Multiple myeloma is a malignant disorder of plasma cells characterized by:
Incidence
Approximately 50 cases per million population; 15% of lymphoid malignancies; 2% of all malignancies; twice as common in black than white people; slightly more common in males than in females; median age at diagnosis 71 years.
Aetiology and pathogenesis
The aetiology is unknown. The cell of origin is probably a post-germinal centre B-lymphoid cell. The cells all secrete the same immunoglobulin (Ig) or Ig component, e.g. part of a heavy chain attached to a light chain or light chain (κ or λ). Rarely (<1%), the cells are non-secretory. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) from myeloma cells themselves or accessory cells promotes plasma cell growth. Tumour necrosis factor and IL-1 mediate bone resorption. Oncogene mutations (e.g. ras, p53, myc) and translocations to 14q occur. Cyclin D1 is often overexpressed.
Clinical features
- Bone pain, especially lower backache, or pathological fracture due to skeletal involvement.
- Bone marrow failure due to marrow infiltration.
- Infection – lack of normal immunoglobulins (immune paresis) and neutropenia.
- Renal failure occurs in up to one-third patients and is caused by hypercalcaemia, infection, deposition of paraprotein or light chains, uric acid or amyloid.
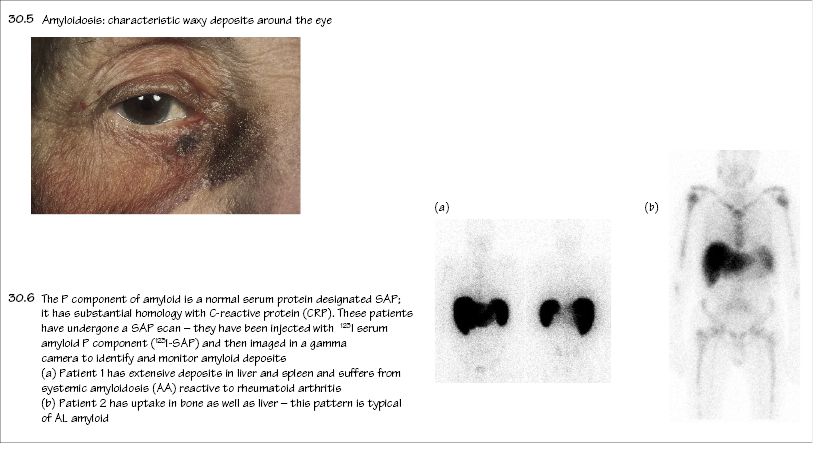
- Amyloidosis may cause macroglossia, hepatosplenomegaly, cardiac or renal failure, carpal tunnel syndrome and autonomic neuropathy.
Laboratory features
- Anaemia is frequent, often with neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate often >100 mm/h.
- Blood film shows rouleaux with a bluish background staining, caused by the protein increase. Leucoerythroblastic picture may be present.
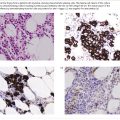
- Bone marrow shows >10% plasma cells, often with multinucleate and other abnormal forms (Fig. 30.1). These cells are CD138+.
- A paraprotein in serum and/or Bence Jones protein (light chains) in urine with suppression of normal serum immunoglobulins is usual (Fig. 30.2a,b).
- The paraprotein is IgG in 70%; IgA in 20%; IgM is uncommon; IgD and IgE are rare.
- Serum light chain (either κ or λ) increased with abnormal light chain ratio.
- Serum β2 microglobulin (β2

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree