two 2-g doses (2 capsules) twice daily.
 Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to any component of the formulation
omeprazole
 Brand Name(s): Prilosec, Zegerid
Brand Name(s): Prilosec, Zegerid
Chemical Class: Benzimidazole derivative
To maintain healing of erosive esophagitis: PO 20 mg/day.
Pathologic hypersecretory conditions: PO Initially, 60 mg/day up to 120 mg 3 times a day.
Helicobacter pylori duodenal ulcer: PO 20 mg once daily or 40 mg/day as a single or in 2 divided doses in combination therapy with antibiotics. Dose varies with regimen used.
Active benign gastric ulcer: PO 40 mg/day for 4–8 wk.
OTC use (frequent heartburn): PO 20 mg/day for 14 days. May repeat after 4 mo if needed.
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
ondansetron hydrochloride
(on-dan-seh’-tron hye-droe-klor’-ide)
 Brand Name(s): Zofran, Zofran ODT
Brand Name(s): Zofran, Zofran ODT
Chemical Class: Carbazole derivative
 Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting
 Contraindications: None known.
Contraindications: None known.
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology:
 Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Unlabeled Uses: Control of bleeding esophageal varices, treatment of AIDS-associated secretory diarrhea, chemotherapy-induced diarrhea, insulinomas, small-bowel fistulas, control of bleeding esophageal varices
Unlabeled Uses: Control of bleeding esophageal varices, treatment of AIDS-associated secretory diarrhea, chemotherapy-induced diarrhea, insulinomas, small-bowel fistulas, control of bleeding esophageal varices Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:

 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of anorexia, apathy, borderline personality disorder, Huntington’s disease; maintenance of long-term treatment response in schizophrenic patients; nausea; vomiting
Unlabeled Uses: Treatment of anorexia, apathy, borderline personality disorder, Huntington’s disease; maintenance of long-term treatment response in schizophrenic patients; nausea; vomiting






 Side Effects:
Side Effects: Brand Name(s): Dipentum
Brand Name(s): Dipentum Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Brand Name(s): Xolair
Brand Name(s): Xolair Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: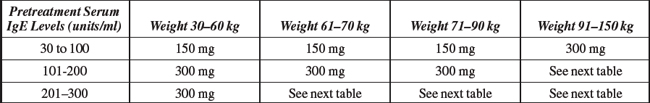
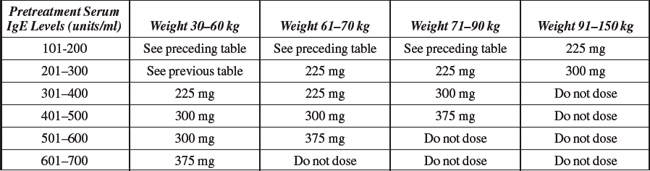
 Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology:
 Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Unlabeled Uses: H. pylori-associated duodenal ulcer (with amoxicillin and clarithromycin), prevention and treatment of NSAID-induced ulcers, treatment of active benign gastric ulcers
Unlabeled Uses: H. pylori-associated duodenal ulcer (with amoxicillin and clarithromycin), prevention and treatment of NSAID-induced ulcers, treatment of active benign gastric ulcers Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring Parameters Geriatric side effects at a glance:
Geriatric side effects at a glance:
 U.S. Regulatory Considerations
U.S. Regulatory Considerations
 Clinical Pharmacology:
Clinical Pharmacology: Available Forms:
Available Forms: Indications and Dosages:
Indications and Dosages: Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Reactions
Serious Reactions Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education


